HASIL ANALISIS SEM part 1
Summary
TLDRThe transcript details a tutorial on Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) using AMOS software. The instructor explains how to combine structural relationships and measurement models, emphasizing the need for understanding the connections between variables like price, product quality, and purchase intention. The session guides participants through creating and adjusting models, inputting data, and adjusting variables. Key concepts covered include confirmatory factor analysis, structural equation modeling, and the correct setup of indicators and variables. The focus is on ensuring participants grasp the process thoroughly to successfully apply SEM techniques in research.
Takeaways
- 😀 SEM (Structural Equation Modeling) combines structural relationships and measurement models to analyze complex relationships between variables.
- 😀 Structural relationships refer to the connections between variables, while measurement models focus on the indicators used to measure these variables.
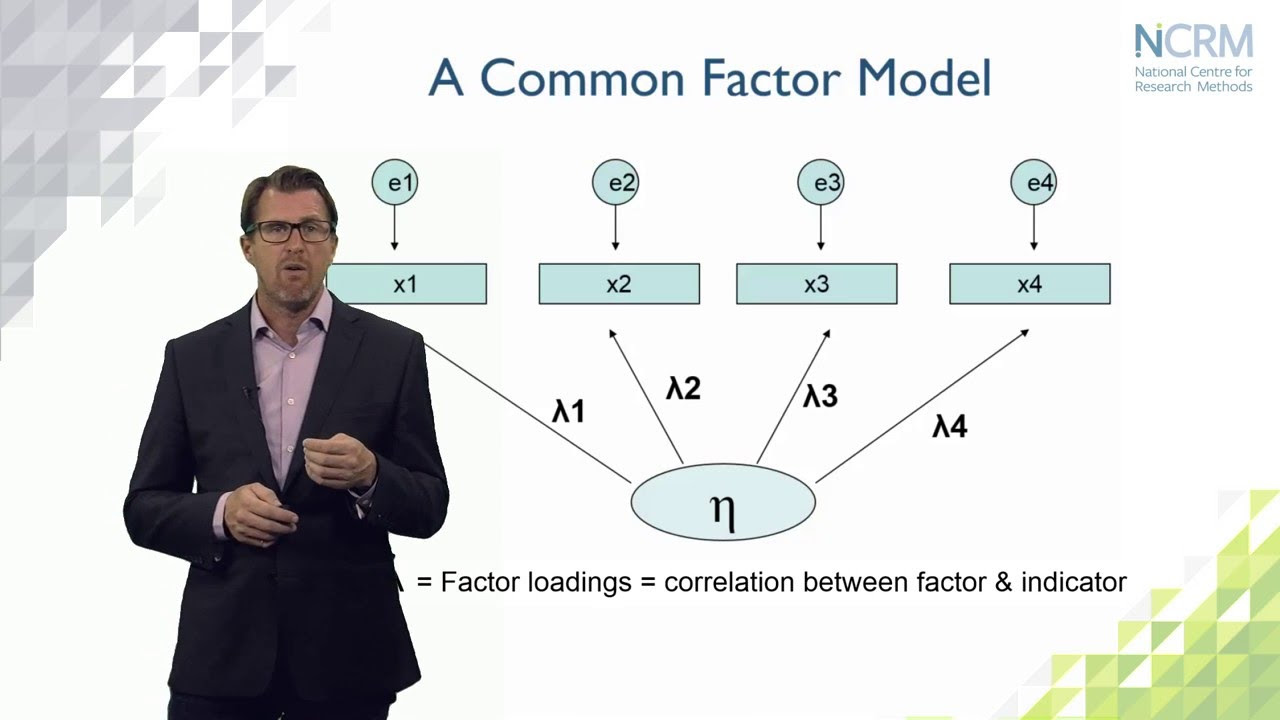
- 😀 Measurement models are also known as Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA), where the goal is to confirm the relationships between observed variables and their underlying factors.
- 😀 When conducting SEM in software like AMOS, start by drawing the structural relationships and measurement models separately before combining them.
- 😀 Structural relationships are illustrated with arrows connecting independent and dependent variables, while measurement models are shown with ellipses and boxes representing latent and observed variables.
- 😀 SEM involves both structural and measurement models, which need to be carefully integrated to ensure a correct analysis.
- 😀 Always ensure you have clear, named indicators for each variable, as these are the elements being measured (e.g., survey questions or response items).
- 😀 For a successful SEM model, it’s essential to avoid skipping steps and address any questions before moving forward.
- 😀 Use appropriate software settings, like changing paper orientation to landscape, for better visualization of SEM diagrams.
- 😀 Error terms should be labeled and placed for each affected variable, ensuring that the model accounts for measurement errors.
- 😀 Properly organizing and naming variables in the SEM model is crucial for avoiding errors, especially when the software might reject two-word variable names.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of using SEM (Structural Equation Modeling) in the script?
-The main purpose of using SEM is to analyze the relationships between variables (structural model) and the measurement of those variables through indicators (measurement model), as demonstrated in the transcript using AMOS software.
What are the key components involved in creating an SEM model as described in the script?
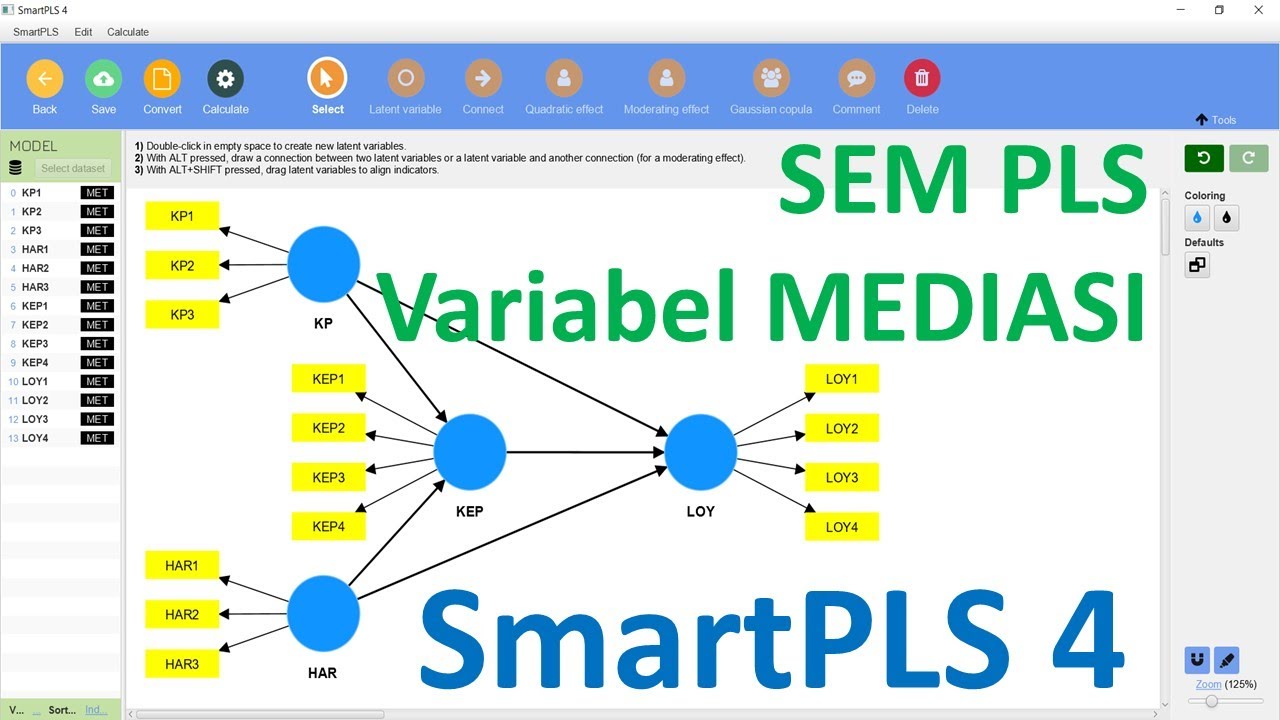
-The key components include latent variables (e.g., Price, Product Quality, and Purchase Intention), indicators (which measure the variables), and the relationships between these variables, represented by arrows. The model also includes exogenous (independent) and endogenous (dependent) variables.
What role do indicators play in the SEM model?
-Indicators are used to measure the latent variables. For example, in the script, 'Price' has indicators that are based on survey responses, and these indicators are used in the measurement model to assess the latent construct.
How does the script explain the relationship between structural and measurement models in SEM?
-The script explains that the structural model represents the relationships between latent variables (e.g., Price affecting Purchase Intention), while the measurement model involves the indicators that measure these latent variables. Both models are combined into a single SEM model for analysis.
What software is being used in the process described in the script, and what is its purpose?
-The software used is AMOS (Analysis of Moment Structures), which is used to create and analyze Structural Equation Models. It helps visualize and compute the relationships between latent and observed variables in SEM.
What is the significance of the coding system mentioned in the script (e.g., 'E11', 'D1')?
-The coding system is used to label the indicators and variables within the SEM model for clarity and organization. For example, 'E11' represents the first indicator of an exogenous variable, and 'D1' represents the first indicator of an endogenous variable.
How does the speaker suggest handling layout adjustments in the SEM model diagram?
-The speaker suggests adjusting the layout by rotating the indicators, switching between portrait and landscape paper formats, and repositioning elements for clarity and to avoid overlapping. These adjustments ensure the diagram is well-organized and easy to read.
What is the process for naming the variables and indicators in the SEM model as explained in the transcript?
-The process involves clicking on a variable or indicator, entering a name or code (e.g., 'Price,' 'Product Quality'), and ensuring there are no spaces in the names of variables. For indicators, a system like 'E11' or 'D1' is used for clarity.
Why does the speaker emphasize the importance of understanding the material and asking questions during the process?
-The speaker stresses the importance of understanding the material fully before proceeding with the modeling process. If any part is unclear, students are encouraged to ask questions immediately to avoid mistakes and ensure accurate modeling.
What does the speaker mean by 'structural equation modeling' and how is it applied in this context?
-'Structural Equation Modeling' refers to the process of combining both the structural model (relationships between variables) and the measurement model (indicators measuring those variables). In this context, it’s applied by integrating both models into a single diagram for analysis and visualization in AMOS.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)