Staphylococcus Aureus
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive overview of *Staphylococcus aureus*, highlighting its defining characteristics, such as its gram-positive, catalase-positive, coagulase-positive nature, and its clustering behavior. It explores key virulence factors, including Protein A, penicillin-binding proteins (notably in MRSA), TSST-1 (toxic shock syndrome toxin), enterotoxin B (cause of food poisoning), and exfoliative toxin (responsible for scalded skin syndrome). The video also covers diagnostic tips for distinguishing *S. aureus* from other staphylococci and discusses treatment options, with emphasis on managing MRSA infections. A helpful mnemonic and clinical correlations for exam prep are included throughout.
Takeaways
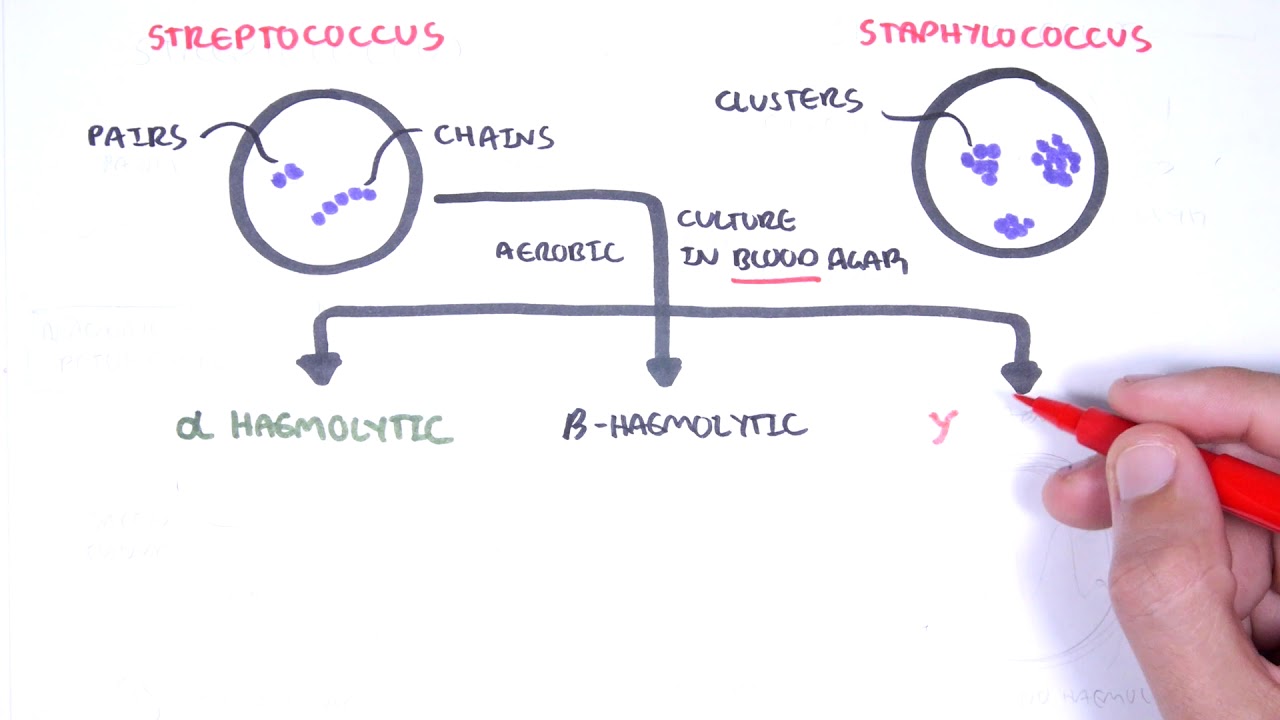
- 😀 Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive, coagulase-positive, and beta-hemolytic bacterium that occurs in clusters.
- 😀 The term 'coccus' refers to the round shape of the bacterium, and 'clusters' means that Staphylococcus aureus forms groups of these cocci when observed under the microscope.
- 😀 A useful mnemonic to remember the characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus is associating it with a 'positive aura' since everything about it is positive (Gram-positive, catalase-positive, coagulase-positive).
- 😀 The key difference between Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis is that Staph aureus is coagulase-positive, while Staph epidermidis is coagulase-negative.
- 😀 Virulence factors of Staphylococcus aureus include: protein A (prevents complement activation and phagocytosis), altered penicillin-binding proteins (which confer methicillin resistance), super antigen TSST-1 (causes toxic shock syndrome), enterotoxin B (causes food poisoning), and exfoliative toxin (causes scalded skin syndrome).
- 😀 Protein A binds to the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G, preventing the immune system from recognizing and destroying the bacteria.
- 😀 Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has altered penicillin-binding proteins, making it resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics such as methicillin.
- 😀 Toxic shock syndrome (TSS) is caused by the super antigen TSST-1, which over-stimulates T cells and induces massive cytokine release, leading to fever, shock, and organ failure.
- 😀 Enterotoxin B from Staphylococcus aureus is heat-stable and causes food poisoning within 2-6 hours of ingestion, regardless of cooking temperature.
- 😀 Exfoliative toxin from Staphylococcus aureus causes scalded skin syndrome by cleaving the inter-epidermal cell connections, leading to skin sloughing, particularly in children.
Q & A
What is the gram stain result for Staphylococcus aureus?
-Staphylococcus aureus is gram-positive.
What are the defining biochemical characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus?
-Staphylococcus aureus is catalase positive, coagulase positive, beta-hemolytic, and occurs in clusters.
What is the mnemonic used to remember the defining characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus?
-The mnemonic is 'aura'—Staphylococcus aureus equals aura. The 'positive aura' helps to remember that it is gram-positive, catalase positive, coagulase positive, and beta-hemolytic.
How does Staphylococcus aureus differ from Staphylococcus epidermidis?
-The major difference is that Staphylococcus aureus is coagulase positive, while Staphylococcus epidermidis is coagulase negative.
What is the role of Protein A in the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus?
-Protein A binds to the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G, preventing complement activation and phagocytosis, allowing Staphylococcus aureus to evade immune clearance.
What does the alteration of penicillin-binding proteins in MRSA lead to?
-In MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), the alteration of penicillin-binding proteins makes it resistant to methicillin, allowing the bacteria to maintain its structural integrity despite antibiotic treatment.
What is toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1), and how does it cause toxic shock syndrome?
-TSST-1 is a superantigen that binds to MHC class II molecules and T-cell receptors, causing an uncontrolled release of cytokines like interleukin-2 and TNF-alpha, leading to severe inflammation, high fever, and multi-organ failure.
Which clinical conditions are most associated with toxic shock syndrome caused by TSST-1?
-Toxic shock syndrome is most commonly associated with tampon use and nasal packing, both of which can provide a conducive environment for the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and production of TSST-1.
What does enterotoxin B do, and how is it related to food poisoning?
-Enterotoxin B is a heat-stable toxin produced by Staphylococcus aureus that causes food poisoning. It remains active even if the food is cooked, and symptoms typically appear within 2 to 6 hours after ingestion.
What is exfoliative toxin, and what disease does it cause?
-Exfoliative toxin is a protease that cleaves inter-epidermal cell junctions, leading to skin sloughing and causing Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS), typically affecting young children.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Staphylococcus aureus Causes, Symptoms, identification, Treatment, and Prevention (English)

Micologia, Virologia e Microbiologia Clínica 03/02

Identifikasi Staphylococcus part 1
Microbiology - Streptococcus species

Classification of Bacteria (Antibiotics - Lecture 1)

Micologia, Virologia e Microbiologia Clínica 03/03
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
