A2.2 Organelles and Drawing Cells [IB Biology SL/HL]
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and identifying key organelles in eukaryotic cells, including the nucleus, rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. It highlights how to spot these structures in micrographs and how to accurately draw them for scientific presentations. Key features, such as ribosomes, lysosomes, and vacuoles, are also covered, along with tips for distinguishing between cell types like prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The video emphasizes drawing techniques and proper labeling for IB-style cell illustrations, offering practical advice for biology students studying cell structure and function.
Takeaways
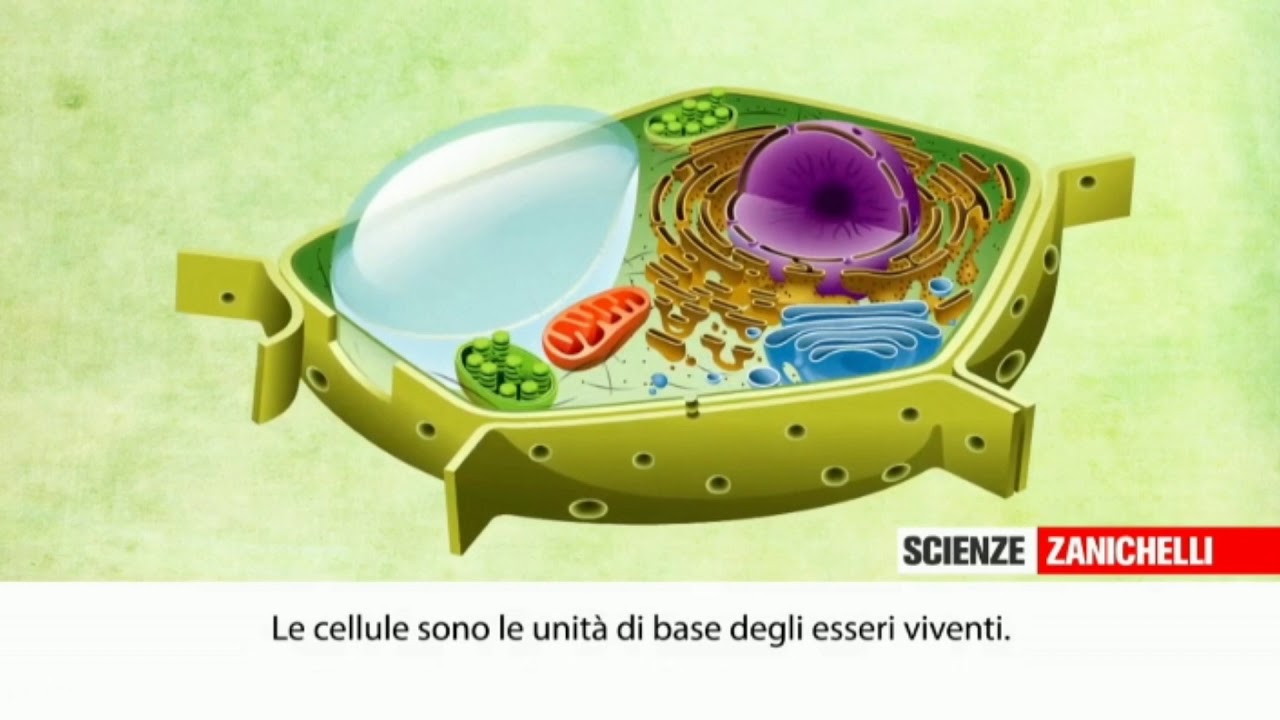
- 😀 The nucleus in eukaryotic cells has a double membrane and pores, containing DNA associated with histone proteins. The nucleolus, a dark spot, is where ribosomes are made.
- 😀 The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is a membrane-bound structure with ribosomes attached, and it is the site of protein synthesis for proteins that are secreted from the cell.
- 😀 The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) lacks ribosomes and is associated with lipid production. It is sometimes difficult to identify but can be recognized by its smooth, circular or hole-like structures.
- 😀 The Golgi apparatus (GGI) looks like a Wi-Fi symbol and is responsible for processing proteins received from the RER, packaging them into vesicles for transport outside the cell.
- 😀 Lysosomes are spherical structures found primarily in animal cells, containing enzymes used for digesting food or breaking down old cell parts. They are highly stained and dark in micrographs.
- 😀 Mitochondria are characterized by a double membrane, with an inner membrane folded into cristae. They are involved in aerobic cellular respiration, not just energy production as commonly stated.
- 😀 Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis and can be found both freely in the cytoplasm and attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). They appear as small dots in micrographs.
- 😀 Chloroplasts in plant cells have a double membrane and contain stacks of thylakoid discs filled with chlorophyll, which gives them a dark appearance in micrographs due to the pigment's light-absorbing properties.
- 😀 Plant cells typically have a large central vacuole that takes up most of the space, while animal cells have smaller vesicles, which are used for transport within the cell.
- 😀 Microtubules and centrioles are important for cell division, with microtubules moving chromosomes and centrioles acting as anchors in animal cells. The cytoskeleton provides structure and flexibility to cells.
Q & A
What is the function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell?
-The nucleus stores all the DNA in the cell, which is associated with histone proteins, and serves as the site of DNA replication and transcription.
How can you identify the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) in micrographs?
-The rough endoplasmic reticulum can be identified by its flattened sacs with ribosomes attached to the outer membrane, giving it a 'rough' appearance.
What is the difference between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
-The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) has ribosomes attached to its surface, while the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell?
-The Golgi apparatus processes proteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum, wraps them in vesicles, and ships them out of the cell or to other locations within the cell.
How do lysosomes function in animal cells?
-Lysosomes contain enzymes that digest food, destroy old cell parts, and help with cellular waste management. They are easily identified due to their dark staining in micrographs.
What is the function of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells?
-Mitochondria are the site of aerobic cellular respiration, where energy is produced. They have a double membrane, and the inner membrane contains folds called cristae.
Where are ribosomes found in a cell, and what is their role?
-Ribosomes are found either freely floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. They are responsible for protein synthesis.
What distinguishes a chloroplast from other organelles?
-Chloroplasts have a double membrane and contain stacks of thylakoid discs. These structures are filled with chlorophyll, which gives them a darker appearance in micrographs.
What are vacuoles and how do they differ in plant and animal cells?
-Vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs used for storage. In plant cells, a large central vacuole occupies most of the cell's volume, while in animal cells, vacuoles are smaller and less prominent.
How can you differentiate between flagella and cilia?
-Flagella are long, whip-like structures that usually appear singly or in pairs, whereas cilia are shorter and more numerous, often lining the surface of cells.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)