Econofísica - 8 Modelando cenários com melhores hipóteses Excel
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces a financial model for calculating expected returns and standard deviation based on different economic states: Expansion, Normal, and Recession. With given probabilities for each state, the script demonstrates how to calculate the expected return (15%) and the standard deviation (7.07%) using historical data. The model is applied to simulate asset performance and provides insights into how future projections may differ from historical trends. It emphasizes the importance of understanding risk and return in financial decision-making, making it relevant for analysts and investors seeking to forecast asset behavior.
Takeaways
- 😀 The model discussed is a discrete model used for evaluating asset performance in different economic states.
- 😀 There are three possible economic states: expansion (25% probability), normal (50% probability), and recession (25% probability).
- 😀 The return associated with each state is: 25% for expansion, 15% for normal, and 5% for recession.
- 😀 Expected return is calculated by multiplying the return of each state by its respective probability and summing the results, yielding a 15% expected return.
- 😀 The formula for calculating variance involves the sum of squared deviations of each return from the expected return, weighted by probabilities.
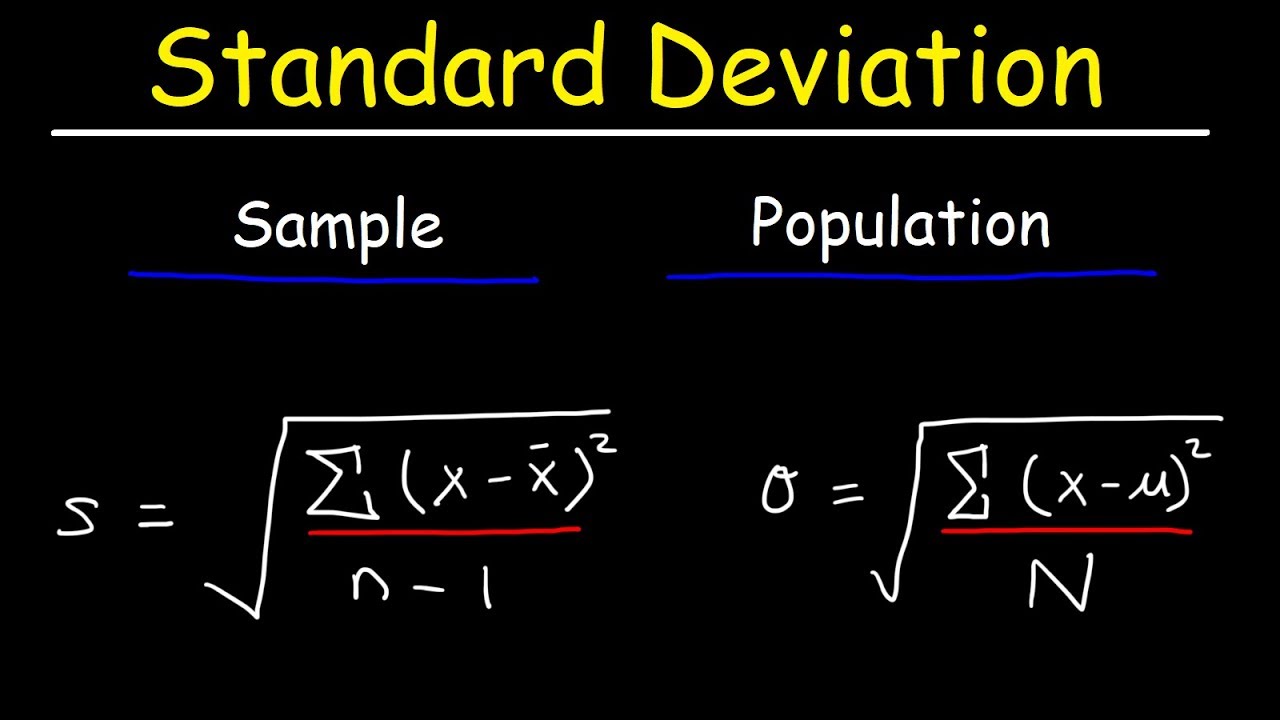
- 😀 After calculating variance, the standard deviation is derived as the square root of the variance, resulting in a value of 7.07%.
- 😀 This model can be used to simulate asset behavior using historical data, providing insights into potential future performance.
- 😀 A comparison of two simulation curves—one based on historical data and another based on the calculated mean and standard deviation—shows how the asset's behavior may differ in the future.
- 😀 Using simulated data (instead of historical data) can reveal different patterns and trends in the asset's performance.
- 😀 This model is useful for predicting asset performance and can be applied to other relevant events, not just economic states.
- 😀 The speaker encourages engagement and feedback from viewers, highlighting the importance of simulations and predictions in asset analysis.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The video script discusses the application of a discrete model to calculate the expected return and standard deviation for an asset, using different economic states (expansion, normal, and recession).
What are the three economic states mentioned in the video?
-The three economic states mentioned are expansion, normal, and recession.
What is the probability of each economic state occurring?
-The probabilities are 25% for expansion, 50% for normal, and 25% for recession.
What are the associated returns for each economic state?
-The returns are 25% for expansion, 15% for normal, and 5% for recession.
How is the expected return calculated in the model?
-The expected return is calculated by multiplying each state's return by its probability and then summing the results. For example: 25% * 25% (for expansion) + 50% * 15% (for normal) + 25% * 5% (for recession). This gives an expected return of 15%.
What is the formula for variance, and how is it used in the video?
-The formula for variance is the sum of the squared differences between each return and the expected return, weighted by their probabilities. This formula helps in calculating the variance and ultimately the standard deviation of the returns.
How is the standard deviation calculated in the model?
-The standard deviation is calculated by first computing the variance using the formula, then taking the square root of the variance. In this case, the variance is 0.0050, and the standard deviation is 7.07%.
Why is understanding the standard deviation important in financial modeling?
-Understanding the standard deviation is important because it helps measure the risk or volatility of an asset's returns, which is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
How can this model be used in simulations?
-This model can be used to simulate different scenarios for an asset's return based on the probabilities and expected returns. By using historical data or simulated data, different curves of asset value evolution can be generated.
What does the speaker suggest about using historical data versus simulated data?
-The speaker suggests that using simulated data based on the model’s expected return and standard deviation might yield a different scenario compared to using historical data, and this can help better understand future behavior of an asset.
What additional learning resource does the speaker mention?
-The speaker mentions a quantitative modeling course that goes deeper into such financial topics and is offered multiple times.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)