Diffusion and osmosis | Membranes and transport | Biology | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video explains key concepts in chemistry, including the nature of solutions, diffusion, and osmosis. The speaker starts with the basics of solutes and solvents, using water and sugar as examples, to illustrate how molecules move from areas of high concentration to low concentration. It then introduces diffusion, the process of particles spreading out, and explores osmosis, a special type of diffusion where water moves through a semi-permeable membrane to balance concentrations. The video aims to simplify these concepts with visual aids and clear explanations, making them accessible even for beginners in the field of chemistry.
Takeaways
- 😀 Water is the solvent in the example, and sugar is the solute, making the whole mixture a solution.
- 😀 Diffusion refers to the spreading of particles from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
- 😀 Concentration is the amount of a substance (solute) present in a given volume of space.
- 😀 A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solute, while a hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solute.
- 😀 Diffusion occurs randomly, with molecules naturally moving toward areas of lower concentration.
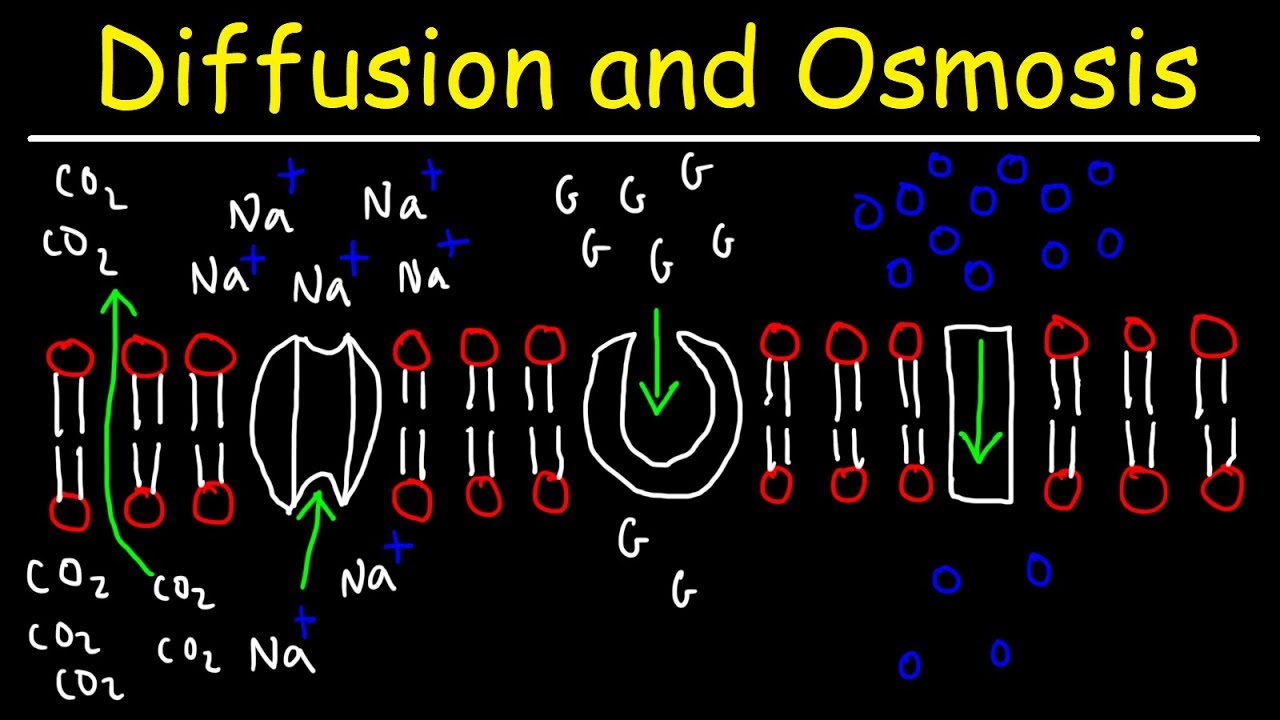
- 😀 Semi-permeable membranes allow water to pass through but may block larger solutes like sugar.
- 😀 Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion where water molecules move across a semi-permeable membrane from lower to higher solute concentration.
- 😀 Molecules move in random directions due to their kinetic energy, leading to diffusion and osmosis over time.
- 😀 Water moves from areas of lower solute concentration (hypotonic) to areas of higher solute concentration (hypertonic) in osmosis.
- 😀 The process of diffusion continues until equilibrium is reached, where concentrations are equal on both sides of a membrane.
Q & A
What is the definition of a solution in the context of the video?
-A solution is a mixture of a solvent and a solute, where the solvent dissolves the solute. In the example provided, water is the solvent, and sugar is the solute.
What distinguishes the solvent from the solute in a solution?
-The solvent is the substance present in a greater amount, while the solute is present in a smaller amount. In the example, water is the solvent, and sugar is the solute.
How is concentration defined in this context?
-Concentration refers to the amount of a substance (solute) present per unit volume of space. A higher concentration means more solute in a given space, while a lower concentration means less solute.
What is diffusion, and how does it work in terms of molecules?
-Diffusion is the process by which molecules spread from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, driven by the random motion of molecules.
What are hypertonic and hypotonic solutions?
-A hypertonic solution has a higher concentration of solute compared to another solution, while a hypotonic solution has a lower concentration of solute.
What is the significance of a semi-permeable membrane in osmosis?
-A semi-permeable membrane allows some substances, such as water, to pass through, but not others, such as large solutes like sugar. This selective permeability is key in osmosis.
What is the process of osmosis, and how is it different from regular diffusion?
-Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration (hypotonic) to high solute concentration (hypertonic). Unlike regular diffusion, osmosis specifically concerns water.
Why do water molecules tend to move into a hypertonic solution in osmosis?
-Water molecules move into a hypertonic solution because the concentration of solute is higher on that side, and the system seeks to equilibrate the concentrations by diluting the higher solute concentration with water.
How does the presence of solute molecules affect the movement of water in osmosis?
-Solute molecules block the water molecules' ability to pass through the semi-permeable membrane, making it more likely for water to move toward the area with more solute to balance the concentration on both sides.
What happens when the concentrations of solute and solvent reach equilibrium in osmosis?
-At equilibrium, the concentrations of solute and solvent on both sides of the membrane become equal, and the movement of molecules will be balanced, with no net movement of water or solute.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)