VIDEOAULA | Física | Ensino Médio | Fundamentos da Eletrodinâmica I
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Professor Márcio explains key concepts of electricity, focusing on potential energy, electric fields, and capacitors. He illustrates how electric charges interact, how energy is stored and transferred in electric fields, and the role of capacitors in devices like camera flashes and defibrillators. The professor also relates these concepts to real-world scenarios, such as airplane safety during thunderstorms, demonstrating the importance of electrostatic shielding. Through engaging examples, the video provides a thorough understanding of these fundamental electrical principles and their practical applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 The energy potential of electric fields refers to the energy stored in a system, which can cause movement in charges.
- 😀 Work in an electric field is defined as the variation in energy as a charge moves through that field.
- 😀 Electric potential is the energy per unit charge at a point in space, and it is an important factor in determining how energy is distributed in an electric field.
- 😀 The potential difference (DP) is the difference in electric potential between two points, and it drives the flow of electric charge.
- 😀 The electric potential created by a charge is a scalar quantity, meaning it does not depend on direction, only on magnitude.
- 😀 Capacitors store electric charge and energy, and they are used in devices like camera flashes and defibrillators to release energy quickly.
- 😀 Capacitors consist of two parallel plates with opposite charges and are often used to accumulate and release electrical energy.
- 😀 The capacitance of a capacitor is determined by the area of the plates, the distance between them, and the dielectric material between them.
- 😀 In static electricity, charges accumulate on the surface of a body, and for a spherical body, the electric field inside is zero.
- 😀 The concept of 'pointed regions' explains that in objects like airplanes, electric charge tends to accumulate at the tips or edges, which can influence the behavior of lightning strikes.
- 😀 Practical applications of capacitors include not only camera flashes but also medical devices like defibrillators, which use capacitors to deliver life-saving shocks during cardiac arrest.
Q & A
What is electrical potential energy?
-Electrical potential energy is the energy stored in a system due to the positions of electric charges relative to each other. It has the potential to do work when charges move in an electric field.
How is the energy between two charges calculated?
-The energy between two charges is calculated using the formula: U = k * q1 * q2 / r, where 'k' is the electrostatic constant, 'q1' and 'q2' are the magnitudes of the charges, and 'r' is the distance between the charges.
What is the relationship between work and energy in electric fields?
-In electric fields, work is the energy transferred when a charge moves through the field. As a charge moves, its potential energy changes, converting into kinetic energy or vice versa, in accordance with the conservation of energy.
What is the concept of electric potential?
-Electric potential is the amount of potential energy per unit charge at a specific point in space. It indicates the ability of the point to do work on a charge placed at that location.
What does the term 'voltage' or potential difference mean?
-Voltage, or potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. It is the energy required to move a unit charge between those points.
What is the function of a capacitor?
-A capacitor stores electric charge and energy. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material. The capacitor stores energy in the form of an electric field between the plates.
How is the energy stored in a capacitor calculated?
-The energy stored in a capacitor is given by the formula: E = Q^2 / 2C, where 'E' is the energy, 'Q' is the charge stored, and 'C' is the capacitance of the capacitor.
What are the applications of capacitors in everyday life?
-Capacitors are used in a variety of applications, such as in camera flashes to store and quickly release energy for a burst of light, in defibrillators to deliver a shock to the heart, and in electronic devices to smooth voltage fluctuations.
How do capacitors work in medical devices like defibrillators?
-In defibrillators, capacitors store electrical energy and then release it in a controlled manner to shock the heart back into rhythm during a cardiac arrest.
Why are airplanes safe during thunderstorms, especially when struck by lightning?
-Airplanes are safe during thunderstorms because they act as a Faraday Cage. The electric charges accumulate on the exterior of the plane, creating a protective shield. The electric field inside the plane remains zero, ensuring the passengers are not affected by lightning.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Kurikulum Merdeka Rangkuman IPA Kelas 9 Bab 4 Listrik Statis dan Listrik Dinamis

BAB 4 : LISTRIK, MAGNET DAN SUMBER ENERGI ALTERNATIF | Part 1 : LISTRIK STATIS | IPA Kelas 9 Kumer

Medan, Beda Potensial dan Energi Listrik

BAB 4 LISTRIK, MAGNET DAN SUMBER ENERGI ALTERNATIF - PART 1 (IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka)

LISTRIK STATIS (POTENSIAL LISTRIK & ENERGI POTENSIAL LISTRIK) | FISIKA SMA KELAS XII
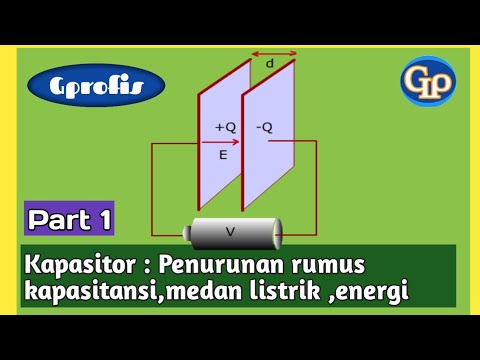
F86 - Kapasitor : Penurunan rumus kapasitansi,potensial listrik dan energi listrik
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
