IV regression lecture 1: Intuition of IV regression / IV with a binary instrument
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the limitations of OLS regression for causal inference when endogeneity is present and introduces Instrumental Variable (IV) regression as an alternative. Using an economic example related to maternal labor supply, the video demonstrates how IV regression can be used to estimate causal effects by addressing issues like omitted variables or measurement error. The method relies on finding a valid instrument that satisfies two key assumptions: exogeneity and relevance. Through a practical example involving the number of children and child sex composition, the video shows how IV can reveal the true causal effect on labor supply.
Takeaways
- 😀 OLS regression can estimate causal effects only if the exogeneity assumption is satisfied, but this assumption is often not plausible due to confounding variables, measurement error, or equilibrium conditions.
- 😀 Omitted variables, measurement error, and confounding factors can violate the exogeneity assumption in OLS regression, leading to biased estimates of causal effects.
- 😀 Instrumental variable (IV) regression is introduced as an alternative to OLS when exogeneity assumptions are violated, helping to estimate causal effects more reliably.
- 😀 The video uses an example of maternal labor supply to demonstrate how IV regression works, specifically focusing on the effect of having more than two children on weeks worked.
- 😀 For a binary regressor (e.g., having more children), the OLS estimator is calculated as the difference in the average outcomes between two groups (those with exactly two children vs. those with more).
- 😀 The calculation of the OLS estimator is intuitive, as it compares the difference in outcomes divided by the difference in the regressor (e.g., having more kids).
- 😀 The OLS estimator becomes less intuitive when using binary regressors, but the general principle remains: compare differences in outcomes between groups with different values of the regressor.
- 😀 IV regression relies on the use of an instrument, which must satisfy two assumptions: it must be exogenous (not correlated with the error term) and relevant (correlated with the regressor).
- 😀 Exogeneity of an instrument ensures that the comparison between groups is driven solely by the regressor and not by confounding factors, revealing the causal effect.
- 😀 The video introduces a clever instrument in the maternal labor supply example: the 'same sex' variable (whether the first two children are the same sex) is used as an instrument for deciding to have more children, under the assumption it satisfies both exogeneity and relevance.
Q & A
What is endogeneity, and why does it pose a problem in OLS regression?
-Endogeneity occurs when the regressor is correlated with the error term in a regression model. This poses a problem in OLS (Ordinary Least Squares) regression because it leads to biased estimates of the causal effect, violating the assumption of exogeneity required for OLS to yield valid results.
What are some common reasons why OLS regression might be biased due to endogeneity?
-Common reasons for endogeneity in OLS regression include omitted variables (unobserved factors influencing both the regressor and the outcome), measurement error (using imprecise proxies for the regressor), and equilibrium conditions where the regressor and outcome are jointly determined.
How does Instrumental Variable (IV) regression address the problem of endogeneity?
-IV regression addresses endogeneity by using an instrument—an external variable that is correlated with the endogenous regressor but not with the error term. This allows for the estimation of causal effects by isolating the variation in the regressor that is not influenced by the error term.
What are the two key assumptions that must be satisfied for IV regression to work?
-The two key assumptions for IV regression are: 1) **Exogeneity**: The instrument must not be correlated with the error term. 2) **Relevance**: The instrument must be correlated with the endogenous regressor, ensuring that the instrument has explanatory power.
Can you explain the concept of an instrument using the example from the video?
-In the example, the regressor of interest is 'more kids' (whether a mother has more than two children). The instrument is 'same sex' (whether the first two children are of the same sex). This instrument is assumed to be exogenous because the decision to have more children based on the sex of the first two is unlikely to be influenced by unobserved factors like childcare availability.
What is the role of the 'same sex' instrument in the maternal labor supply example?
-'Same sex' is used as an instrument to determine the variation in the number of children mothers have (more kids = 1 if they have more than two children). The instrument helps separate the exogenous variation in the number of children from any confounding factors, like differences in childcare availability, that might otherwise bias the results.
Why can't OLS regression be used in this maternal labor supply example?
-OLS regression cannot be used in this example because the regressor, 'more kids,' is likely endogenous. Factors such as childcare availability or parental preferences may simultaneously affect both the number of children and the amount of labor a mother supplies, leading to bias in the OLS estimates.
What does the IV estimator estimate in this context, and how is it calculated?
-The IV estimator in this context estimates the causal effect of having more children on the number of weeks a mother works. It is calculated by comparing the difference in the outcome variable (weeks worked) between groups that differ in the instrument (same sex) but not in confounding factors, thereby isolating the effect of the regressor.
How does sorting the sample into different groups help in identifying causal effects?
-Sorting the sample into different groups based on the instrument (e.g., same sex) helps ensure that the groups differ only in the regressor (more kids) and not in any confounding factors (such as childcare). This allows the IV estimator to capture the true causal effect by comparing the groups in a way that isolates the influence of the regressor on the outcome.
What does the exogeneity assumption mean in the context of IV regression?
-The exogeneity assumption in IV regression means that the instrument must be unrelated to the error term in the regression model. This ensures that any variation in the regressor (e.g., more kids) induced by the instrument (e.g., same sex) is not confounded by unobserved factors that could otherwise bias the causal estimate.
What is the 'relevance' assumption in IV regression, and why is it important?
-The relevance assumption in IV regression states that the instrument must be correlated with the regressor. This is important because if the instrument has no explanatory power over the regressor, it will not help to isolate the variation in the regressor that is needed to estimate the causal effect.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Regression and Matching | Causal Inference in Data Science Part 1
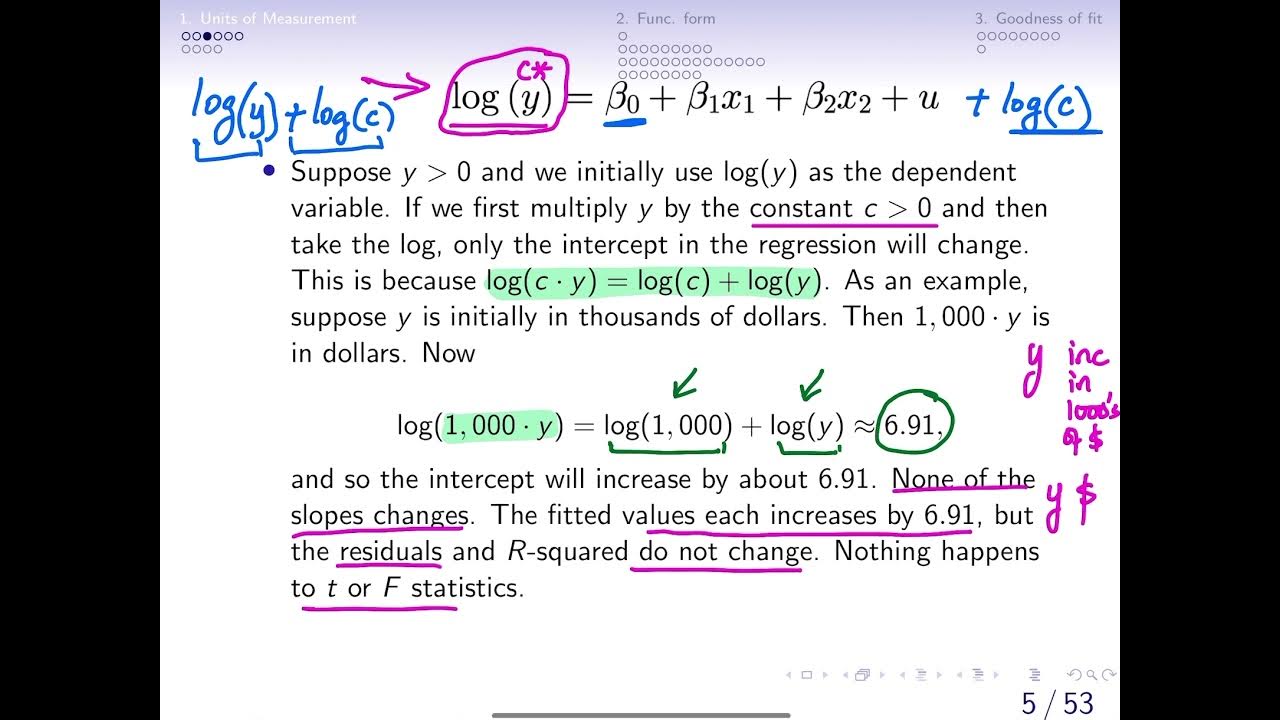
6.1 Effects of Data Scaling on OLS statistics (changing units of measurement)

Konsep Dasar Regresi Logistik

Regresi Linear Sederhana dengan Ordinary Least Square

35. Regressione Lineare Semplice (Spiegata passo dopo passo)
Regresi Ordinal dan Multinomial Logistik Pada Data Crosssection dengan Minitab
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
