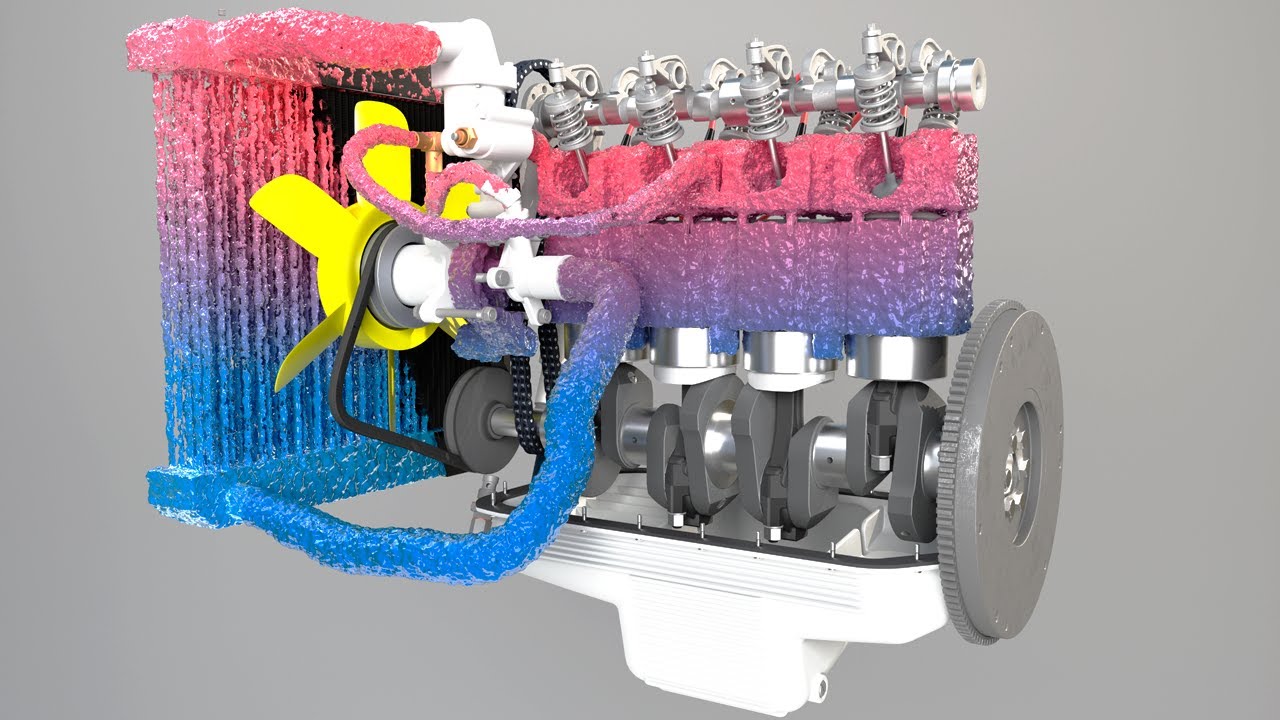
SISTEM PENDINGIN, Part 4: Cara Kerja Sistem Pendingin (Konvensional)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the working mechanism of a conventional car cooling system, focusing on key components like the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and cooling fan. It outlines how these elements work together to maintain the engine's optimal temperature by circulating coolant through the engine and radiator. The script covers the process from engine startup to coolant circulation, thermostat regulation, and pressure control through the radiator cap. Viewers gain a clear understanding of how the system prevents overheating and ensures engine efficiency, while also highlighting the importance of each component in the overall cooling process.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video explains how a conventional cooling system in an engine works, focusing on the function of various components.
- 😀 The cooling fan is directly connected to the engine's crankshaft, meaning its speed increases and decreases with the engine's RPM.
- 😀 The water pump circulates coolant through the engine's water jacket to absorb heat from the engine block and cylinder head.
- 😀 The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant based on temperature, opening at a preset temperature (e.g., 65°C) to allow coolant to reach the radiator.
- 😀 The radiator consists of tubes and fins that dissipate heat by allowing air to pass through, aided by the cooling fan.
- 😀 Coolant flows from the engine's water jacket to the radiator, where it cools down before returning to the engine to absorb more heat.
- 😀 The radiator cap maintains pressure in the cooling system, releasing excess coolant to the reservoir tank if the pressure or temperature is too high.
- 😀 When the coolant heats up and expands, the radiator cap opens to release excess pressure, preventing damage to the system.
- 😀 As the coolant cools down and contracts, the radiator cap helps draw coolant back from the reservoir tank to maintain system volume.
- 😀 Understanding the function of each component, such as the water pump, thermostat, and radiator cap, is essential to comprehending the cooling system's operation.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the thermostat in the conventional cooling system?
-The thermostat regulates the flow of coolant by controlling when it enters the radiator. It opens once the engine reaches a certain temperature, typically around 65°C, allowing the coolant to move to the radiator for cooling.
How does the cooling fan work in a conventional system?
-The cooling fan is mechanically connected to the engine and rotates as the engine runs. Its speed is directly linked to the engine's speed, meaning it spins faster when the engine is running faster to help cool the radiator more effectively.
What role does the water pump play in the cooling system?
-The water pump circulates coolant through the engine, specifically around the water jacket, to absorb heat from the engine. It ensures that the coolant is constantly moving to maintain optimal engine temperature.
What happens when the engine's coolant reaches the thermostat’s set temperature?
-Once the engine coolant reaches the thermostat's set temperature (65°C in this case), the thermostat opens, allowing the coolant to flow into the radiator to be cooled before it returns to the engine.
How does the radiator cool the coolant?
-The radiator cools the hot coolant by allowing it to pass through metal pipes surrounded by fins. As air flows through the radiator (assisted by the cooling fan), heat from the coolant is dissipated into the surrounding air.
Why is the radiator cap important in the cooling system?
-The radiator cap maintains the pressure in the cooling system. If the pressure exceeds the design limit, the cap opens to release excess coolant into the reservoir tank, preventing damage to the system due to over-pressurization.
What happens to the coolant when it cools down?
-As the coolant cools, it contracts. This contraction creates a vacuum that draws coolant from the reservoir tank back into the radiator, ensuring that the system remains filled with coolant without air pockets.
What is the purpose of the reservoir tank in the cooling system?
-The reservoir tank serves as a storage for excess coolant. When the coolant expands due to heat, it is directed into the reservoir. When the system cools and contracts, the coolant is drawn back into the radiator from the reservoir.
Why is the cooling system considered 'conventional' in this script?
-The cooling system is considered 'conventional' because the cooling fan is mechanically driven by the engine's crankshaft, and its speed is directly tied to the engine's RPM, as opposed to being controlled by electric sensors or switches.
What would happen if the radiator cap failed to open under high pressure?
-If the radiator cap fails to open under high pressure, the system could become over-pressurized, leading to potential damage such as bursting hoses, leaking coolant, or warping components like the radiator or engine block.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)