SPOTLIGHT: Asexual Reproduction in Plants | Encyclopaedia Britannica
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the fascinating world of plant reproduction, focusing on asexual methods such as the use of bulbs, rhizomes, gemmae, and runners. It explains how plants like irises, liverworts, and strawberries utilize these mechanisms to reproduce efficiently, often in response to adverse conditions. The script highlights the advantages of asexual reproduction for commercial growers, as it ensures consistency and faster growth compared to seeds. Additionally, it touches on the survival benefits of diversity through sexual reproduction in a changing environment, emphasizing its importance for long-term survival.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Asexual reproduction in plants allows them to reproduce without the need for gametes, using methods like bulbs, plantlets, or cuttings.
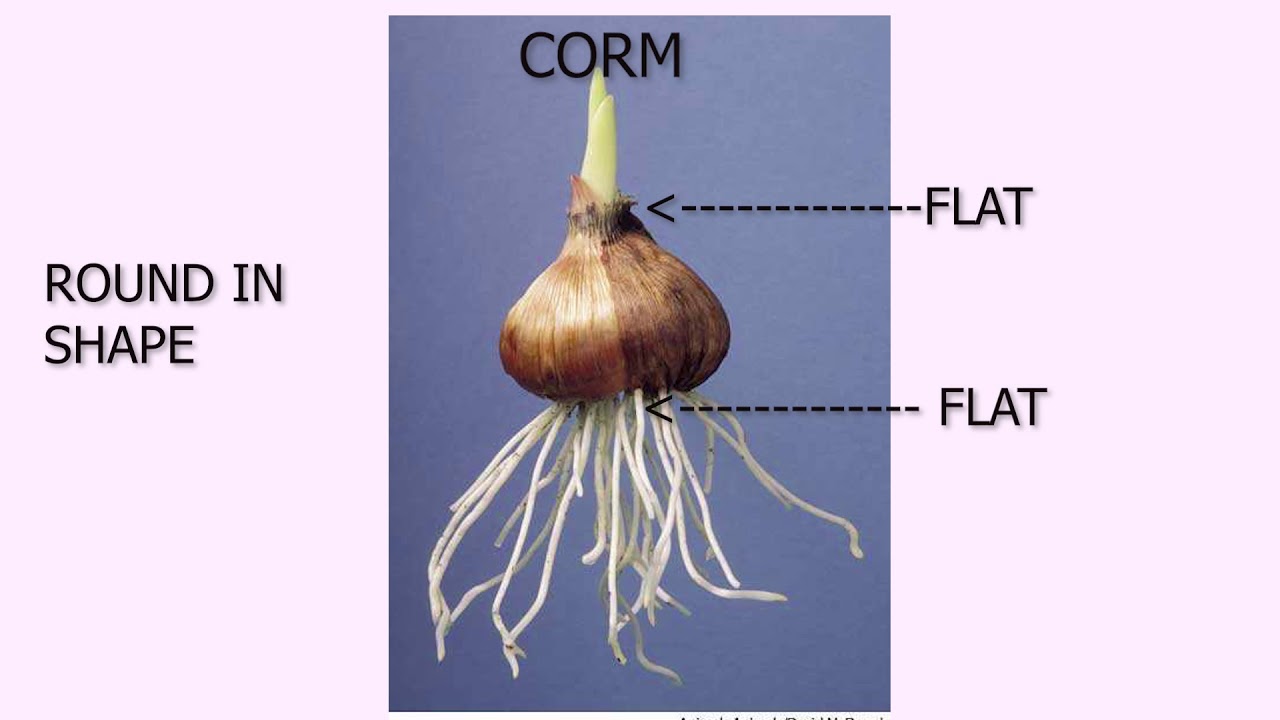
- 🌸 Bulbs are important for plant survival, enabling rapid growth after adverse conditions by acting as a type of 'parenting organ.'
- 🌷 Irises use swollen rhizomes as a means of asexual reproduction, allowing them to survive harsh conditions and grow when the environment is favorable.
- 🍃 Liverworts reproduce asexually through small green discs called gemmae, which grow inside special cups and scatter away to grow into new plants.
- 🌿 Some plants, like the bamboo, develop miniature plantlets on the edges of their leaves, which eventually drop off to form independent plants.
- 🍓 Strawberry plants propagate asexually through runners that create new plantlets at the end, helping them spread quickly.
- ✂️ Plant growers often use cutting methods to propagate plants asexually, taking advantage of the ability of stem cells to trigger root growth.
- 🛠️ Asexual reproduction offers a reliable and faster alternative to seed propagation, making it valuable for commercial growers who need consistent quality.
- 💪 In stable environments, asexual reproduction is advantageous as it preserves successful plant characteristics, ensuring survival.
- 🌍 In changing environments, however, sexual reproduction, with its resulting diversity, helps ensure long-term survival and adaptability of plant species.
Q & A
What is a key characteristic of plants that reproduce asexually using bulbs?
-Bulbs enable plants to reproduce asexually without producing gametes, allowing them to survive in adverse conditions and grow quickly when the time is right.
How do irises reproduce asexually, and what role do their swollen rhizomes play?
-Irises reproduce asexually using swollen rhizomes, which function as storage organs. These rhizomes help the plant survive harsh conditions and then grow when conditions are favorable.
What is the function of gemmae in the reproduction of certain plants like liverworts?
-Gemmae are small discs of green tissue that grow inside special cups on plants like liverworts. When mature, they break off due to external factors like raindrops and grow into new plants.
What is asexual reproduction in plants, and how does it differ from sexual reproduction?
-Asexual reproduction in plants does not involve the fusion of gametes (sexual reproduction), and instead relies on methods like bulbs, rhizomes, gemmae, or plantlets to produce offspring that are genetically identical to the parent plant.
How do plants like the 'bopm' reproduce asexually?
-Plants like the 'bopm' reproduce asexually by developing miniature plantlets at the edges of their leaves. These plantlets eventually drop off and grow into independent plants.
How do strawberry plants propagate asexually?
-Strawberry plants propagate asexually by producing plantlets at the end of long runners. These plantlets can establish new plants independently.
Why is asexual reproduction beneficial for commercial growers?
-Asexual reproduction is beneficial for commercial growers because it is faster and more reliable than growing plants from seeds. It also ensures consistency in plant quality.
What role do stem cells play in asexual reproduction through cutting?
-Stem cells in plant cuttings trigger the formation of root cells, allowing the cutting to develop roots and grow into a new plant.
What is the advantage of asexual reproduction in stable environments?
-In stable environments, asexual reproduction allows plants to exploit a favorable niche, ensuring the persistence of successful plant varieties.
Why is sexual reproduction important for plant survival in changing environments?
-Sexual reproduction promotes genetic diversity, which increases a plant species' ability to adapt and survive in changing environments, providing an advantage over asexually reproduced plants.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

IPA Kelas 9 : Sistem Perkembangbiakan Tumbuhan (Part 1 : Perkembangbiakan Vegetatif)

SCIENCE06L13: Vegetative Propagation in Plants

SISTEM REPRODUKSI PADA HEWAN DAN TUMBUHAN | RINGKAS

Materi IPA Kelas 9 - Sistem Reproduksi/Perkembangbiakan pada Hewan

REPRODUCTION DES PLANTES 🌱 (Sexuelle, asexuée, avec des fleurs et sans fleurs)
Modification in Underground Stem
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
