Economic Policies in 'Arthashastra ' and its relevance in Today's Economy
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture, Dr. Padmashri Muma explores the economic policies outlined in Chanakya's *Arthashastra* and their continued relevance in today's economy. Focusing on taxation, sources of revenue, and labor policies, Dr. Muma discusses Chanakya's principles of limited, equitable taxation and progressive fiscal strategies. The lecture also highlights labor laws, including fair wages, skill development, and worker welfare, paralleling modern policies like MGNREGA. Finally, the speaker draws connections between Chanakya's views on governance, corruption, and social welfare with contemporary practices, showcasing the enduring impact of his economic philosophy on modern governance.
Takeaways
- 😀 Chanakya's Arthashastra presents a balanced approach to taxation, advocating for progressive tax rates and the well-being of the people, not just the king.
- 😀 Chanakya emphasized the importance of diverse taxes, including land taxes, transaction taxes, customs duties, and royalties from natural resources.
- 😀 He highlighted the importance of providing fair wages, ethical treatment, and skill development for workers, including various categories like bonded labor, casual labor, and self-employed individuals.
- 😀 In today's context, modern Indian tax systems, like income tax and GST, reflect Chanakya's principles of fair taxation and equitable distribution of wealth.
- 😀 Chanakya’s economic theory includes a focus on maximizing government revenue from public enterprises and crown properties, which remains relevant today.
- 😀 Welfare policies in modern India, such as poverty alleviation programs, public distribution systems, and employment generation schemes, are aligned with Chanakya’s vision of promoting the people's well-being.
- 😀 The **MNREGA** (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act) is an example of a modern policy inspired by Chanakya’s approach to ensuring employment and social security for citizens.
- 😀 Chanakya’s anti-corruption policies stressed identifying corrupt practices and imposing punishments such as fines, imprisonment, or even death, mirroring today’s anti-corruption laws and authorities like the Enforcement Directorate.
- 😀 The central idea of Chanakya’s governance is the prosperity of the people, ensuring that both the ruler and the subjects benefit from sound economic policies.
- 😀 Chanakya's concept of a prosperous state is one where both the state and the citizens thrive through balanced economic strategies that promote welfare, fairness, and growth.
Q & A
What are the main economic policies proposed by Chanakya in his *Arthashastra*?
-Chanakya's *Arthashastra* covers various economic policies including taxation, revenue generation, labor classification, and governance. He emphasized a fair and balanced taxation system, state revenue from land, trade, and production, the protection of laborers' rights, and governance focused on the welfare of the people.
How did Chanakya define the role of taxation in governance?
-Chanakya viewed taxation as a necessary tool for the welfare of the state, but he stressed that taxes should be equitable and proportional to the wealth of the individual. The government should also be transparent and informative about its tax policies to avoid alienating the people.
What are the different categories of labor according to Chanakya, and what rules did he propose for each?
-Chanakya classified labor into categories such as bonded labor, casual labor, contractual workers, and self-employed individuals. He advocated for fair wages and ethical treatment, emphasizing that bonded labor should be protected, casual laborers should be paid based on the nature of their work, and self-employed individuals should earn based on their skill or service.
How do Chanakya's tax policies relate to modern tax systems?
-Chanakya’s principles of proportional taxation and revenue generation from multiple sources are reflected in modern tax systems, where income tax is levied based on a person’s earning capacity, and governments collect revenue through various sources such as corporate taxes, excise duties, and customs taxes.
What modern programs reflect Chanakya's policies on poverty alleviation and welfare?
-Programs like the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) and the Public Distribution System (PDS) in India are modern examples of policies inspired by Chanakya’s focus on welfare, job creation, and poverty alleviation for disadvantaged sections of society.
In what ways does Chanakya's *Arthashastra* address corruption in governance?
-Chanakya identified 40 types of corruption and misconduct by government servants. He proposed strict punishments, including fines, imprisonment, and even death, for those involved in corruption, demonstrating his belief in just and fair governance. Modern anti-corruption institutions like the Enforcement Directorate and Income Tax authorities reflect this principle.
What is the relationship between Chanakya’s economic policies and modern labor laws?
-Chanakya’s detailed classification of labor categories, with specific rules for each, aligns with modern labor laws that protect various types of workers, including casual workers, contract workers, and self-employed individuals. His focus on fair treatment and equitable wages is also evident in contemporary labor rights frameworks.
How does Chanakya's approach to state revenue generation compare to modern public sector enterprises?
-Chanakya's concept of revenue generation from state-controlled activities, such as trade, land, and resources, is similar to how modern governments generate revenue from public sector enterprises. Examples include revenue from businesses like BPCL and HPCL in India, where the state owns shares and generates profits.
Why does Chanakya emphasize the role of the government in ensuring the prosperity of its people?
-Chanakya believed that a prosperous ruler would ensure the prosperity of the people through effective governance, welfare programs, and promoting commercial activities. His philosophy emphasized that the wealth and welfare of the state depend on the well-being and economic opportunities available to its citizens.
What key lessons can modern leaders learn from Chanakya's *Arthashastra* in terms of governance and economic management?
-Modern leaders can learn the importance of fair taxation, ethical governance, equitable labor policies, and ensuring that state resources are used for public welfare. Chanakya’s teachings emphasize balancing the interests of the government and the people, promoting long-term economic stability, and preventing corruption.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
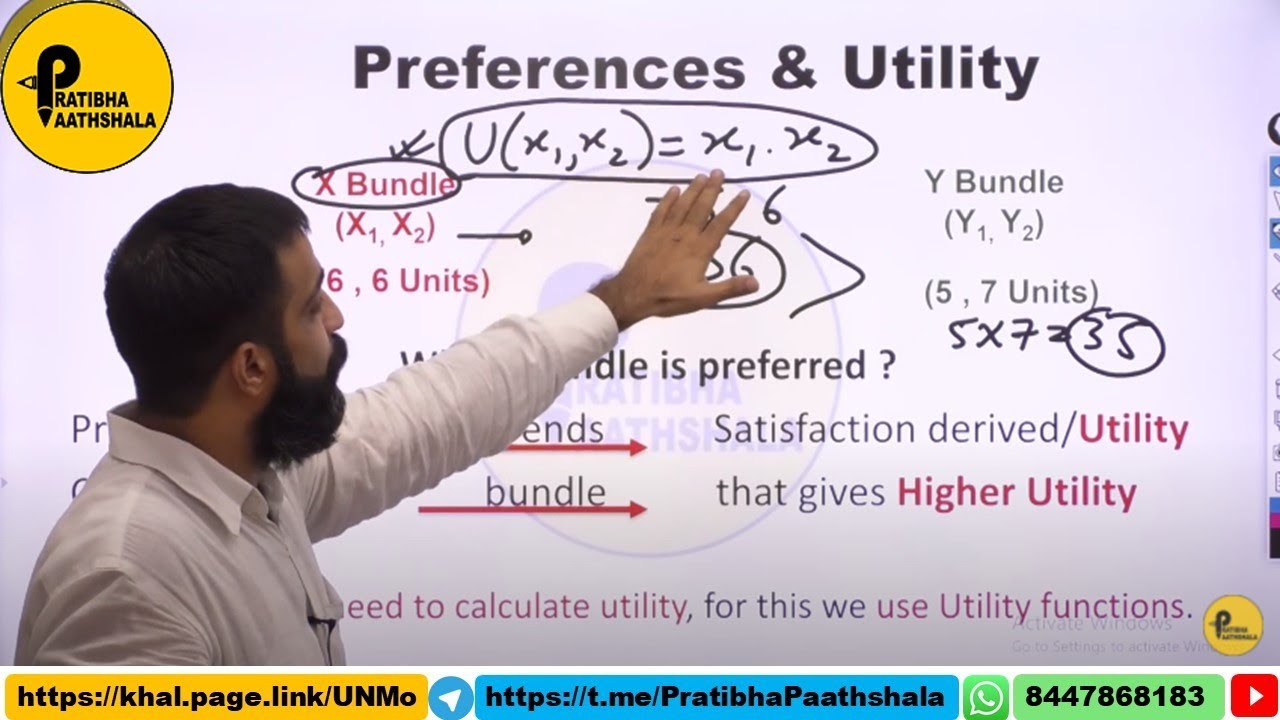
Preferences| Strict & Weak Preference| Varian Ch 3| BA (H) Economics| NTA NET Economics| IES |

2020. 청소년 인문학 콘서트(의사가 알려주는 청소년 식생활 지침)

A concept of Differential Equation
ANATOMI KERANGKA MANUSIA - DASAR OSTEOLOGI

Perception - Part 4

Lecture # 40-41 | Composite Materials | All Key concepts in just 30 Minutes

Sebuah gambaran: Konsep, Metodologi, dan Teknologi Sistem Pendukung Keputusan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
