Process Analysis and Design in Process Strategy
Summary
TLDRThis video covers process analysis and design tools to help organizations align their processes with their competitive strategy, whether focusing on differentiation, low-cost, or quick response. The tools explored include flowcharts, time-function maps, value stream maps, process charts, and service blueprinting, each offering unique insights into process optimization. By identifying value-added versus non-value-added activities, organizations can improve efficiency and customer satisfaction. The video also discusses methods for improving service productivity, such as automation and self-service, using real-world examples like fast food and oil change processes to illustrate the concepts.
Takeaways
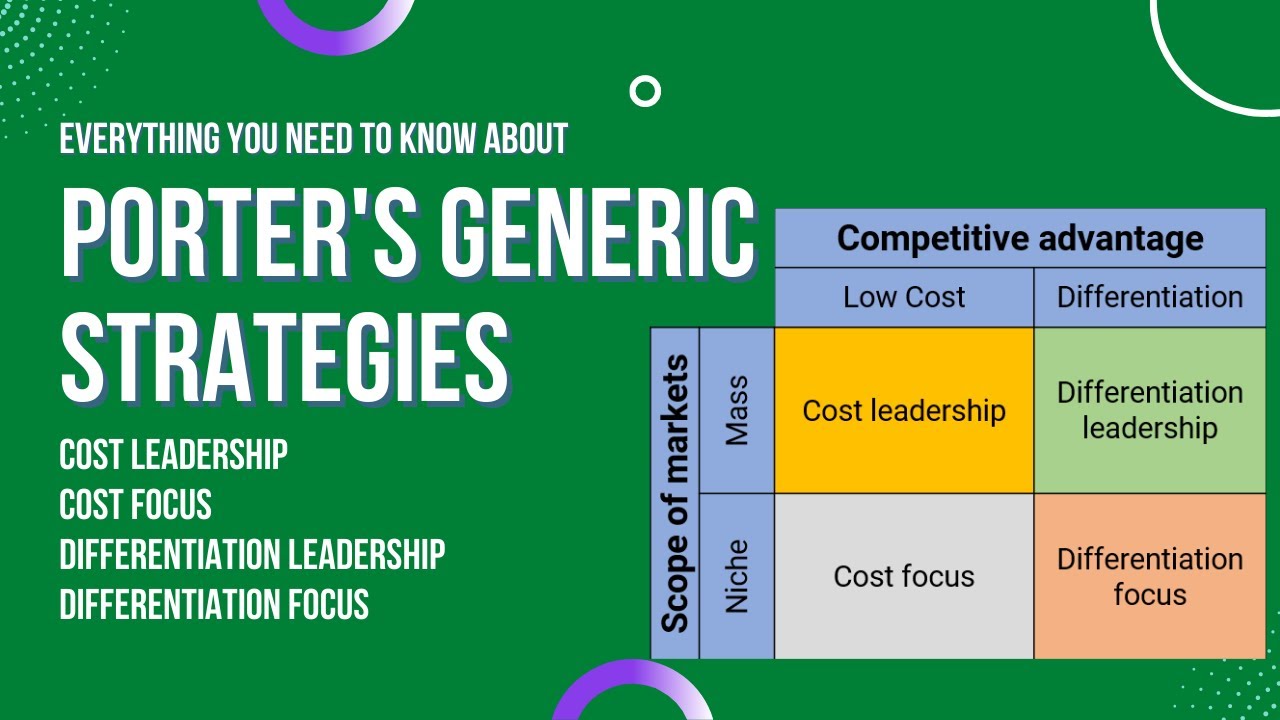
- 😀 A key focus when analyzing and designing processes is whether they align with the company's competitive advantage, such as differentiation, low-cost strategy, or quick response.
- 😀 When designing processes, ask four key questions: Does the process achieve competitive advantage? Does it eliminate non-value-added steps? Does it maximize customer value? Will it help win orders?
- 😀 Flowcharts are a simple yet widely used tool to visualize the movement of materials, people, and actions in a process. They help identify actions, decisions, and steps in the process.
- 😀 Time Function Mapping adds time elements to flowcharts, enabling better analysis of time spent at each step of a process and identifying areas for improvement, such as reducing wait times.
- 😀 A Time Function Map helps identify non-value-added activities, as seen in the example of reducing a 52-day process to 6 days by eliminating or improving steps with excessive wait times.
- 😀 Value Stream Mapping extends Time Function Mapping by including external factors like customers and suppliers, helping organizations assess value beyond their internal operations.
- 😀 A Process Chart uses specific symbols (e.g., circles for operations, arrows for transportation, squares for inspections) to classify steps in a process and identify value-added versus non-value-added activities.
- 😀 Service Blueprinting focuses on customer interactions in service processes, detailing how different levels of interaction between customers and service providers impact the service experience.
- 😀 In service processes, there are three levels of customer interaction: Level 1 (customer in control), Level 2 (interaction with service provider), and Level 3 (service provided while customer is not involved).
- 😀 The Service Process Matrix helps determine the right combination of customization and labor interaction in service processes. It categorizes service types from high customization (e.g., private banking) to low customization (e.g., fast food).
- 😀 Improving service productivity can involve techniques like self-service, which reduces the need for labor-intensive customer interactions. Examples include self-checkout at supermarkets.
Q & A
What is the main goal of process analysis and design in the context of competitive advantage?
-The main goal is to determine if the process aligns with the company's competitive strategy, whether it focuses on differentiation, quick response, or low-cost strategy. The aim is to design processes that eliminate non-value-added steps and maximize customer value, helping to win orders and maintain a competitive edge.
What are the four key questions to ask when designing processes within an organization?
-1. Is this process designed to achieve competitive advantage? 2. Does it eliminate steps that don’t add value? 3. Does it maximize customer value as perceived by the customer? 4. Will this process help to win orders?
How does a flowchart help in process analysis?
-A flowchart provides a big-picture view of a process, showing the movement of materials, people, and products. It identifies actions and decisions, helping to visualize each step and understand the process flow.
What is the difference between a time function map and a flowchart?
-A time function map adds a time element to a flowchart, showing the time required for each step in a process, even including wait times. It helps to analyze where time is being spent and identify areas for improvement.
What is value stream mapping, and how does it differ from a time function map?
-Value stream mapping extends a time function map by adding external factors such as suppliers and customers, showing the flow of materials and information beyond the organization. It includes both value-added and non-value-added time, highlighting inefficiencies in the entire supply chain.
Can you give an example of a process improvement from the time function map example provided?
-In the provided example, a process initially took 52 days to complete, with significant wait times. After analysis, non-value-added steps were eliminated or improved, reducing the lead time to just 6 days, saving 46 days in the process.
What does a process chart focus on, and how does it classify activities?
-A process chart focuses on the key activities within a process and classifies them using symbols like circles (operations), arrows (transportation), squares (inspection), and others. It helps to identify which activities are value-added (operations) and which are non-value-added (transportation, delays, etc.).
What is service blueprinting, and how does it help in process design?
-Service blueprinting is a process analysis technique that focuses on the customer-provider interaction. It outlines the stages of service delivery, identifying moments of truth where customer interaction occurs, and highlights areas for improving service quality and process efficiency.
What are the three levels of customer interaction in service blueprinting?
-1. Level 1: The customer is in control and decides if they want the service. 2. Level 2: The customer interacts with the service provider during service delivery. 3. Level 3: The service is delivered without customer interaction, and the provider takes full control of the process.
What is a Pokey Yoke, and how does it relate to service blueprinting?
-A Pokey Yoke is a foolproof mechanism designed to prevent mistakes in a process. In service blueprinting, it refers to procedures that ensure quality and minimize errors, such as using checklists or automated reminders to avoid service failures, like ensuring the correct steps are followed in an oil change.
How does the service process matrix help in designing processes?
-The service process matrix helps organizations determine the right mix of customer interaction and customization based on their service model. By balancing labor and customization, businesses can align their process design with the level of service and customer experience they aim to provide.
What is the importance of finding the right balance between cost and customer interaction in service design?
-Finding the right balance ensures that processes are efficient while still meeting customer expectations. Too much interaction can slow down service and increase costs, while too little interaction might reduce the quality of the customer experience. A well-designed process strikes a balance to optimize both cost and service quality.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)