Studi Kasus: Metode Fuzzy Mamdani
Summary
TLDRIn this session on artificial intelligence, the focus is on implementing the Mamdani fuzzy inference method through a case study involving an electronics factory. The discussion highlights the process of fuzzification, rule evaluation, and aggregation to determine optimal production levels based on demand and inventory. Key concepts include defining fuzzy variables, creating membership functions, and deriving production outcomes using logical rules. The analysis contrasts this method with the Tsukamoto fuzzy approach, ultimately demonstrating the unique insights gained from applying Mamdani's framework to manage production effectively under varying constraints.
Takeaways
- 😀 The session focuses on implementing the Mamdani fuzzy logic method in a case study involving an electronic factory.
- 😀 The factory's demand and supply dynamics are analyzed, highlighting discrepancies between requested and produced items.
- 😀 Fuzzification involves determining fuzzy variables, membership functions, and degrees of membership for demand, supply, and production.
- 😀 Three fuzzy variables are identified: demand (high/low), supply (high/low), and production (increase/decrease).
- 😀 The degrees of membership for demand and supply are calculated based on given numerical values.
- 😀 Rule evaluation combines different scenarios to determine how production should adjust based on demand and supply conditions.
- 😀 Logical consistency is essential in evaluating fuzzy rules to ensure feasible production outcomes.
- 😀 The aggregation process combines the outcomes from various rules to determine overall production adjustments.
- 😀 The defuzzification process uses the centroid method to convert fuzzy output into a crisp production value.
- 😀 The final production value determined by the Mamdani method is lower than that from the Tsukamoto method, indicating different approaches yield different outputs.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video transcript?
-The primary focus is on implementing fuzzy logic using the Mamdani method to solve a production case study in an electronics factory.
What problem does the factory face regarding production?
-The factory has a demand of 4000 units but only has 300 units in stock, leading to a significant shortfall.
What are the fuzzy variables identified in the case study?
-The fuzzy variables are demand, supply, and production, each categorized into fuzzy sets.
How is fuzzification performed in this context?
-Fuzzification involves determining the fuzzy sets for each variable and calculating the degrees of membership for the specific values of demand and supply.
What inference rules are established for production?
-Inference rules relate combinations of demand and supply (e.g., if demand is high and supply is low, production should decrease) to determine appropriate production levels.
What method is used for defuzzification in the case study?
-The centroid method is used for defuzzification, which calculates a crisp output based on the area under the fuzzy production curve.
What is the final recommended production level for the factory?
-The final recommended production level is approximately 4200 units.
How does the Mamdani method differ from other fuzzy methods like Tsukamoto?
-The Mamdani method uses a more comprehensive approach to fuzzy inference, incorporating fuzzy rules and evaluating the minimum degree of membership, while Tsukamoto typically uses weighted averages for defuzzification.
What is the significance of checking the logical consistency of the rules?
-Checking logical consistency ensures that the rules applied in the inference process make sense and lead to practical and reasonable production recommendations.
How does this fuzzy logic approach benefit the factory's decision-making process?
-This fuzzy logic approach allows the factory to manage uncertainties and make informed production decisions that can adapt to varying demand and supply conditions.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Fuzzy SUGENO alias TAKAGI-SUGENO-KANG | Sistem Inferensi Fuzzy | Studi Kasus Mesin Cuci Otomatis

Fuzzy TSUKAMOTO | Sistem Inferensi Fuzzy | Contoh Studi Kasus dan Langkah Penyelesaiannya
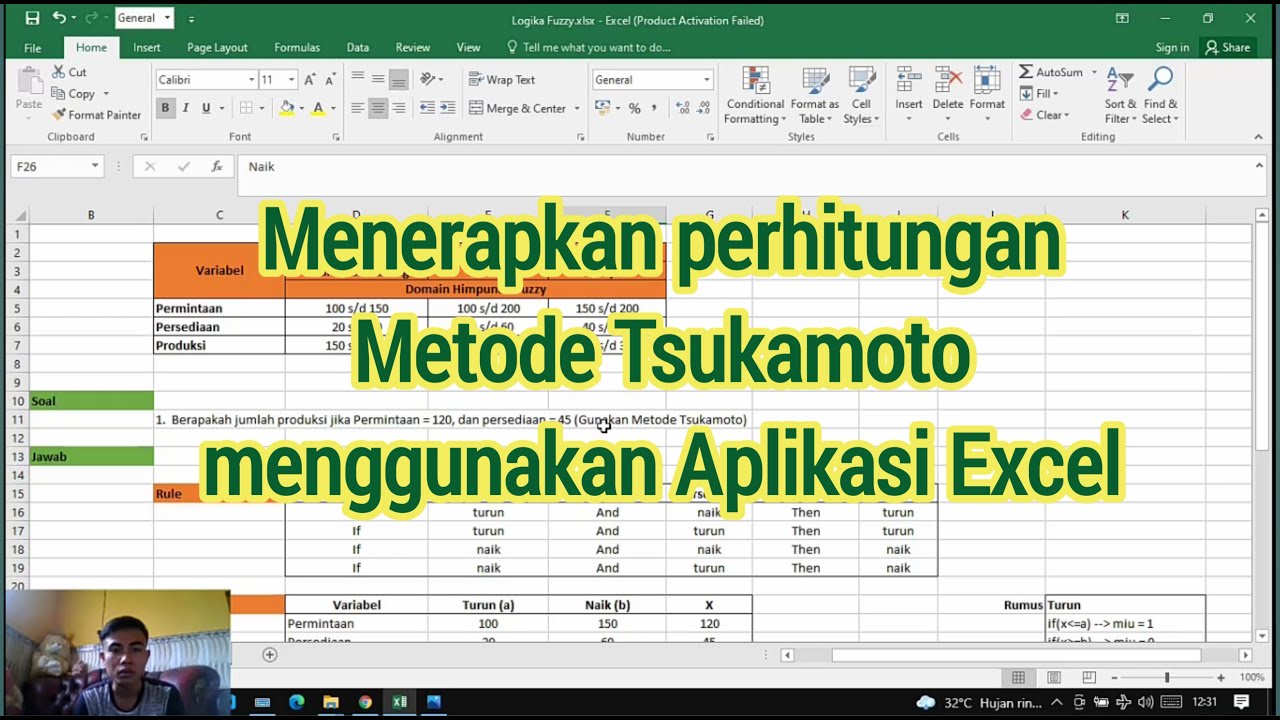
Perhitungan Metode Tsukamoto Menggunakan Aplikasi Microsoft Excel

[JST INFORMATIKA UNINDRA] Grup 2 Kelas X8C | Tentang McCulloch Pitts

Logika Fuzzy MAMDANI dengan MATLAB | Fuzzy Logic Designer Toolbox

Fuzzy Logic (1/7)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
