Cholinergic agonists || Mechanism, actions, side effects & uses
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth exploration of cholinergic agonists, detailing their classification into directly and indirectly acting types. It highlights their mechanisms of action, including effects on various receptors, and discusses clinical applications such as treating glaucoma, xerostomia, and bladder hypotonia. The transcript covers specific drugs like pilocarpine, carbamylcholine, and sevimeline, noting their therapeutic uses and potential side effects, such as bradycardia and blurred vision. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of cholinergic agonists in medical practice and their varied physiological effects.
Takeaways
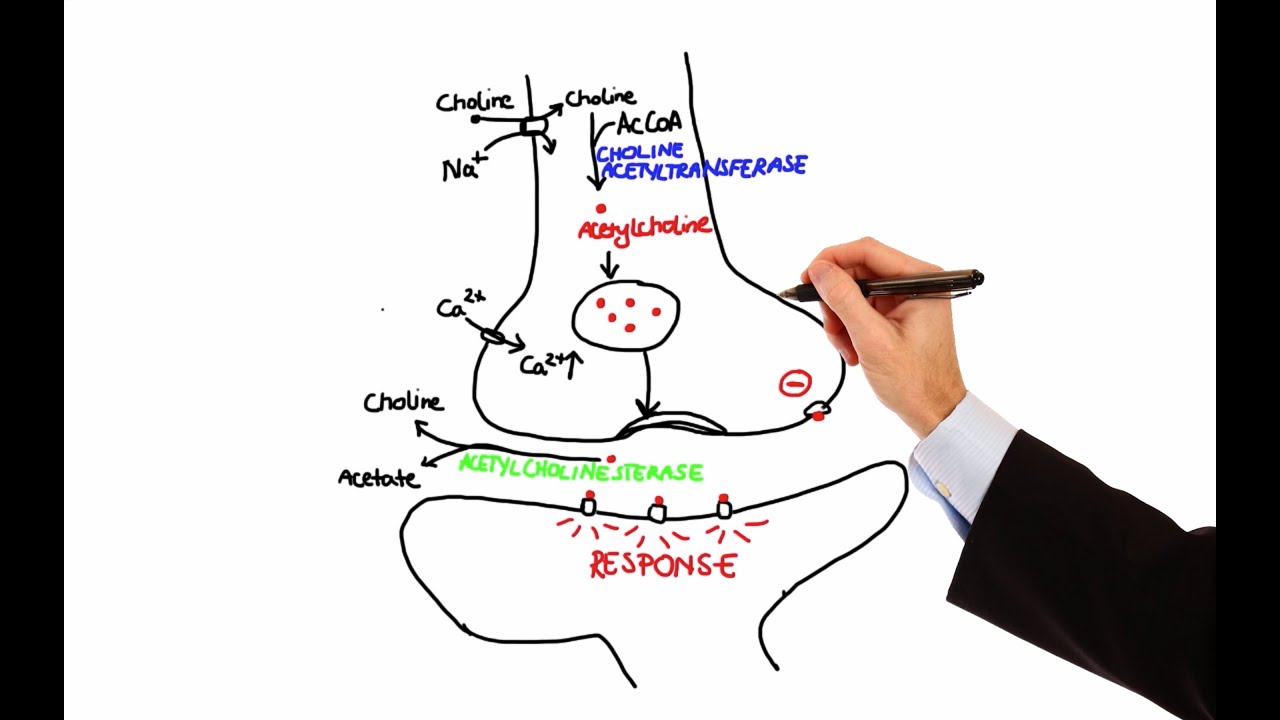
- 😀 Cholinergic agonists activate cholinergic receptors, leading to increased secretions and muscle contractions.
- 😀 They are classified into directly acting agonists (e.g., acetylcholine) and indirectly acting agonists (e.g., acetylcholinesterase inhibitors).
- 😀 Acetylcholine is rapidly metabolized, limiting its clinical use.
- 😀 Carbachol is more stable than acetylcholine and is used to lower intraocular pressure in glaucoma.
- 😀 Pilocarpine is effective in treating both glaucoma and xerostomia, stimulating salivary secretion.
- 😀 Bethanechol is used for bladder hypotonia, promoting contraction and relieving urinary retention.
- 😀 Common side effects of cholinergic agonists include bradycardia, hypotension, and blurred vision.
- 😀 Pilocarpine can be used in emergency situations for sudden increases in intraocular pressure.
- 😀 Xerostomia can occur in patients undergoing radiation therapy for head and neck cancers, where pilocarpine can provide relief.
- 😀 Sjogren's syndrome can be treated with cholinergic agonists to stimulate both salivary and tear secretion.
Q & A
What are cholinergic agonists?
-Cholinergic agonists are substances that activate cholinergic receptors in the body, mimicking the effects of acetylcholine.
How do directly acting cholinergic agonists differ from indirectly acting ones?
-Directly acting agonists bind to and activate cholinergic receptors, while indirectly acting agonists increase acetylcholine levels by inhibiting its breakdown.
Why is acetylcholine not commonly used therapeutically?
-Acetylcholine is rapidly metabolized by cholinesterases, making its effects short-lived, and it is non-selective, leading to unwanted side effects.
What is carbachol, and what are its therapeutic uses?
-Carbachol is a directly acting cholinergic agonist that affects both muscarinic and nicotinic receptors, primarily used in treating glaucoma.
What is the role of bethanechol in medical treatment?
-Bethanechol is a selective muscarinic agonist used to treat urinary retention by stimulating bladder contractions.
How does pilocarpine function in the treatment of glaucoma?
-Pilocarpine decreases intraocular pressure by contracting the ciliary muscle and the constrictor muscle of the iris, thus facilitating drainage of aqueous humor.
What conditions can pilocarpine address aside from glaucoma?
-Pilocarpine is also used to treat xerostomia (dry mouth) in patients post-radiation therapy and in conditions like Sjogren's syndrome.
What are the common side effects associated with cholinergic agonists?
-Common side effects include bradycardia, hypotension, increased gastrointestinal motility (leading to diarrhea), bronchoconstriction, and blurred vision.
What is Sjogren's syndrome, and how can it be treated with cholinergic agonists?
-Sjogren's syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that reduces saliva and tear production, and it can be treated with drugs like sevinelin, which stimulates secretions.
What is bladder hypotonia, and which cholinergic agonist can be used to treat it?
-Bladder hypotonia is a condition characterized by reduced bladder contractions leading to urinary retention, and it can be treated with bethanechol.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Pharmacology - CHOLINERGIC DRUGS (MADE EASY)

Farmacodinâmica DESCOMPLICADA

Agonistas Colinérgicos (parte 1 - receptores) | Aula 9 | Farmacologia rápida e fácil | Flavonoide

Agonistas Colinérgicos (Diretos/Muscarínicos) | Aula 10 | Farmacologia rápida e fácil | Flavonoide

HYDRAULIC ACTUATORS VICKERS HYDRAULIC TRAINING VEDIO BY MR PAUL COOK

Barang Tambang #1 (Pengertian dan Klasifikasi Barang Tambang)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
