Jaringan epidermis tumbuhan - jaringan dewasa tumbuhan biologi sma materi kelas
Summary
TLDRThis video lesson explores the protective tissues of plants, focusing on the epidermis and its various modifications. It explains the structure and functions of epidermal tissue, highlighting its role in safeguarding plants from environmental threats. The video also discusses various derivatives of epidermis, such as trichomes, root hairs, and stomata, detailing their specific functions and adaptations to different environments. The mechanisms of stomatal opening and closing are explained, emphasizing their importance in gas exchange and water regulation. Overall, the lesson provides a comprehensive overview of how protective tissues contribute to plant survival.
Takeaways
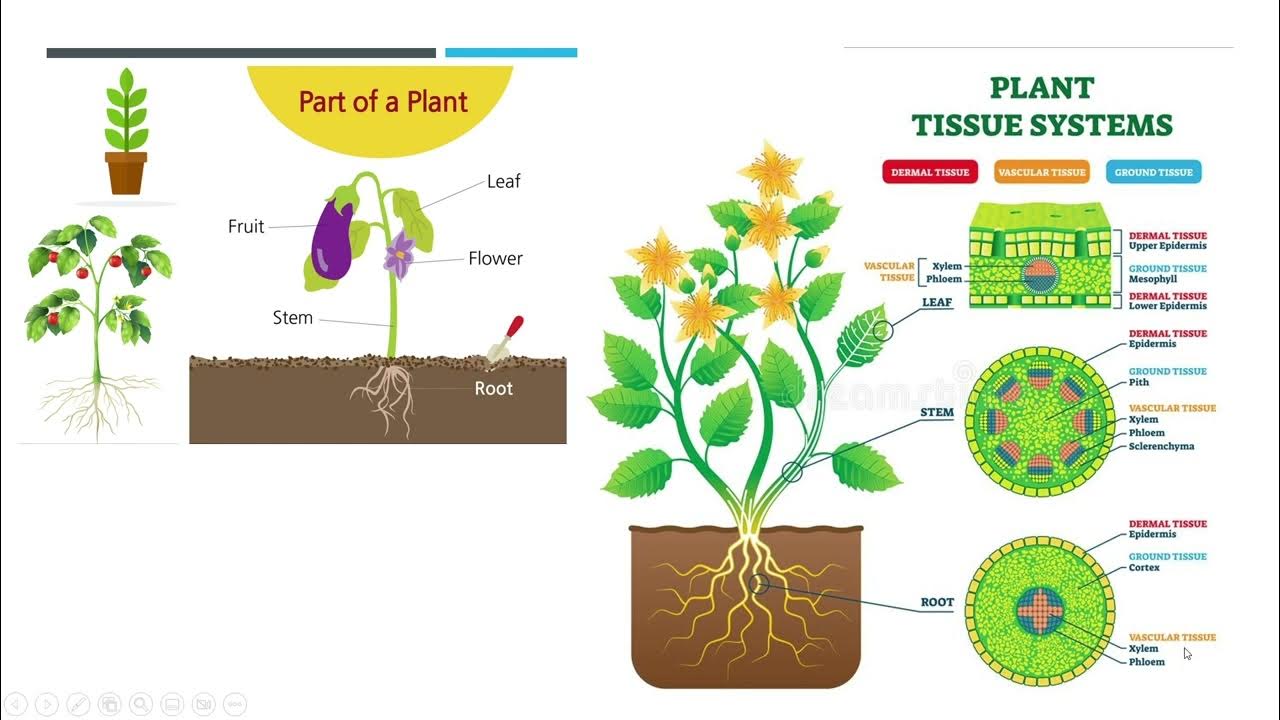
- 🌱 Epidermal tissue is the outer protective layer of plants, similar to human skin, shielding internal structures from environmental threats.
- 🔍 The epidermis consists of tightly packed cells with minimal intercellular spaces, which helps prevent pathogen invasion.
- 💧 Large vacuoles in epidermal cells maintain turgidity, contributing to the tissue's protective function against external stress.
- ☀️ Most epidermal cells are transparent, allowing sunlight to penetrate for photosynthesis while containing few chloroplasts.
- 🌿 Trichomes are hair-like extensions of epidermal cells that reduce water loss and may produce substances to deter herbivores.
- 🌾 Root hairs are specialized extensions that enhance water and mineral absorption exclusively at the root level.
- 🌵 Emergences are sharp projections on various plant parts that can serve as false thorns, helping to protect the plant.
- 🌬️ Stomata, composed of guard cells, facilitate gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide) and regulate water loss through transpiration.
- 💡 Different plant types exhibit various stomatal adaptations (e.g., mesophytes, hydrophytes, xerophytes) to manage water effectively.
- 🔄 The mechanism of stomatal opening and closing involves potassium ion movement, which regulates guard cell turgidity and stomatal pore size.
Q & A
What are the two main types of plant tissues?
-The two main types of plant tissues are meristematic tissues, which facilitate growth, and mature tissues, which include protective, fundamental, vascular, and secretory tissues.
What is the primary function of the epidermis in plants?
-The epidermis serves as the outermost protective layer of plants, safeguarding inner structures from temperature changes, mechanical damage, and harmful organisms.
What characteristics define epidermal tissue?
-Epidermal tissue is located on the outermost layer, composed of tightly packed cells with large vacuoles, and is often transparent to allow sunlight penetration for photosynthesis.
What are trichomes and their role in plants?
-Trichomes are hair-like projections on epidermal tissue that help reduce water loss and deter herbivores.
How do root hairs differ from trichomes?
-Root hairs are extensions of epidermal cells found specifically in roots, functioning to enhance the absorption of water and nutrients from the soil, while trichomes can be found on leaves and stems.
What is the purpose of emergences in plants?
-Emergences are sharp protrusions on plants that serve as a deterrent against herbivores and can be found on various plant parts like stems and fruits.
What are stomata, and why are they important?
-Stomata are small pores in the epidermis of leaves that facilitate gas exchange, allowing oxygen and carbon dioxide to enter and exit, which is crucial for photosynthesis and transpiration.
How do guard cells function in regulating stomata?
-Guard cells control the opening and closing of stomata by changing their shape based on the accumulation of potassium ions and water pressure, responding to environmental conditions.
What distinguishes adaxial stomata from abaxial stomata?
-Adaxial stomata are located on the upper surface of the leaf, while abaxial stomata are found on the lower surface; their positioning can influence water loss and gas exchange efficiency.
How do xerophytes adapt their stomata to survive in arid environments?
-Xerophytes typically have stomata that are sunken and predominantly located on the underside of the leaves, which helps reduce water loss in dry conditions.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

7-1 Types of Dicotyledon Plant Tissues (Cambridge AS A Level Biology, 9700)

Epidermis - The Surface Tissue | Don't Memorise
Module 6: Cell Modifications- General Biology I

Struktur dan Fungsi Jaringan Tumbuhan (Part-1)

ICSE Class 9 Biology Plant and Animal Tissues 1 – Plant Tissues

Pembelajaran anatomi batang
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
