Precipitation Gravimetry
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the concept of precipitation gravimetry, detailing how to determine the composition of an analyte through the formation of insoluble precipitates. It explains the chemical reactions that yield precipitates, the filtration and drying processes for collecting pure samples, and the principles of quantitative analysis. An example illustrates how to analyze a magnesium halide salt by determining the identity of its halogen through stoichiometric calculations. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of gravimetric analysis in accurately quantifying chemical substances.
Takeaways
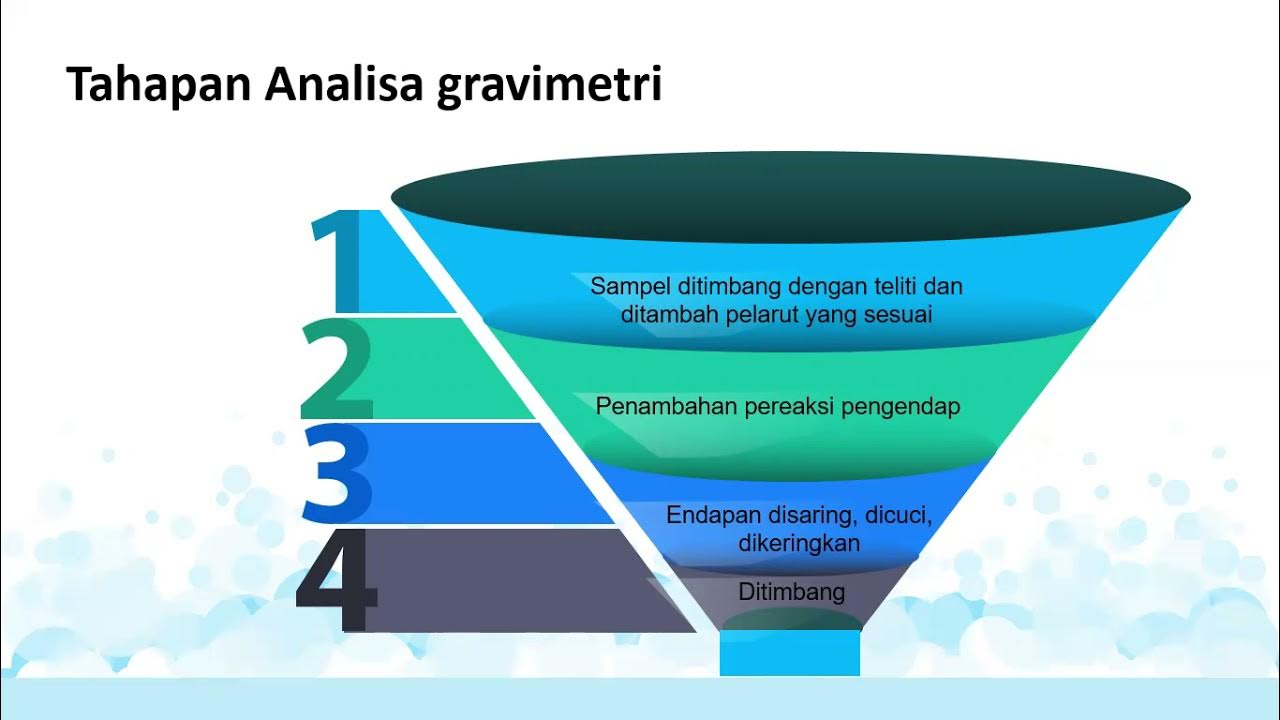
- 😀 Precipitation gravimetry is a technique used to determine the composition of an analyte by forming a solid precipitate from a chemical reaction.
- 🧪 A double decomposition reaction occurs when two ionic compounds in solution exchange ions to form a precipitate and a soluble product.
- 💧 A precipitate is a solid that forms in a reaction and can be collected through filtration from the liquid solution.
- 🔍 Filtration involves using filter paper and a funnel to separate the precipitate from the surrounding liquid, not to be confused with 'funneling.'
- 🌡️ The precipitate must be dried to remove moisture, ideally in a thermostatic drying oven at 110 degrees Celsius to avoid decomposition.
- ⚖️ Gravimetric analysis quantifies the amount of analyte based on the mass of the precipitate formed during the reaction.
- 🔗 The mass of the precipitate can be linked to the mass of the original analyte using balanced chemical equations.
- 📏 Analytical balances are used to measure the mass of the precipitate with high precision, often to four decimal places.
- 🔬 The example of sodium chloride reacting with silver nitrate demonstrates how to calculate the mass of the original analyte from the precipitate formed.
- 🧪 In the example problem, the identity of a halogen in a magnesium halide salt is determined through mass measurements and stoichiometry.
Q & A
What is precipitation gravimetry?
-Precipitation gravimetry is a quantitative analytical method that involves the formation of a solid precipitate from a solution, allowing for the analysis of the amount of a specific analyte based on mass measurements.
What happens when lead nitrate is mixed with potassium iodide?
-When lead nitrate is mixed with potassium iodide, a bright yellow precipitate of lead iodide is formed, despite both lead nitrate and potassium iodide being colorless and soluble in water.
What is a precipitate?
-A precipitate is a solid product formed in a chemical reaction that occurs when two solutions are mixed, resulting in an insoluble compound.
How is a precipitate collected from a solution?
-A precipitate is collected by filtration, where a mixture is poured through filter paper in a funnel, allowing the liquid to pass through while retaining the solid on the paper.
Why is it necessary to rinse the precipitate after filtration?
-Rinsing the precipitate with distilled or deionized water removes any remaining dissolved ions that could contaminate the solid, ensuring a pure sample for analysis.
What is the purpose of drying the precipitate?
-Drying the precipitate fully removes any traces of water, which is crucial for accurately measuring its mass and determining the amount of analyte in the original solution.
What is the significance of achieving constant mass during drying?
-Achieving constant mass during drying confirms that all water has been removed from the precipitate, ensuring accurate mass measurements for quantitative analysis.
How does the balanced equation relate to gravimetric analysis?
-The balanced equation provides the stoichiometric relationships between reactants and products, allowing the mass of the precipitate to be linked to the mass of the analyte in the original solution.
In the example provided, how do you determine the mass of sodium chloride from silver chloride?
-To determine the mass of sodium chloride, you first find the moles of silver chloride produced, using its mass and molar mass, and then use the mole ratio from the balanced equation to calculate the mass of sodium chloride.
What is the identity of the halogen X in the magnesium halide salt MGX2 when given the mass of magnesium hydroxide precipitate?
-The identity of the halogen X can be determined by calculating the molar mass of the magnesium halide salt using the mass of the precipitate and the known molar mass of magnesium hydroxide, revealing that the halogen present is bromine.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Reaksi Kimia - Reaksi Pengendapan

Kelarutan dan Hasil Kali Kelarutan (3) | Prakiraan Pengendapan | Menentukan Massa Endapan

O-Level Chemistry | 16 | Qualitative Analysis [1/3]
Analisa Gravimetri

Precipitation Reactions and Precipitation Curve (Diagnostic Immunology) (FL-Immuno/56)

[FSH SPECIAL TOPICS] Types of Gravimetry - Analytical Chemistry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
