ATP: adenosín trifosfato | Energía y enzimas | Biología | Khan Academy en Español
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the significance of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as the energy currency in biological systems. The presenter breaks down the complex molecular structure of ATP into its components: adenosine and three phosphate groups. Emphasizing the high-energy bonds between phosphates, the video illustrates how energy is stored and released through hydrolysis, transforming ATP into adenosine diphosphate (ADP). It highlights the role of ATP in biochemical processes, such as photosynthesis and muscle contraction, underscoring its vital function in energy transfer within living organisms.
Takeaways
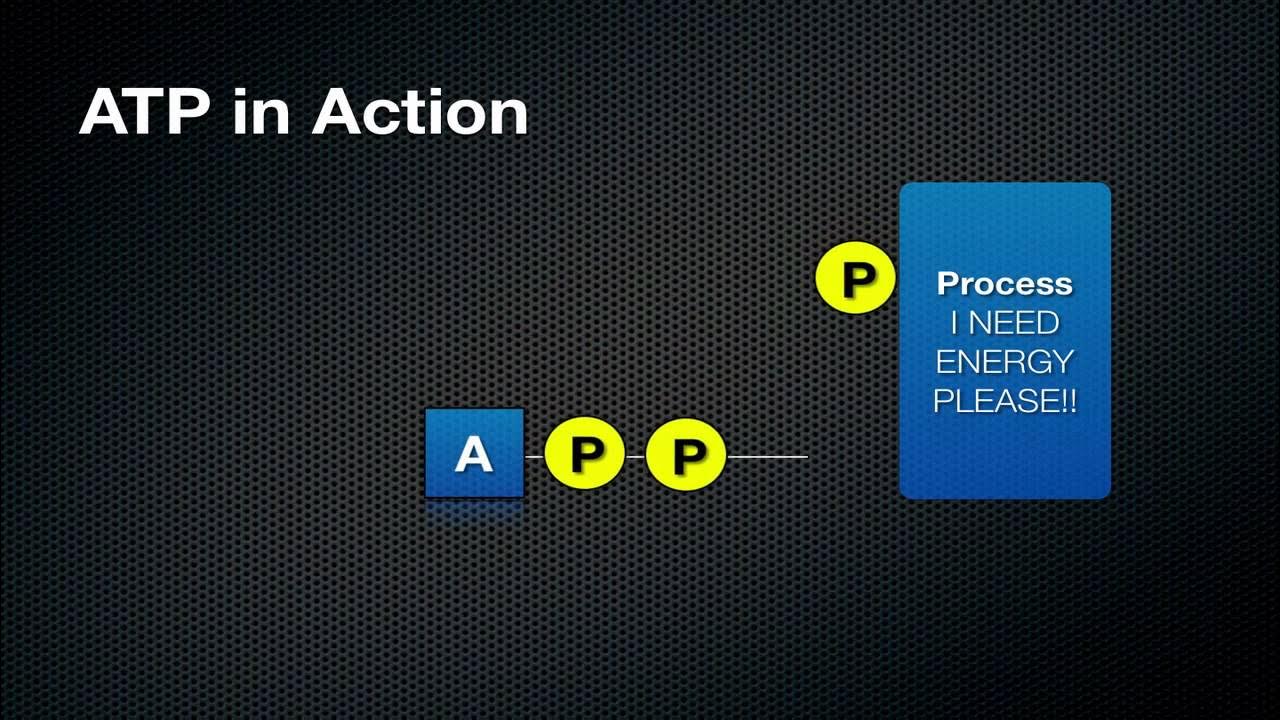
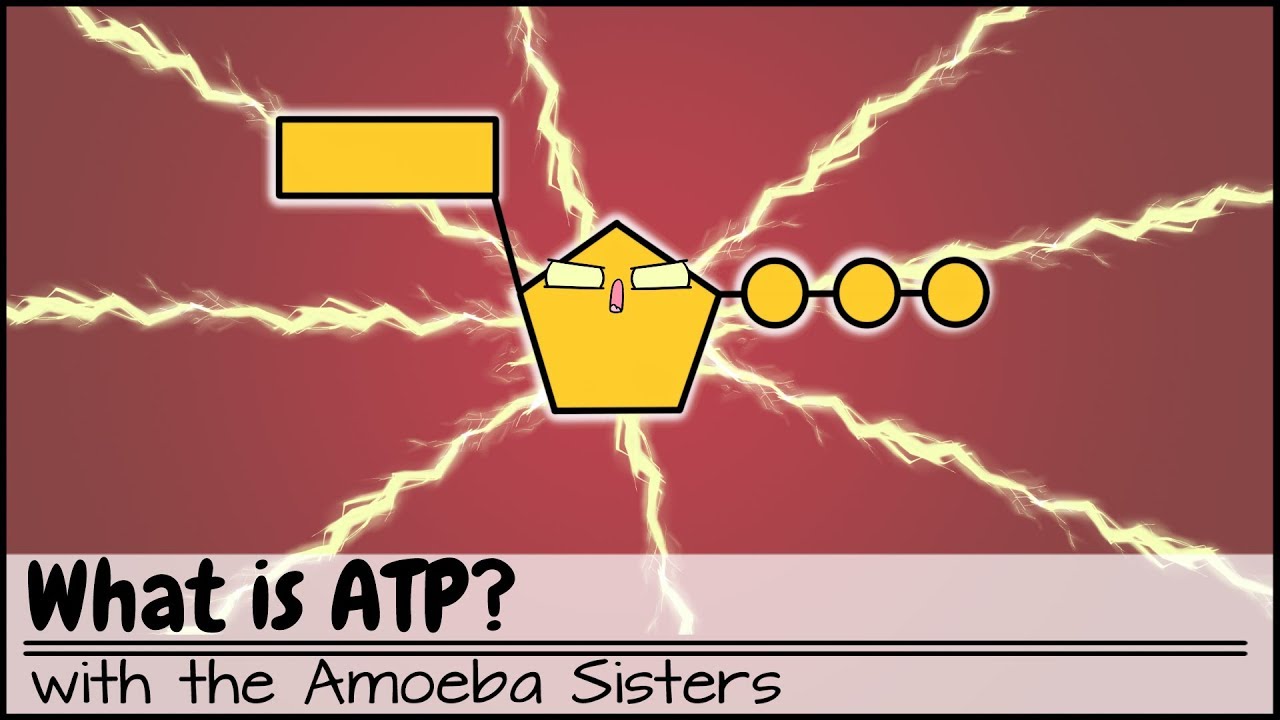
- 😀 ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is commonly referred to as the energy currency of biological systems.
- 🔍 The molecular structure of ATP consists of adenosine and three phosphate groups, which are essential for its energy-storing capabilities.
- ⚡ The high-energy bonds between phosphate groups in ATP release energy when broken, facilitating various biological processes.
- 💡 The concept of energy storage can be understood through the analogy of potential energy, similar to someone poised to jump from a height.
- 🌊 Hydrolysis of ATP involves the addition of water, resulting in the release of one phosphate group and the formation of ADP (adenosine diphosphate).
- 🔄 The process of converting ADP back to ATP involves energy input, often derived from metabolic processes like photosynthesis.
- 🔥 Energy released from ATP hydrolysis can be utilized for various functions, including heat generation and conformational changes in proteins.
- 🔗 The three high-energy phosphate bonds in ATP are crucial for its role in energy transfer within cells.
- 🌱 Photosynthesis is one example where light energy is converted into chemical energy, forming ATP.
- 🔄 Biological systems constantly cycle between ATP and ADP, managing energy flow essential for life.
Q & A
What does ATP stand for?
-ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate.
Why is ATP referred to as the 'energy currency' of biological systems?
-ATP is called the 'energy currency' because it stores and transports chemical energy within cells for biochemical processes.
What are the main components of an ATP molecule?
-An ATP molecule consists of adenosine (which includes adenine and ribose) and three phosphate groups.
How does ATP store energy?
-ATP stores energy in the high-energy bonds between its phosphate groups, particularly the bonds connecting the last two phosphate groups.
What happens during the hydrolysis of ATP?
-During hydrolysis, one phosphate group is released from ATP, converting it to ADP and releasing energy that can be used by the cell.
Can you explain the analogy used to describe energy states in ATP?
-The analogy compares electrons in high-energy bonds to a person on a cliff ready to jump; breaking the bond releases energy similar to the potential energy being released when the person jumps.
What is the significance of the released energy from ATP?
-The released energy from ATP is utilized for various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, active transport, and biosynthesis.
How does photosynthesis relate to ATP production?
-In photosynthesis, light energy is used to add a phosphate group to ADP, regenerating ATP, which then serves as an energy source for cellular activities.
What is the difference between ATP and ADP?
-ATP (adenosine triphosphate) has three phosphate groups, while ADP (adenosine diphosphate) has two phosphate groups. ATP releases energy when converted to ADP.
What role does ATP play in biochemical reactions?
-ATP provides the energy necessary to drive endergonic reactions, facilitating processes such as enzyme activity and molecular movement within the cell.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)