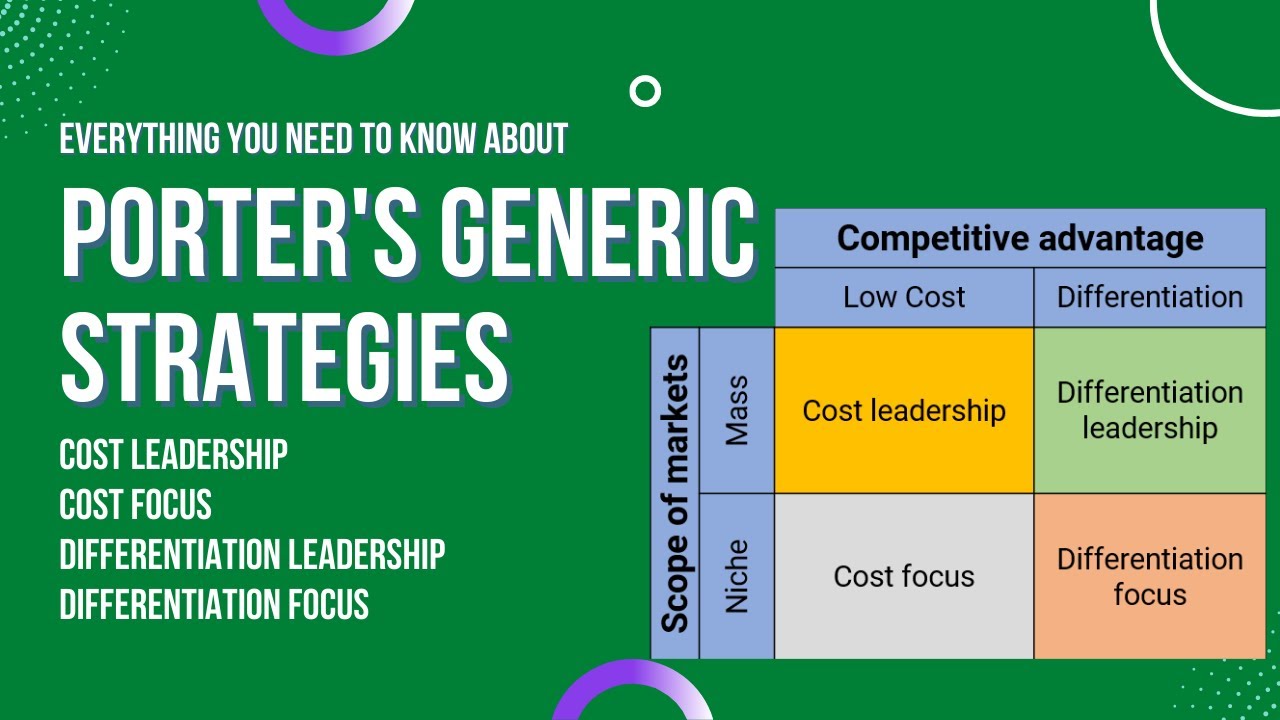
Cost leadership: When a company sells cheap and makes money
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores the cost leadership strategy, which involves producing goods or services at a lower cost than competitors to attract price-sensitive customers. It explains how companies can achieve this by focusing on efficiency, leveraging economies of scale and scope, optimizing process design, and lowering input costs. Several examples, including Boeing, Walmart, and McDonald's, highlight how businesses reduce unitary costs by increasing production, outsourcing labor, and minimizing services. Ultimately, cost leadership requires constant improvements in operational processes to maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
Takeaways
- 💡 Cost leadership strategy focuses on offering products or services at lower prices than competitors.
- 📉 Companies using this strategy win price-sensitive customers, but often have lower profit margins per unit.
- 🏭 To sell at lower prices, companies must focus on efficiency in their operations.
- 📊 Economies of scale are key to reducing unit costs; larger production spreads fixed costs over more units.
- ✈️ An example of economies of scale is Boeing's success with the 747 compared to Concorde, which failed due to low production numbers.
- 🧀 Economies of scope involve savings from producing complementary products under one roof, like P&G's acquisition of Gillette or producing milk and cheese together.
- ⚙️ Process design improvements can lead to cost reductions by increasing efficiency, as seen with Ford's Model T assembly line.
- 🛠 Success in cost leadership requires aligning process technologies with organizational structure, product design, and management systems.
- 🌍 Firms with lower input costs, such as those benefiting from lower wages in developing countries, can gain a significant cost advantage.
- 🏢 Companies like Walmart, IKEA, Amazon, and McDonald's achieve cost leadership through strategies like outsourcing, minimal services, and efficient operations.
Q & A
What is the main goal of a cost leadership strategy?
-The main goal of a cost leadership strategy is to produce products or provide services at a lower cost than competitors, thereby attracting price-sensitive customers and gaining a larger market share.
What is the trade-off for companies that adopt a cost leadership strategy?
-The trade-off is that while companies sell more units due to lower prices, they also earn lower margins per unit, which can reduce overall profitability unless they maintain a high volume of sales.
How do economies of scale help companies lower their costs?
-Economies of scale allow companies to lower unitary costs by spreading fixed costs over a larger number of units, thus reducing the cost per unit as output increases.
What are fixed costs, and how do they relate to economies of scale?
-Fixed costs are expenses that do not change regardless of how many units are produced. Economies of scale reduce the cost per unit by spreading these fixed costs over a larger quantity of output.
Can you provide an example from the airline industry that illustrates economies of scale?
-An example is Boeing 747, where the development costs were spread across 1,415 aircrafts, making the project profitable. In contrast, Concorde was unprofitable because only 20 planes were built, despite similar development costs.
What is an economy of scope, and how does it differ from an economy of scale?
-An economy of scope is a cost-saving advantage that arises when producing complementary products under the same operations. Unlike economies of scale, which focus on increasing output to reduce costs, economies of scope focus on producing multiple products efficiently together.
What role does process design play in achieving cost leadership?
-Process design plays a crucial role in cost leadership by finding ways to reduce input for each unit of output. Efficient processes can dramatically lower production costs, as seen in the example of Ford's Model T assembly line.
How do companies benefit from lower input costs, and what are some sources of these advantages?
-Companies benefit from lower input costs by paying less for raw materials, labor, or procurement, which gives them a cost advantage over competitors. This can come from lower wage rates, access to cheaper raw materials, or better supplier negotiations.
What are some examples of companies that have successfully implemented a cost leadership strategy?
-Companies like Walmart, IKEA, Amazon, McDonald's, Dell, Zara, and Southwest Airlines are well-known for pursuing cost leadership strategies, focusing on efficiency and offering lower-priced products and services.
What challenges do companies face in maintaining a cost leadership strategy in highly competitive markets?
-The challenge is that cost leadership requires constant focus on efficiency and process redesign. In competitive markets, it's difficult to maintain a cost advantage without continuous innovation and optimization of operating processes.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)