Chemical Safety in the Laboratory
Summary
TLDRThe video emphasizes the importance of laboratory safety, focusing on proper handling of chemicals to protect human health and the environment. It covers the safety measures outlined in Philippine law, including chemical exposure risks, such as inhalation, skin contact, and ingestion, and the use of protective equipment like gloves, goggles, and respirators. Additionally, it addresses emergency procedures, chemical disposal, and equipment requisition in laboratory settings, ensuring compliance with safety standards and reducing risks. The message encourages scientists to stay informed and work safely for successful experiments.
Takeaways
- 🔒 Safety is the top priority when working in laboratories, and learning the rules with enthusiasm is encouraged.
- ⚗️ Chemical safety involves handling substances in a way that protects both human health and the environment.
- 🇵🇭 Republic Act 11058 in the Philippines strengthens compliance with occupational safety and health standards.
- 🌬️ Inhalation is the most common way chemicals can harm workers, through exposure to gases, vapors, mists, dust, fumes, and smoke.
- 🍽️ Eating or drinking in the laboratory is strictly prohibited to prevent contamination from chemicals.
- 👀 Skin, eye, and respiratory exposure to chemicals can lead to irritation, burns, or even poisoning, making proper protection critical.
- 📄 Safety Data Sheets (SDS) provide vital information on chemical properties, hazards, safe handling, and emergency measures.
- 📊 OSHA standardized hazard labels, like skull and crossbones or flame icons, indicate the type and severity of chemical risks.
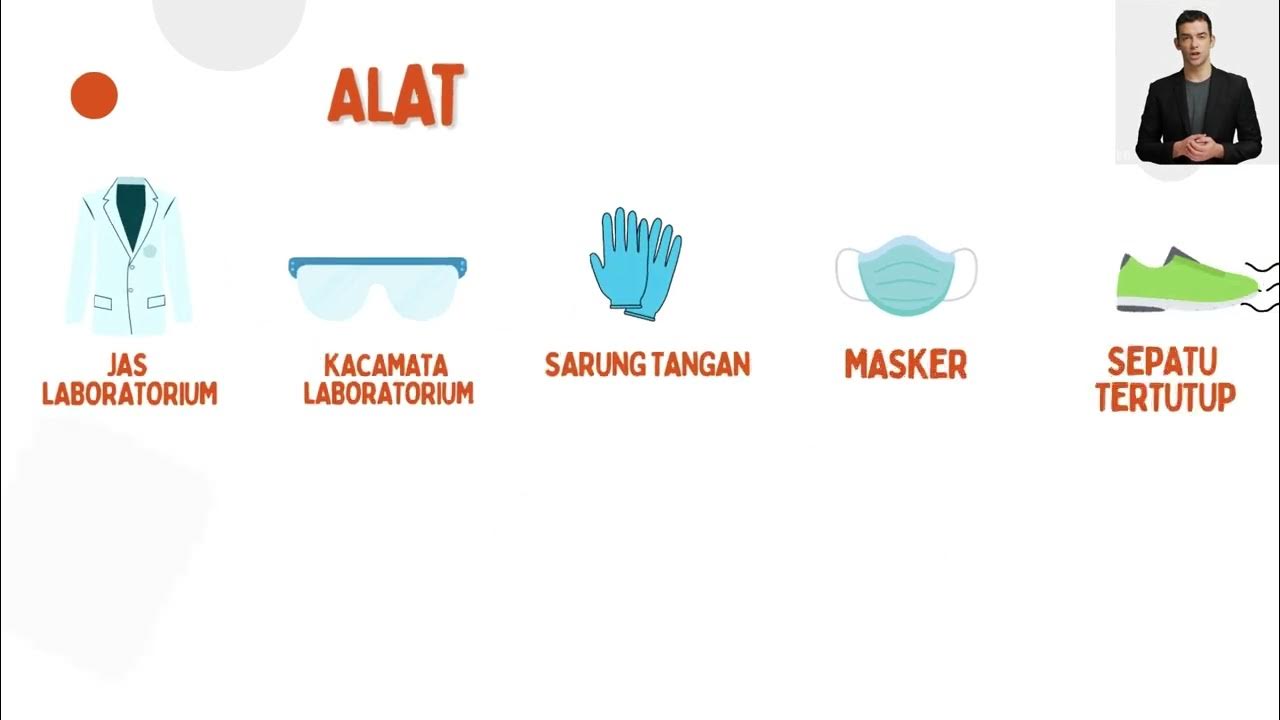
- 🧤 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) like gloves, lab coats, and safety glasses should be selected based on the specific risk assessment.
- 🚒 In emergencies such as spills or fires, immediate action like evacuation or using fire extinguishers is necessary to minimize harm.
Q & A
What is Republic Act 11058 and why is it important for laboratory safety?
-Republic Act 11058 is a law in the Philippines that strengthens compliance with occupational safety and health standards. It ensures that workers are provided with a safe and healthy work environment, including those working in laboratories with hazardous chemicals.
What are the most common ways chemicals can expose workers to health risks?
-Chemicals can expose workers to health risks through inhalation, ingestion, skin exposure, and injection. Inhalation is the most common route, involving exposure to gases, vapors, mists, dust, fumes, and smoke.
Why is eating or drinking prohibited in the laboratory?
-Eating or drinking in the laboratory is prohibited because food and drink can absorb chemical vapors, leading to accidental ingestion of harmful substances. This practice is also banned by the OSH sanitation standard.
What information does a Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provide?
-A Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provides essential information on the properties of chemicals, their hazards, safe handling procedures, storage guidelines, and emergency measures in case of exposure, spills, or accidents.
What do the standardized pictograms on chemical labels signify?
-The standardized pictograms caution users about specific hazards, such as health risks (e.g., cancer, respiratory issues), flammability, skin irritation, pressurized gas hazards, corrosive materials, explosive risks, and environmental harm.
How does the NFPA hazard diamond system work?
-The NFPA hazard diamond uses a color-coded system with four sections: blue for health, red for flammability, yellow for reactivity, and white for specific hazards. Each section is rated from 0 to 4 to indicate the level of risk.
What are the general guidelines for the proper disposal of chemical waste?
-Chemical waste must be properly labeled before disposal, and labels can be obtained from the PUP CS laboratory. The DENR has strict policies regarding the handling of hazardous chemical waste, as outlined in the 2013-22 Administrative Order.
What protective equipment should be used in the lab for chemical safety?
-Lab workers should use appropriate PPE such as lab coats, chemical-resistant gloves, safety glasses with side shields, face shields, and respirators. The type of PPE depends on the specific risks identified during a risk assessment.
How should laboratory chemicals be stored to ensure safety?
-Chemicals should be stored according to their specific hazards. Acids should be kept separate from bases, flammables should be stored in safe containers away from ignition sources, and peroxide-forming chemicals should be stored in airtight, dark, and cool conditions.
What should be done in case of a large chemical spill or emergency in the lab?
-For large chemical spills or emergencies like toxic gas leaks, the area should be evacuated immediately. Close doors and windows, activate fire alarms, and call emergency services (e.g., 911). The incident should be reported to the laboratory supervisor.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Keselamatan Kerja di Laboratorium IPA Mata Kuliah Pendalaman Materi IPA

Segurança em Laboratório - Aula 01 #quimicaexperimental

Safety in the Veterinary Hospital- Disc 1

Bab 1 Hakikat Ilmu Sains dan Metode Ilmiah #2 (Laboratorium IPA) | IPA SMP 7 | Sekolah Penggerak

K3 (Kesehatan dan Keselamatan Kerja) Laboratorium Teknologi Pangan dan Hasil Pertanian

Keselamatan Kerja di Laboratorium | Tata Tertib & Simbol Bahan - Sains
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
