vodcast 9 2 gas laws pt1 rough ios
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script covers gas laws, focusing on Boyle's, Charles', and Gay-Lussac's laws. It explains how pressure, volume, and temperature relate in gas behavior, emphasizing the importance of using Kelvin for temperature. The script guides viewers through algebraic problem-solving, illustrating each law with examples. It concludes with the combined gas law, a comprehensive formula for scenarios where multiple variables change.
Takeaways
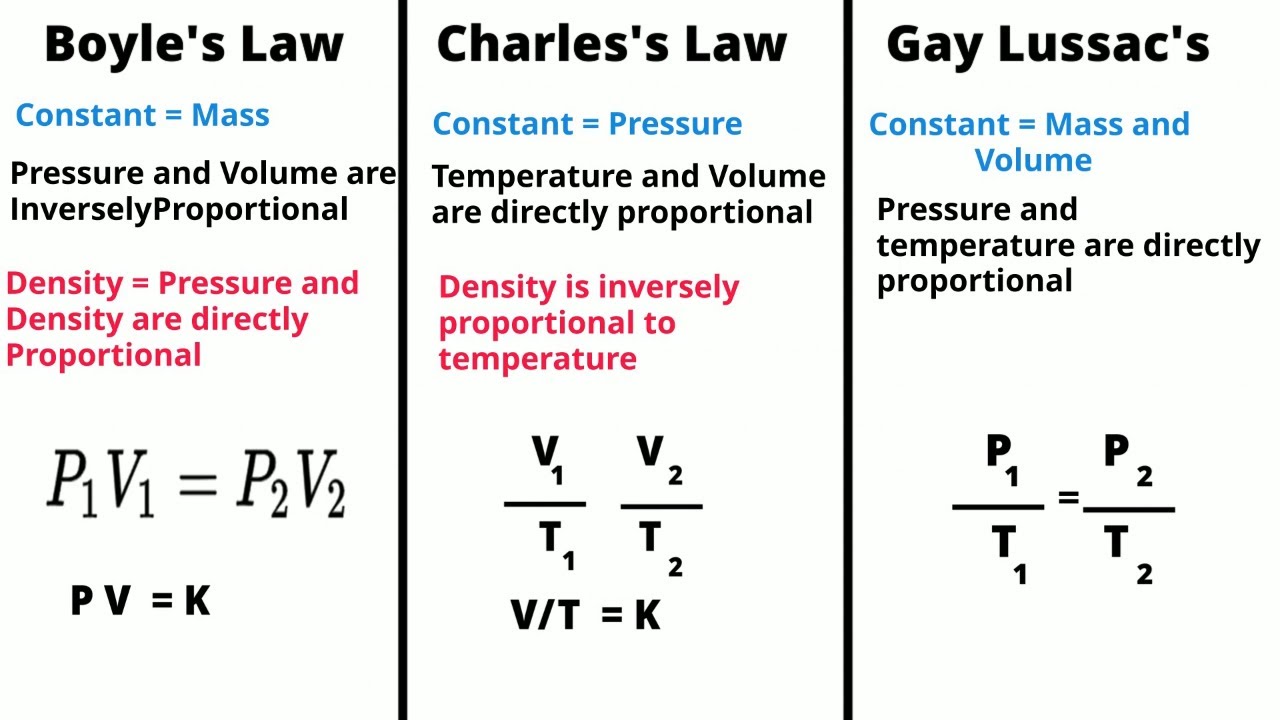
- 📜 Boyle's Law explains the inverse relationship between pressure and volume at constant temperature.
- 📐 Algebra is crucial when solving gas law problems, and all temperatures must be in Kelvin.
- 🌡 Temperature always needs to be converted to Kelvin by adding 273 to the Celsius value.
- 📉 Boyle's Law formula: P1 * V1 = P2 * V2, showing how pressure and volume change inversely.
- 📊 Charles's Law demonstrates the direct relationship between volume and temperature at constant pressure.
- 🚀 Charles's Law formula: V1 / T1 = V2 / T2, where temperature and volume rise and fall together.
- 🔄 Gay-Lussac's Law illustrates the direct relationship between pressure and temperature at constant volume.
- 🧮 The Combined Gas Law merges Boyle's, Charles's, and Gay-Lussac's laws into one formula: P1 * V1 / T1 = P2 * V2 / T2.
- 📝 When using the Combined Gas Law, if a variable is constant, it can be canceled out to simplify the equation.
- 🔧 Solving gas law problems requires methodically plugging values into the appropriate formula and applying algebra to isolate the unknown variable.
Q & A
What are the three key variables in gas laws?
-The three key variables in gas laws are pressure (P), temperature (T), and volume (V).
What does Boyle's Law state?
-Boyle's Law states that the volume of a fixed mass of gas varies inversely with the pressure at constant temperature.
How do you convert Celsius to Kelvin?
-To convert Celsius to Kelvin, you add 273 to the temperature in degrees Celsius.
What is the mathematical formula for Boyle's Law?
-The mathematical formula for Boyle's Law is P1V1 = P2V2.
What does Charles's Law state?
-Charles's Law states that the volume of a fixed mass of gas varies directly with the Kelvin temperature at constant pressure.
What is the mathematical formula for Charles's Law?
-The mathematical formula for Charles's Law is V1/T1 = V2/T2.
What is the combined gas law and when is it used?
-The combined gas law is an equation that combines Boyle's, Charles's, and Gay-Lussac's laws into one formula. It is used when none of the variables (pressure, volume, or temperature) are held constant.
What is the combined gas law formula?
-The combined gas law formula is PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature in Kelvin.
Why is it important to keep track of the units when solving gas law problems?
-It is important to keep track of the units when solving gas law problems because they must be consistent throughout the calculations, and the final answer should reflect the correct unit for the variable being solved for.
What is the significance of the 'PTV' model mentioned in the script?
-The 'PTV' model is a physical representation that helps visualize the relationships between pressure, temperature, and volume as described by the gas laws. It is a tool for understanding how changes in one variable affect the others.
Why is it crucial to perform algebraic manipulations step by step when solving gas law problems?
-Performing algebraic manipulations step by step ensures that each calculation is clear and accurate, reducing the chance of errors. It also helps in understanding the relationship between the variables in the gas laws.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

IPA FISIKA : Gas Ideal Hukum Charles, Hukum Gay Lussac dan Hukum Boyle (Simulasi)

Gas Law Formulas and Equations - College Chemistry Study Guide
Gas Laws-Boyle's-Charles's-Gay Lussac's

S1.5.3 The gas laws (part 1)

FISIKA KELAS XI | TEORI KINETIK GAS (PART 1) - Hukum-Hukum Gas Ideal

Teori Kinetik Gas • Part 1: Sifat Gas Ideal & Hukum-Hukum Gas Ideal
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
