Understanding Cancer B2 Cell cycle clocks
Summary
TLDRScientists have unraveled the mystery of how cells control division through the 'Cell Cycle Clock'. This complex molecular system integrates signals from neighboring cells to decide if a cell should progress through the four stages of the cell cycle: G1 (growth and DNA preparation), S (DNA synthesis), G2 (second growth phase), and M (mitosis). The cycle's progression is regulated by internal clocks, ensuring precise control of cell growth and division in tissues.
Takeaways
- 🔍 For years, scientists were puzzled about how cells controlled cell division.
- 📢 Scientists have discovered that chemical messages from neighboring cells influence cell division.
- 🕰️ These influences are managed by a complex group of molecules known as the 'Cell Cycle Clock'.
- 🔄 The Cell Cycle Clock integrates signals to decide if a cell should progress through growth and division stages.
- 🌱 If the Cell Cycle Clock approves, the cell grows and divides, following the cell cycle's four stages.
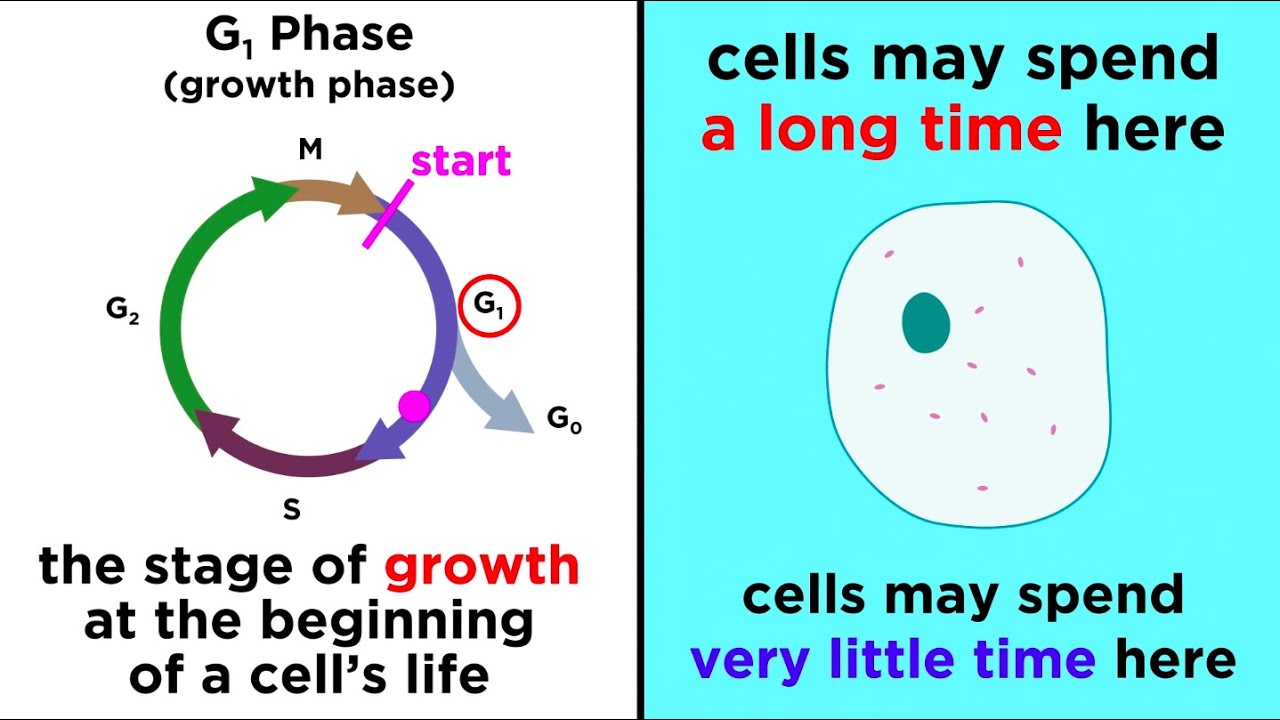
- 📈 The G1 or 'gap 1' stage is where the cell increases in size and prepares to duplicate its DNA.
- 🔬 The S phase, or 'synthesis', is when the cell actually copies its DNA.
- 🔄 After DNA replication, the G2 or second 'gap' period occurs before cell division.
- 🔄 The cell divides during the M phase, named for 'mitosis'.
- 📍 New daughter cells enter G1 immediately, influenced by signals from neighbors and decisions from their cell cycle clocks.
- 🔄 Depending on signals and internal decisions, cells may repeat the cycle or halt temporarily or permanently.
Q & A
What was the mystery surrounding cell division for many years?
-The mystery was how cells controlled their cell division.
What do scientists now understand about cell division control?
-Scientists now understand that chemical messages from neighboring cells affect the 'Cell Cycle Clock', which is a group of molecules that determine whether a cell should move through each stage of growth and division.
What is the role of the 'Cell Cycle Clock' in cell division?
-The 'Cell Cycle Clock' integrates signals received from neighboring cells and determines whether the cell should proceed through the stages of growth and division.
What happens if the 'Cell Cycle Clock' gives a 'yes' signal?
-If the 'Cell Cycle Clock' gives a 'yes' signal, the cell grows and divides.
How many stages does the cell cycle consist of?
-The cell cycle is composed of four stages.
What occurs during the G1 or 'gap 1' stage of the cell cycle?
-During the G1 stage, the cell increases in size and prepares to copy its DNA.
What is the S phase of the cell cycle, and what happens during this phase?
-The S phase, or 'synthesis' phase, is when the cell copies its DNA.
What is the G2 stage and what happens after DNA is copied?
-The G2 stage is the second 'gap' period that occurs after the DNA is copied, before the cell divides.
What is the M phase of the cell cycle, and what happens during this phase?
-The M phase, or 'mitosis', is the stage in which the cell divides.
What happens to the new daughter cells after division?
-The new daughter cells immediately enter the G1 stage, depending on the signals they receive from neighboring cells and the decisions made by their 'Cell Cycle Clock'.
How is cell growth and division controlled in normal tissues?
-In normal tissues, cell growth and division are precisely controlled by internal 'Cell Cycle Clocks'.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)