Monkeypox (Mpox) Symptoms, Prevention, vaccine & Treatment #mpox
Summary
TLDRMonkeypox, previously known as monkey pox, is a viral disease similar to smallpox but less severe. Discovered in 1958, it was first reported in humans in 1970. Caused by the monkeypox virus, it has two clades: West African and Congo Basin, with the latter being more severe and contagious. Transmission occurs through contact with infected animals or humans, including via bodily fluids and respiratory droplets. Symptoms include fever, rash, and swollen lymph nodes. Diagnosed through PCR testing, there's no specific treatment, but the smallpox vaccine offers up to 85% protection.
Takeaways
- 🐒 **Monkeypox Origin**: Previously known as monkey pox, the disease was first discovered in monkeys in 1958 and first reported in humans in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- 🦠 **Virus Classification**: Monkeypox is caused by the monkeypox virus, which belongs to the orthopoxvirus genus in the Poxviridae family, related to the smallpox virus.
- 🌐 **Geographic Clades**: There are two main clades of the monkeypox virus: the West African and the Congo Basin, with the latter causing more severe illness and being more contagious.
- 🐇 **Animal Reservoirs**: The virus can be transmitted by various animals, including rope squirrels, tree squirrels, Gambian pouched rats, and different monkey species.
- 🤝 **Human Transmission**: Transmission between humans occurs through close contact with infected skin lesions, bodily fluids, respiratory droplets, or contaminated objects.
- 🤰 **Congenital Infection**: Transmission can occur from mother to fetus via the placenta, leading to congenital monkeypox, and during close contact after birth.
- ⏱️ **Incubation Period**: The incubation period for monkeypox is typically 6 to 14 days, but it can range from 5 to 21 days.
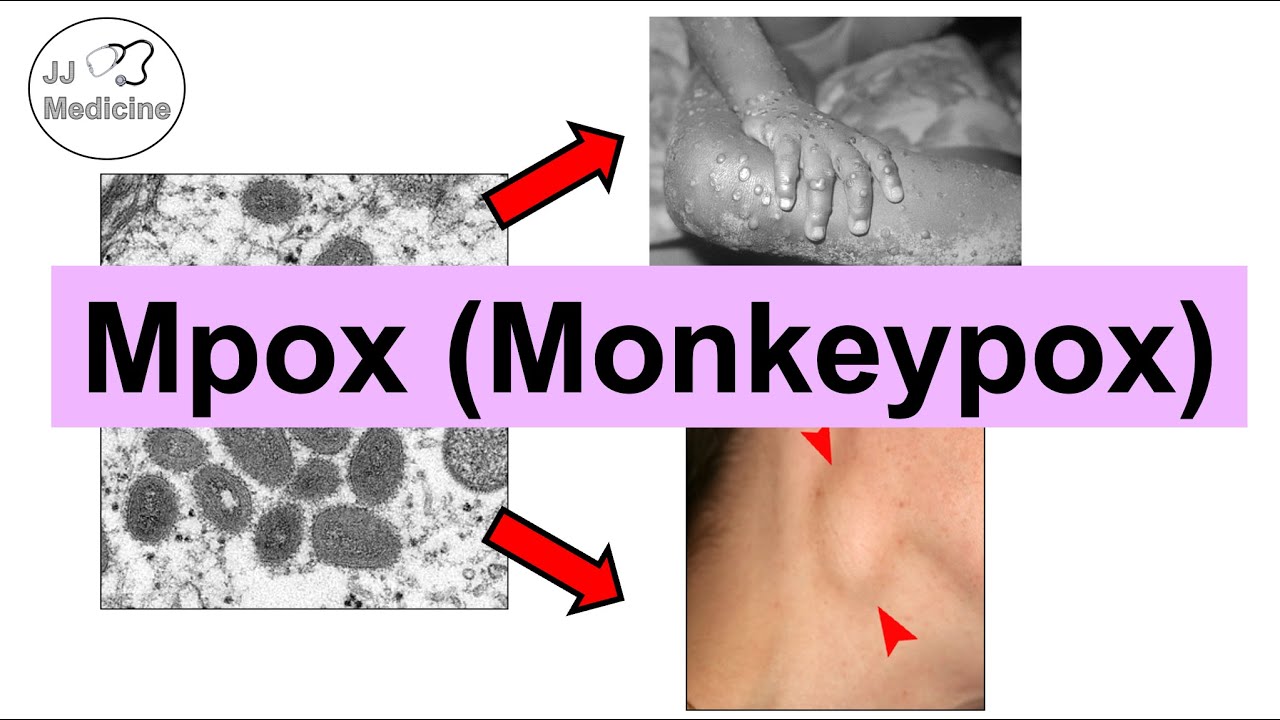
- 🤒 **Symptoms**: Initial symptoms include fever, chills, headache, lymph node swelling, back pain, muscle aches, and fatigue, followed by a characteristic rash.
- 🧬 **Diagnosis**: Diagnosis is suspected based on rash appearance, contact history, or travel to endemic areas, and confirmed through PCR testing detecting viral genetic material.
- 💊 **Treatment Options**: There are no specific treatments for monkeypox, but options include antivirals and the vaccinia immune globulin intravenous.
- 💉 **Vaccination**: The smallpox vaccine can protect against monkeypox with up to 85% efficacy, and vaccination post-exposure may prevent the disease or reduce severity.
Q & A
What is the former name of the disease now known as monkeypox?
-The former name of monkeypox was 'monkey pox'.
In what year was monkeypox first discovered?
-Monkeypox was first discovered in 1958 during outbreaks in monkey colonies.
Where was the first human case of monkeypox reported?
-The first human case of monkeypox was reported in the Democratic Republic of Congo in 1970.
Which virus causes monkeypox?
-Monkeypox is caused by the monkeypox virus, a member of the orthopoxvirus genus in the Poxviridae family.
How many main clades of the monkeypox virus are there?
-There are two main clades of the monkeypox virus: the West African clade and the Congo Basin clade.
Which clade of the monkeypox virus is considered more contagious?
-The Congo Basin clade is considered more contagious compared to the West African clade.
What animals can transmit the monkeypox virus to humans?
-Monkeypox virus can be transmitted by contact with infected animals such as rope squirrels, tree squirrels, Gambian pouched rats, and different species of monkeys.
How is monkeypox transmitted from one person to another?
-Transmission from one person to another can occur by close contact with infected skin lesions, bodily fluids, respiratory droplets, and contaminated objects such as clothing, towels, or bedding.
What is the typical incubation period for monkeypox?
-The incubation period of monkeypox is usually 6 to 14 days but can range from 5 to 21 days.
What are the initial symptoms of monkeypox?
-Initial symptoms of monkeypox include fever, chills, intense headache, swelling of the lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy), back pain, muscle aches, and lack of energy.
How is a monkeypox diagnosis confirmed?
-Diagnosis of monkeypox is confirmed through PCR testing, which detects the presence of the viral genetic material.
Are there any specific treatments available for monkeypox infection?
-According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there are no specific treatments available for monkeypox infection.
What is the efficacy of the smallpox vaccine in protecting against monkeypox?
-The smallpox vaccine can protect individuals from getting monkeypox with an efficacy of up to 85%.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Mpox (Monkeypox) | Transmission, Pathophysiology, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment

What is mpox and how do you protect yourself? | Al Jazeera NewsFeed

MPOX 1.1

Monkeypox Virus | Introduction #worldhealthorganization

What Causes Monkeypox? | Monkeypox Outbreak 2022 | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz

Monkeypox Virus | 5 Things You Should Know About MonkeyPox Outbreak
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
