Implicit Bias | Lesson 2: Attitudes and Stereotypes
Summary
TLDRThis lesson explores how we automatically categorize people based on attributes like age, gender, and race, triggering associated attitudes and stereotypes. Attitudes are evaluative feelings, while stereotypes are specific trait associations. Both can bias our interactions. The script distinguishes between explicit biases, which we're aware of, and implicit biases, which operate unconsciously. It suggests that these biases, formed through exposure, can subtly yet significantly affect our decisions and actions, encouraging viewers to consider their own biases and their origins.
Takeaways
- 🧠 Schemas are mental frameworks that automatically categorize people based on characteristics like age, gender, race, or profession.
- 🤔 When we categorize someone, our brains activate associated attitudes and stereotypes, influencing our thoughts and interactions.
- 📊 Attitudes are evaluative feelings towards a category, either positive or negative, and are like gut reactions.
- 🔍 Stereotypes are specific associations between a category and a trait, such as 'athletic' or 'good at math'.
- 👤 These biases can affect our behavior towards individuals based on the group they are perceived to belong to.
- 😃 Positive attitudes might lead to friendlier interactions, while stereotypes could influence hiring decisions.
- 🏃♂️ Negative stereotypes, like the belief that a group is not athletic, might lead to exclusion from certain activities.
- 🤷♂️ Both explicit and implicit biases are at play; explicit biases are known to us, while implicit biases operate unconsciously.
- 🌐 Biases often stem from exposure to certain contexts, whether through direct contact or indirect sources like media and culture.
- 🔄 We are generally aware of explicit biases and can correct them, but implicit biases are harder to address because we're not aware of them.
- 🌟 Implicit biases, despite being less visible, can significantly impact our actions and decisions in subtle but meaningful ways.
Q & A
What is the role of schemas in our perception of people?
-Schemas are cognitive frameworks that help us categorize people based on salient social categories such as age, gender, race, or profession. They guide our automatic associations and influence how we think about and interact with individuals.
What are attitudes according to social psychologists?
-Attitudes are associations between a category and an evaluative valence, which can be either positive or negative. They are gut feelings or general likes or dislikes towards certain things or groups.
How do stereotypes differ from attitudes?
-Stereotypes are more specific associations between a category and a particular trait, whereas attitudes are broader evaluations of a category. Stereotypes involve assumptions about characteristics that are often not universally true within a group.
Can you provide an example of a stereotype mentioned in the script?
-An example of a stereotype given in the script is the association of the category 'snakes' with the trait 'venomous,' even though not all snakes are venomous.
How does the script illustrate the impact of stereotypes on individuals?
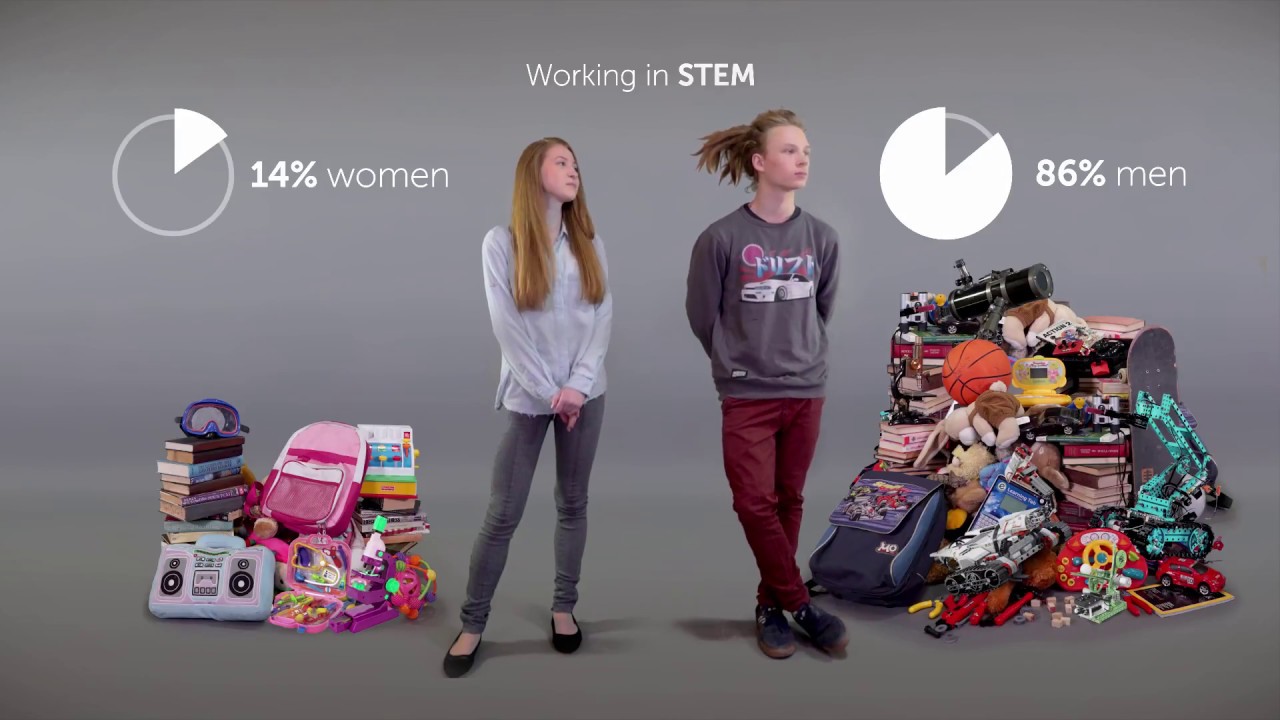
-The script uses the example of the speaker being perceived as Asian, which triggers certain attitudes and stereotypes like being good at math or not athletic, affecting how others might interact with or choose to work with them.
What is the difference between explicit and implicit biases?
-Explicit biases are attitudes and stereotypes that one is aware of and can introspect upon. Implicit biases, on the other hand, are those that operate outside of conscious awareness and are not easily introspected.
Why are implicit biases concerning despite being invisible?
-Implicit biases are concerning because they can influence our actions and decisions in subtle but significant ways without our conscious knowledge, leading to potential unfairness and discrimination.
How do we typically acquire biases?
-Biases are often acquired through exposure to certain contexts, either directly through personal experiences or indirectly through stories, books, movies, social media, and popular culture.
What is the role of direct and vicarious contact in forming our biases?
-Direct contact involves personal interactions that can shape our biases, while vicarious contact refers to learning through observing others or consuming media, both of which contribute to the formation of attitudes and stereotypes.
How can we address our biases?
-We can address our biases by being aware of them, especially our explicit biases, and striving to revise our attitudes and stereotypes based on better information and more accurate representations.
What is the significance of the upcoming Lesson 3 mentioned in the script?
-Lesson 3: Real World Consequences is significant as it likely delves into how biases, both explicit and implicit, manifest in real-world scenarios and the implications they have on individuals and society.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)