MOE - Business Model Canvas
Summary
TLDRThis lecture introduces the Business Model Canvas (BMC), a tool for entrepreneurs and business owners to outline their business concept comprehensively. The BMC is a single-page document divided into nine blocks, covering aspects like customer segments, value propositions, channels, key activities, resources, partners, cost structure, and revenue streams. The lecture guides viewers through understanding each block's purpose and how to fill them out effectively, emphasizing the importance of specificity and coherence in the business model.
Takeaways
- 📈 The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a strategic tool used to outline a business concept comprehensively.
- 🎯 The BMC has three main objectives: to identify the BMC, describe it in each item, and understand how to write one for your business.
- 📝 The BMC is designed to fit on a single sheet of paper, making it a concise and clear overview of a business.
- 🤝 It helps in understanding a business's competitive advantage, value creation, delivery, and capture mechanisms.
- 🚀 The BMC is beneficial for highlighting a business roadmap, reflecting strategic thinking, and connecting ideas with processes.
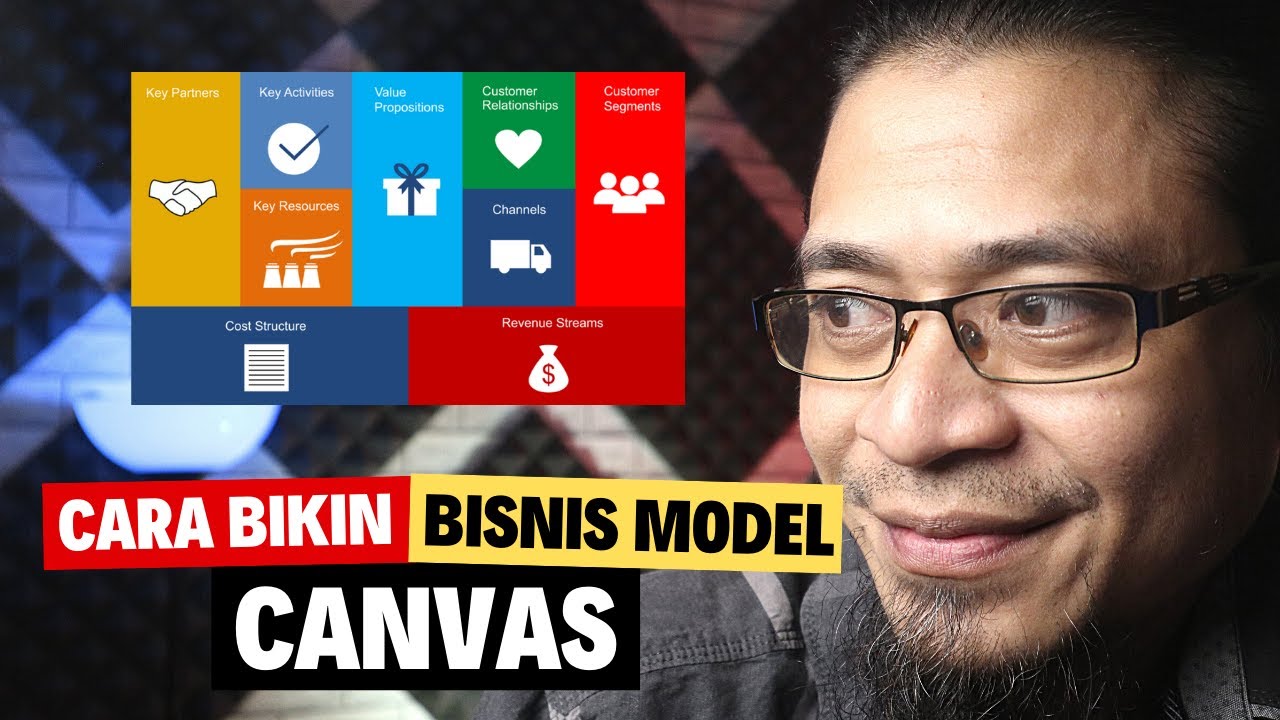
- 👥 'Customer Segments' is the starting block of the BMC, focusing on identifying and detailing potential customer groups.
- 💡 'Value Propositions' is the central block, emphasizing the value a product or service offers to customers.
- 🔗 'Customer Relationships' deals with how a business interacts and maintains relationships with its customers.
- 📍 'Channels' describes where and how customers find and engage with a business.
- 🔑 'Key Activities', 'Key Resources', and 'Key Partners' are operational blocks that define the actions, assets, and collaborations necessary for business operations.
- 💸 'Cost Structure' and 'Revenue Streams' are the financial blocks, detailing the expenses and income sources of the business.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in week six of the course on managing, organization and entrepreneurship?
-The main topic discussed is the business model canvas.
What are the three main objectives of the business model canvas chapter?
-The objectives are to identify the business model canvas, describe it in each item, and understand how to write one for your own business.
What does BMC stand for in the context of the lecture?
-BMC stands for Business Model Canvas, which is a tool to provide a clear overview of a business on a single sheet of paper.
Why is the business model canvas important for businesses?
-It helps entrepreneurs or business owners outline a comprehensive picture of the business concept, understand the business's competitive advantage, and identify areas for improvement.
How does the business model canvas help in strategic thinking?
-It highlights the business roadmap, accurately reflects strategic thinking, and connects ideas with the process to turn them into a business.
What are the nine blocks of the business model canvas?
-The nine blocks are customer segments, customer relationships, channels, value propositions, key activities, key resources, key partners, cost structure, and revenue streams.
Why should you start with customer segments when writing a business model canvas?
-Starting with customer segments helps to understand who needs the product and allows for a more detailed and specific approach to serving the needs of different customer groups.
What is the purpose of the value propositions block in the business model canvas?
-The value propositions block outlines the products and services offered to customers and how they solve their problems or fulfill their needs.
How can you identify the value of your product in the value propositions block?
-You can identify the value by listing product features, benefits, and advantages, and focusing on how these aspects meet the needs of your customer segments.
What does the customer relationships block focus on?
-It focuses on how a business interacts with its customers to maintain relationships, including ways to attract new customers and encourage repeat purchases.
Why are channels important in the business model canvas?
-Channels detail where and how customers find and engage with the business, which is crucial for effective communication and distribution of value propositions.
What are key activities, and how do they relate to the business model canvas?
-Key activities are the actions a business must perform to run operations and produce value propositions. They are essential for understanding the daily operations and identifying new activities or solutions to serve customers.
What are key resources, and how do they fit into the business model canvas?
-Key resources are the necessary tangible assets, such as materials, people, knowledge, or intellectual property, required to perform key activities and create value propositions.
Who are key partners in the context of the business model canvas?
-Key partners are external companies or parties that support and strengthen business operations, helping to increase efficiency and productivity.
What does the cost structure block represent in the business model canvas?
-The cost structure block represents the monetary costs of operating a business, including expenses like raw materials, labor, maintenance, rent, insurance, taxes, and marketing.
How is the revenue streams block different from other blocks in the business model canvas?
-The revenue streams block is focused on the income generated by the business, including various sources such as service fees, product sales, rents, and license fees.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)