2020 Dinamika Gerak II
Summary
TLDRThis physics lesson delves into fundamental concepts such as gravity, normal force, and centripetal force. It explains how gravity varies between Earth and the Moon, affecting an object's weight despite constant mass. The lesson also explores the normal force exerted on objects in contact, the role of gravitational acceleration in determining weight, and the differences between static and kinetic friction. Practical examples and calculations are used to illustrate these forces, providing a comprehensive understanding of their everyday applications.
Takeaways
- 🌍 The video lesson is a continuation of the second lecture on basic physics, focusing on chapter 4 which is about dynamics.
- 📚 Various types of forces are discussed, including gravity, normal force, tension in a rope, and centripetal force due to gravity.
- 🔍 The concept of weight is explained, which is a force directed towards the center of the Earth and is dependent on the mass of the object and the acceleration due to gravity.
- 🌕 The difference in weight on Earth and the Moon is highlighted, showing how weight varies with the gravitational acceleration of different celestial bodies.
- 📉 The script explains that the acceleration due to gravity on Earth is approximately 9.8 m/s², while on the Moon, it is about 1/6th of that value.
- 🧭 The direction of gravity is always towards the center of the Earth, regardless of the object's position.
- 🔄 The normal force is described as acting perpendicular to the surface of contact between two objects.
- 🔄 The script discusses the concept of static and kinetic friction, explaining how they differ and how they relate to the motion of objects.
- 📐 Examples are provided to illustrate the application of Newton's laws to solve for forces acting on objects at rest and in motion.
- 🔗 The tension in a rope is explained, showing how it is the same at all points along the rope when the mass of the rope is negligible.
Q & A
What are the different types of forces discussed in the script?
-The script discusses gravitational force, normal force, tension in a rope, and centripetal force.
What is the definition of weight according to the script?
-Weight is defined as the force exerted on a mass due to gravity, directed towards the center of the Earth, and it is the product of mass and gravitational acceleration at the location of the object.
How does the weight of an object differ on Earth and the Moon?
-The weight of an object differs on Earth and the Moon due to the difference in gravitational acceleration. On Earth, the acceleration due to gravity is approximately 9.8 m/s², while on the Moon, it is about 1/6th of that, resulting in a significantly lower weight.
What is the relationship between mass and weight as explained in the script?
-The script explains that weight is directly proportional to mass, with the weight being the product of mass and gravitational acceleration.
Why does the script mention the speed of light in the context of gravity?
-The script mentions the speed of light to illustrate that the gravitational force on an object is much less than the speed of light, emphasizing the relative magnitudes of different physical quantities.
What is the normal force and how is it related to the contact surfaces?
-The normal force is the force exerted by a surface on an object in contact with it, perpendicular to the surface. It acts to support the object against gravity and is related to the contact surfaces by being perpendicular to them.
How does the script describe the direction of gravitational force?
-The script describes the direction of gravitational force as always towards the center of the Earth, regardless of the object's position.
What is the significance of the gravitational acceleration value at the Earth's surface mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions that the gravitational acceleration at the Earth's surface is approximately 9.8 m/s², which is a constant value used to calculate the weight of objects on Earth.
What are the two types of friction forces discussed in the script?
-The script discusses static friction, which is the force that resists the initiation of sliding motion, and kinetic friction, which is the force that opposes the relative motion of two surfaces in contact.
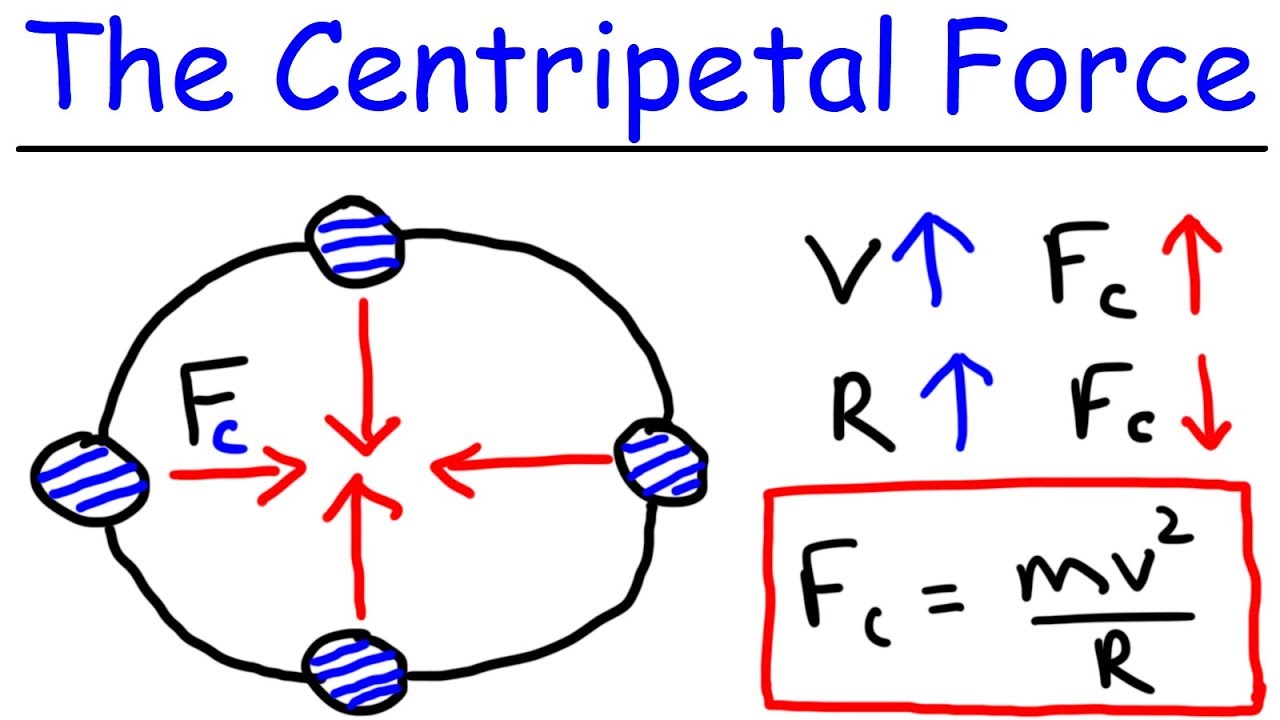
How does the script explain the concept of centripetal force?
-The script explains centripetal force as the force that acts on an object in circular motion, directed towards the center of the circle, and it is required for the object to maintain its circular path.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)