Prinsip Kelistrikan dan Sistem Instalasi Listrik || Prakarya Kelas IX Semester 1
Summary
TLDRThe video introduces the topic of electricity principles and household electrical systems for 9th-grade students. It covers the basics of electricity, including electric charges, currents (DC and AC), and the components involved in household electrical installations like circuit breakers, switches, and outlets. Various types of power plants, such as hydro, steam, and solar, are also discussed. The lesson emphasizes the importance of electrical components in everyday life and ends with an assignment for students to identify five electrical devices at home and document them.
Takeaways
- 💡 The lesson introduces electrical principles and household electrical systems, focusing on the importance of understanding electricity in daily life.
- 🔌 Electricity consists of positive and negative charges, with positive charges flowing from high potential to low potential areas.
- ⚡ Electrical current is defined as the continuous flow of electrons in a conductor, measured in amperes, and comes in two types: direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC).
- 🔋 Various sources of electrical energy are introduced, including hydroelectric, coal, nuclear, wind, and solar power plants, with examples from Indonesia and other countries.
- 🏡 Household electrical installations include components like switches, sockets, cables, and protective devices to ensure safety and proper power distribution.
- 🔌 Key electrical components in homes include the bargainser (electricity meter), MCB (automatic power switch), and KWH meter, which monitors electricity consumption.
- 🚨 Electrical safety devices are crucial for protecting homes from short circuits and power surges, such as fuses and thermos protectors.
- 🛠️ Various types of switches and sockets are explained, highlighting differences in function, installation methods, and power capacities.
- 🔧 The lesson also covers tools used in electrical installations, such as test pens, soldering irons, and wire cutters, which are essential for safe and effective work.
- 📋 The task for students is to identify five electrical devices in their homes, document them in a table, and submit photos for evaluation.
Q & A
What are the two types of electric charge mentioned in the script?
-The two types of electric charge are negative and positive. A body is negatively charged if it has excess electrons and positively charged if it lacks electrons.
What is the definition of electric current as explained in the script?
-Electric current is the continuous flow of electrons through a conductor due to the difference in the number of electrons at different locations. The standard unit of current is the ampere.
What are the two types of electric current?
-The two types of electric current are direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC).
What are some physical concepts that cause electricity according to the script?
-Electricity is caused by several physical concepts: electric charge, electric field, electric potential, electric current, and electromagnetism.
What are three benefits of electric energy mentioned in the script?
-Three benefits of electric energy are: 1) It provides lighting at night, 2) It powers electronic devices such as vacuum tubes and transistors, 3) It is used as an energy source for transportation, heating, telecommunications, and computing.
What are some examples of power plants mentioned in the script?
-Examples of power plants include hydroelectric power plants (e.g., PLTA Bakaru in South Sulawesi), steam power plants (e.g., PLTU Semarang in Central Java), nuclear power plants (e.g., in Japan and the former Soviet Union), coal power plants, solar power plants (e.g., in Karangasem, Bali), and wind power plants (e.g., in Sidrap, South Sulawesi).
What is the function of a 'bargainser' in a household electrical system?
-A 'bargainser' serves as a limiter and meter for the amount of electrical power entering and being used in a household. It has three key parts: the MCB (to automatically cut off electricity if the load exceeds the limit), the electric meter (to measure the amount of electricity consumed), and the spin control (which spins faster when more electricity is used).
What are the two types of electrical protection devices mentioned in the script?
-The two types of electrical protection devices are fuses and thermal protectors. Fuses melt to break the circuit when overloaded, while thermal protectors cut the circuit based on heat.
What is the purpose of a switch in an electrical system?
-A switch functions to connect or disconnect the flow of electricity through a conductor. It can be classified by voltage level (low, medium, high), installation method (in-wall or surface-mounted), and type (on-off or push button).
What are the different types of electrical cables used in household installations?
-The types of cables mentioned are: NIA (PVC-insulated, single-core wire), NHM (multi-core, PVC-insulated, often used for overhead wiring), NYA (black PVC-insulated, typically buried underground), and NYIO (flexible multi-core, used for small speakers or lighting systems).
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

PRINSIP KELISTRIKAN DAN SISTEM INSTALASI LISTRIK ~ MATERI PRAKARYA KELAS 9 BAB 2

SOAL LATIHAN BAB 4 LISTRIK MAGNET DAN SUMBER ENERGI ALTERNATIF (IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka)

BAB 4 LISTRIK, MAGNET DAN SUMBER ENERGI ALTERNATIF - PART 2 (IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka)

KELISTRIKAN PART 1: LISTRIK STATIS (IPA KELAS 9 SMP)

IPA Kelas 9 : Listrik Dinamis 2 (Rangkaian Listrik : Hukum Ohm dan Hukum Kirchhoff)
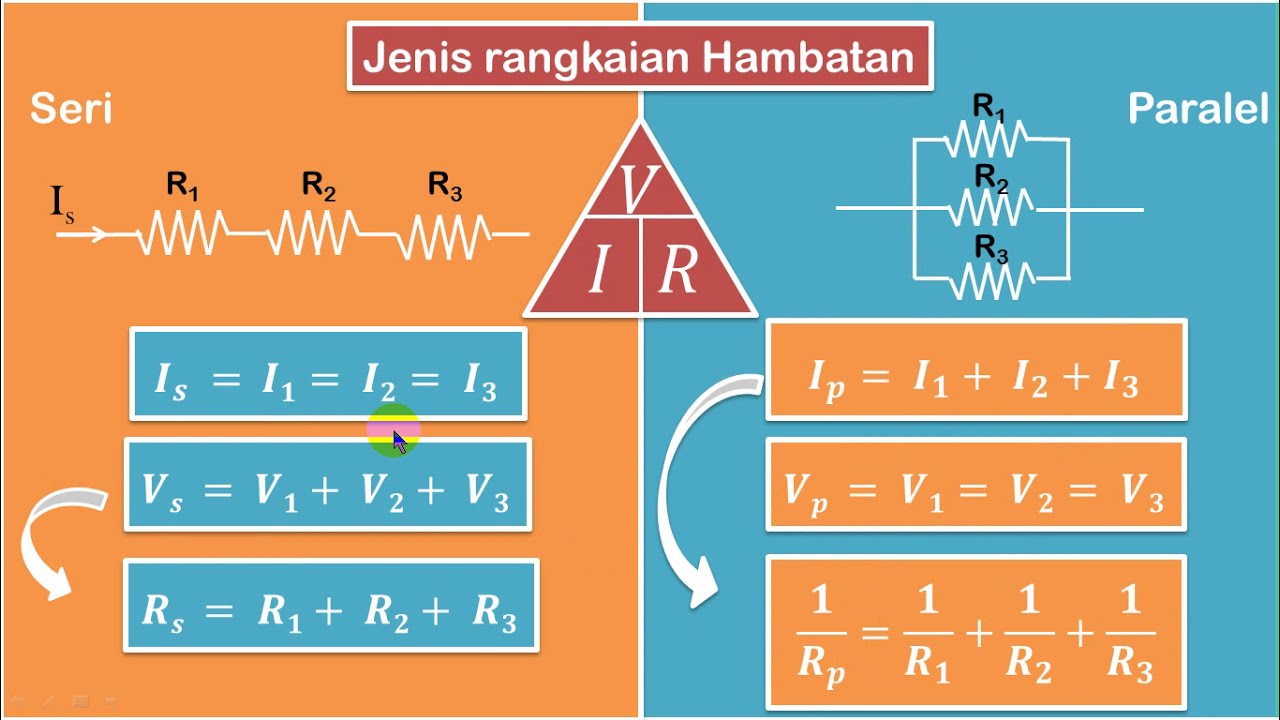
IPA Kelas 9 : Listrik Dinamis 3 (Rangkaian Hambatan Seri dan Paralel)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
