Sistem Pencernaan Manusia: Proses Pencernaan Pada Tubuh Manusia
Summary
TLDRIn this educational dialogue, Pipo and Bol explore the human digestive system. Starting with the mouth, they journey through the esophagus, highlighting peristalsis. The stomach's role in mechanical and chemical digestion is explained, with an emphasis on enzymes like pepsin and hydrochloric acid. The small intestine's three sections—duodenum, jejunum, and ileum—are detailed for their distinct digestive and absorptive functions. The large intestine's absorption of fluids and the role of E. coli in waste processing are also discussed. The conversation ends with a teaser about the causes of stomachaches for their next video.
Takeaways
- 🔁 The process of digestion begins in the mouth and continues through the esophagus to the stomach.
- 🌀 Peristalsis is the wave-like muscle movement in the esophagus that pushes food into the stomach.
- 🍽 The stomach is a highly elastic organ that mechanically and chemically digests food through muscle contractions and gastric juices.
- 🧬 Gastric juices contain enzymes like pepsin, renin, and hydrochloric acid (HCl), which aid in protein breakdown and sterilization.
- 🌟 The small intestine is the primary site for nutrient absorption, being the longest part of the digestive tract at 6 to 7 meters.
- 📌 The small intestine is divided into the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, each with specific roles in digestion and absorption.
- 🔄 The duodenum uses pancreatic enzymes like amylase, trypsin, and lipase, along with bile from the liver, to further digest food.
- 💧 The jejunum continues the digestive process, breaking down food particles from the duodenum.
- 🍹 The ileum is responsible for absorbing nutrients into the bloodstream, with its wall lined with blood vessels for nutrient uptake.
- 🌿 The large intestine absorbs water, vitamins, and minerals from the remaining food, and houses beneficial bacteria like E. coli.
- 🚽 The rectum stores feces temporarily, and the anus is the exit point for waste elimination from the body.
Q & A
What is the function of the esophagus in the digestive process?
-The esophagus is a tube-like channel that connects the oral cavity to the stomach, and it uses peristalsis, a squeezing motion, to push food into the stomach.
How does the stomach contribute to the digestion process?
-The stomach is the most elastic part of the digestive system and performs both mechanical and chemical digestion. Mechanical digestion is done by the stomach wall muscles, while chemical digestion is facilitated by gastric juices containing pepsin, renin, and hydrochloric acid.
What are the three enzymes found in gastric juices, and what are their functions?
-Gastric juices contain pepsin, which breaks down proteins into peptons; renin, which precipitates milk protein into casein; and hydrochloric acid (HCl), which acidifies food and kills germs.
What is the role of the small intestine in digestion, and how is it divided?
-The small intestine is the longest part of the digestive tract, measuring 6 to 7 meters in length. It is divided into three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, and is responsible for the absorption of nutrients and the digestion of food with the help of pancreatic and bile secretions.
What is the specific function of the duodenum in the small intestine?
-The duodenum, also known as the 12-finger intestine, is approximately 25 cm long and aids in food digestion with the help of pancreatic acid and bile, which contain enzymes like amylase, trypsin, and lipase.
How does the jejunum contribute to the digestive process?
-The jejunum, measuring about 2.5 meters in length, is located between the duodenum and ileum and serves to further digest food that has passed through the duodenum.
What is the primary function of the ileum in the small intestine?
-The ileum is responsible for absorbing food juices, with blood vessels on its wall ends that absorb these nutrients and circulate them through the bloodstream to various parts of the body.
What is the purpose of the large intestine in the digestive system?
-The large intestine absorbs fluids, vitamins, and minerals from the remnants of food that have been processed by the small intestine. It also houses beneficial bacteria like E. coli that aid in the spoilage process of food scraps, leading to the formation of feces.
What is the role of the rectum in the digestive process?
-The rectum serves as a temporary storage area for feces. When filled, it signals the brain to induce the feeling of defecation.
How does the anus function in relation to the digestive system?
-The anus is the outlet at the bottom of the buttocks through which feces are expelled from the body.
What causes heartburn, and how is it related to the digestive process?
-Heartburn is not directly mentioned in the script, but it is typically caused by stomach acid backing up into the esophagus, which can be related to the digestive process and the function of the stomach and esophagus.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Pelaksanaan Kewajiban & Hak Warga Masyarakat | Kewajiban & Hak | PKN | SayaBisa

How the Digestive System Works

O estômago
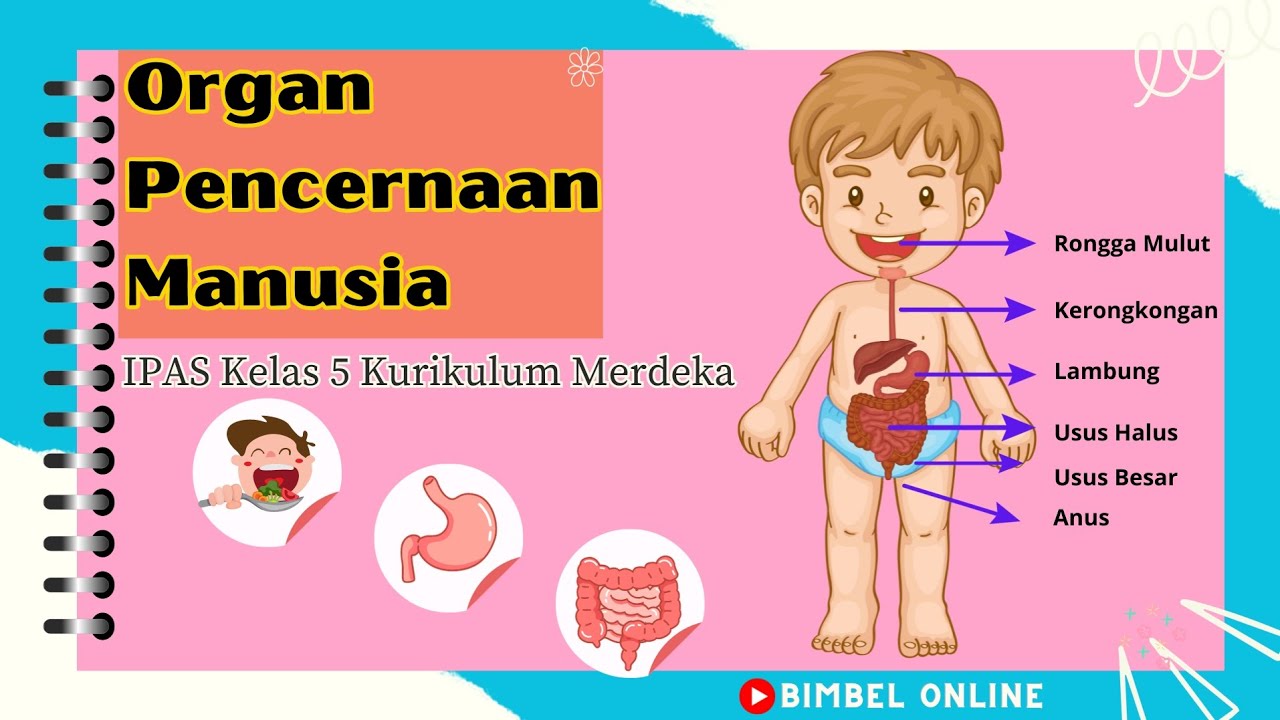
Organ Percernaan Manusia - IPAS Bab 5 Topik B || Kurikulum Merdeka

Apresiasi GTK 2023 Guru Inovatif | Praktik Baik Pembelajaran Berdiferensiasi

Once Upon a Time... Life - The digestion - Hello Maestro
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
