Peristiwa Perpindahan - Bilangan tak Berdimensi
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the host Felix explores dimensionless numbers, crucial in fluid dynamics and heat transfer. He explains the Reynolds number, used to predict flow patterns in fluids, and how it differentiates between laminar and turbulent flow. The video also touches on the Prandtl and Schmidt numbers, important in heat and mass transfer respectively. Felix simplifies complex concepts, making them accessible for understanding fluid dynamics and thermal phenomena without getting lost in dimensions.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video discusses the importance of dimensionless numbers in various scientific phenomena, particularly in fluid dynamics.
- 🔍 Dimensionless numbers like Reynolds, Prandtl, and Nusselt are used to standardize measurements across different units, simplifying calculations and comparisons.
- 🌐 The script explains that dimensionless numbers help in understanding fluid flow patterns, such as whether the flow is laminar or turbulent, based on the Reynolds number.
- 💧 Reynolds number is calculated as the product of fluid density, velocity, and diameter divided by the fluid's viscosity, representing the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces.
- 🌡️ Prandtl number is used in heat transfer and is the ratio of momentum diffusivity to thermal diffusivity, indicating the relative importance of momentum and heat transport.
- 🌡️ Nusselt number is used in heat transfer and is the ratio of convective to conductive heat transfer, aiding in understanding heat transfer efficiency.
- 📊 The video emphasizes that dimensionless numbers are crucial for analyzing graphs and data without confusion regarding units.
- 🔄 The script mentions that if the Prandtl number is high, momentum diffusivity dominates, and if it's low, thermal diffusivity is more significant.
- 🔬 Dimensionless numbers are essential for engineers and scientists to predict and control various physical phenomena in fields like fluid mechanics and heat transfer.
- 📌 The video encourages viewers to explore further into dimensionless numbers and transport phenomena by engaging with the presenter's social media and joining the learning community.
Q & A
What is the purpose of dimensionless numbers in fluid dynamics?
-Dimensionless numbers in fluid dynamics, such as the Reynolds number, are used to characterize the behavior of fluid flows without involving the physical dimensions. They help to standardize the comparison of different flow conditions and are crucial for understanding phenomena like turbulence and laminar flow.
What is the Reynolds number and how is it used?
-The Reynolds number is a dimensionless quantity that describes the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces in a fluid flow. It is used to predict the transition from laminar to turbulent flow. A low Reynolds number indicates that viscous forces dominate, leading to laminar flow, while a high Reynolds number suggests that inertial forces are dominant, resulting in turbulent flow.
How does the Reynolds number affect the flow pattern in a pipe?
-The flow pattern in a pipe is influenced by the Reynolds number. If the Reynolds number is low, the flow tends to be laminar, forming a parabolic velocity distribution. Conversely, a high Reynolds number leads to a more uniform velocity distribution, indicating turbulent flow.
What is the significance of the Prandtl number in heat transfer?
-The Prandtl number is a dimensionless number used in heat transfer to compare the relative rates of momentum diffusivity and thermal diffusivity. It helps determine the dominance of heat transfer mechanisms, such as conduction or convection, and is crucial for designing heat exchangers and understanding thermal boundary layers.
How is the Smith number different from the Reynolds number?
-The Smith number is another dimensionless number used in heat and mass transfer, but it specifically compares the effects of mass diffusivity and momentum diffusivity. It is particularly relevant in processes where mass transfer is influenced by the fluid's velocity and density.
What does the term 'total flux' refer to in the context of fluid dynamics?
-In fluid dynamics, 'total flux' refers to the combined effect of molecular diffusion and convective transport. It is a measure of the overall mass, energy, or momentum transfer across a surface or through a volume, considering both molecular motion and bulk fluid motion.
Why are dimensionless numbers important in the analysis of fluid flow?
-Dimensionless numbers are essential in fluid flow analysis because they allow for the comparison of different flow scenarios in a non-dimensional form. This simplifies the analysis, enables the generalization of experimental results, and helps in predicting the behavior of fluid flows under various conditions.
What is the role of viscosity in determining the Reynolds number?
-Viscosity plays a critical role in determining the Reynolds number as it is one of the factors in the formula (Re = (inertia force) / (viscous force)). A higher viscosity results in a lower Reynolds number, promoting laminar flow, while lower viscosity leads to a higher Reynolds number, potentially causing turbulent flow.
How can one interpret a graph with dimensionless numbers such as the Reynolds number?
-A graph with dimensionless numbers like the Reynolds number can be interpreted by observing how changes in the dimensionless number affect the behavior of the system, such as flow patterns or heat transfer rates. For example, a graph might show how the transition from laminar to turbulent flow occurs at a specific Reynolds number.
What is the significance of the statement 'if the inertia forces are dominant, the flow tends to be turbulent'?
-This statement implies that when inertia forces exceed viscous forces in a fluid, the flow is more likely to be turbulent. Turbulent flow is characterized by chaotic and irregular motion, which is significant for understanding mixing, heat transfer, and drag in fluid systems.
How can one determine if a fluid flow is laminar or turbulent based on the Reynolds number?
-A fluid flow is typically considered laminar if the Reynolds number is below a certain threshold, often around 2000 for flow in pipes. If the Reynolds number exceeds this value, the flow is likely to be turbulent. This determination helps in predicting the flow behavior and designing systems accordingly.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Mata Kuliah - Analisa Dimensi - FT

Heat Transfer - Chapter 8 - Internal Convection - Hydrodynamic Considerations

Практичне заняття "Конвективний теплообмін"
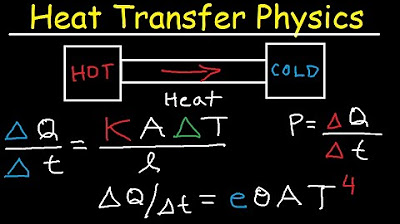
Thermal Conductivity, Stefan Boltzmann Law, Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convecton, Radiation, Physics

Експериментальне визначення коефіцієнтів тепловіддачі при вимушеної течії повітря в трубі

Unit Operation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
