Redes de computadores - Protocolo TCP IP - Informática para concursos - Professor Danilo Vilanova
Summary
TLDRThis script offers an in-depth exploration of the TCP/IP protocol, the backbone of internet communication. It distinguishes TCP/IP from TCP alone, explaining the importance of the former in network regulation. The video delves into the four-layer model of the TCP/IP protocol, comparing it with the seven-layer OSI model. It discusses various application layer protocols such as HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, DNS, SMTP, POP3, and IMAP, highlighting their functionalities and the importance of security in data transmission. The script uses relatable analogies, like postal services, to clarify complex networking concepts, aiming to simplify the understanding of internet protocols for the audience.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script discusses the TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), which is a fundamental protocol governing the internet.
- 🔍 It mentions another protocol, TCP/IP, which is often referred to in questions but is less frequently studied, as it is considered a subset of TCP.
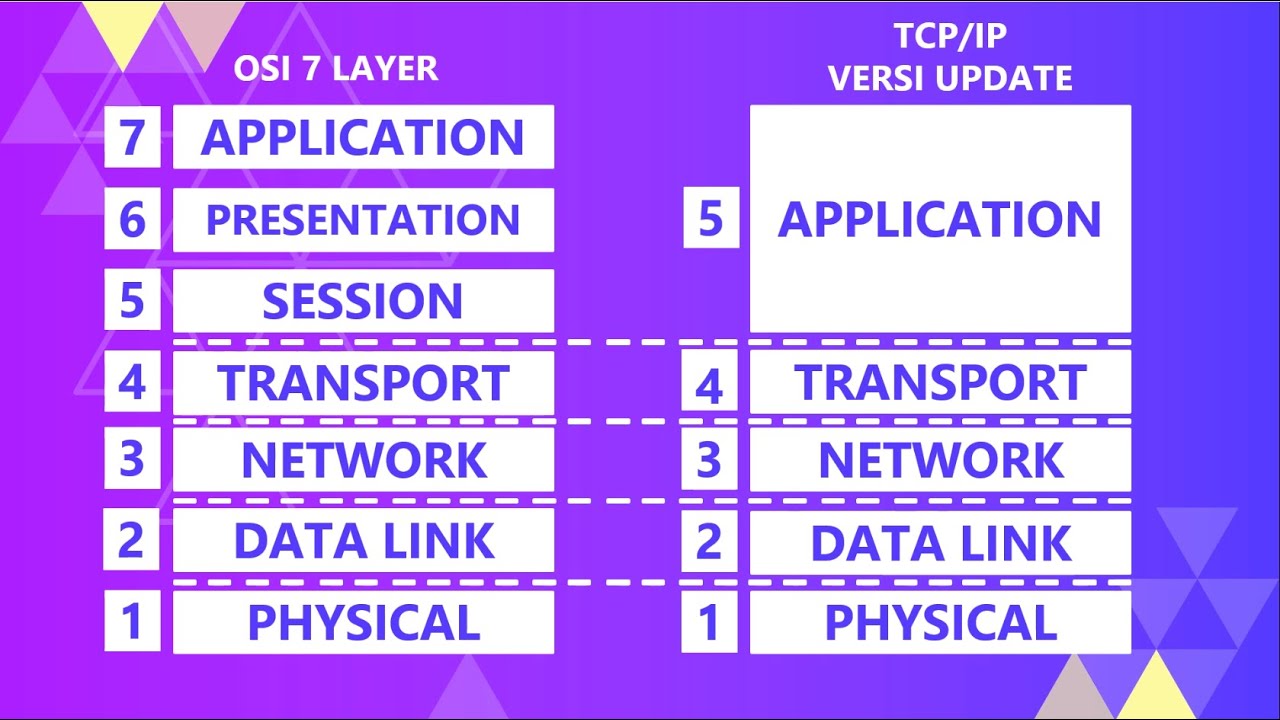
- 🌐 The script explains that TCP/IP is the main protocol for networks, including the internet, intranet, and extranet, and operates through four layers, not seven as sometimes misunderstood.
- 📚 The four layers of the TCP/IP model are the Application layer, Transport layer, Internet layer, and Data Link layer, each with specific functions and protocols.
- 🚚 The Transport layer is responsible for the actual data transportation, with TCP and UDP being key protocols; TCP ensures data delivery while UDP prioritizes speed.
- 🔑 The Internet layer uses IP for identification and routing of packets, while the Data Link layer handles the physical delivery of data to the destination.
- 💌 The script uses the analogy of sending love letters to explain how data packets are sent and received over the internet, emphasizing the role of each layer in the process.
- 🔒 It highlights the importance of security in data transmission, with protocols like HTTPS and FTPS providing encryption and secure data transfer.
- 🌐 The script introduces various application layer protocols such as HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, DNS, SMTP, POP3, IMAP, and NNTP, explaining their purposes and functions.
- 🔍 DNS (Domain Name System) is described as a service that translates domain names into IP addresses, facilitating user-friendly access to websites.
- 📧 The script differentiates between email protocols like SMTP for sending emails and POP3/IMAP for receiving and managing emails, with IMAP being more modern and preferred for keeping emails synchronized across devices.
Q & A
What is the main protocol that governs the internet?
-The main protocol that governs the internet is TCP/IP, which stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol.
What does TCP stand for and what does it signify?
-TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol, which signifies a protocol for reliable transmission of data over IP networks.
What is the difference between TCP and UDP in terms of data transmission?
-TCP provides a reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of a stream of data between applications, while UDP offers a faster, but less reliable, connectionless protocol that does not guarantee delivery or order.
What are the four layers of the TCP/IP protocol suite?
-The four layers of the TCP/IP protocol suite are the Application layer, Transport layer, Internet layer, and Network Interface layer.
What is the role of the Application layer in the TCP/IP model?
-The Application layer is responsible for providing the interface between the user's application programs and the network. It determines the kind of service the application needs to access the network.
Can you explain the function of the Transport layer in the TCP/IP model?
-The Transport layer is responsible for ensuring the reliable transmission of data between host computers. It includes protocols like TCP and UDP that manage the way in which network services are provided to applications.
What is the purpose of the Internet layer in the TCP/IP model?
-The Internet layer is responsible for addressing and routing packets between networks. It uses IP to achieve logical addressing and routing of packets across network boundaries.
What does the Network Interface layer represent in the TCP/IP model?
-The Network Interface layer represents the lowest layer of the TCP/IP model and is responsible for the actual transmission of data over the physical network medium. It deals with the electrical, mechanical, and functional specifications for network devices.
What is VoIP and how does it relate to the protocols discussed in the script?
-VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol. It is a methodology and group of technologies for the delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over Internet Protocol networks. It is related to the protocols discussed in the script as it often uses UDP for its transmission due to its real-time nature.
What are some common protocols associated with the Application layer of the TCP/IP model?
-Some common protocols associated with the Application layer include HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, DNS, SMTP, POP3, IMAP, and Telnet.
What is the purpose of the DHCP protocol mentioned in the script?
-DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It is used for automatically assigning IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to devices on a network, eliminating the need for manual configuration.
Can you describe the role of the DNS protocol in internet connectivity?
-DNS stands for Domain Name System. It is the protocol responsible for translating human-friendly domain names (like www.google.com) into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network.
What is the difference between HTTP and HTTPS protocols?
-HTTP is the protocol for transferring data on the web without security measures, while HTTPS indicates that the HTTP protocol is secured with SSL/TLS, providing encryption and secure data transfer, which is crucial for online transactions and privacy.
What does FTP stand for and what is its role in data transfer?
-FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. It is used for transferring files from one host to another over a network, typically in an anonymous manner, allowing users to upload and download data.
What are the main differences between POP3 and IMAP protocols for email retrieval?
-POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3) is used to retrieve emails from a server to a local device, often removing them from the server, while IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) synchronizes emails between the server and the local device, keeping a copy on both ends.
What is SMTP and what is its role in email communication?
-SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It is the protocol used for sending and relaying email messages over the internet from the sender's mail server to the receiver's mail server.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)