Deformation of the Earth's Crust - Earth and Life Science
Summary
TLDRThis Earth and Life Science lecture delves into the deformation of the Earth's crust, exploring how tectonic plate margins create geologic structures like folds and faults. It revisits Alfred Wegener's continental drift theory, highlighting evidence from geology, fossils, and climate that supports the concept of once-joined continents now separated. The lecture also explains the plate tectonics theory, describing the forces of mantle convection driving plate movement and the three types of plate boundaries—convergent, divergent, and transform—that shape our planet's surface and influence geological hazards.
Takeaways
- 🌍 The Earth's appearance is constantly changing due to endogenic and exogenic processes.
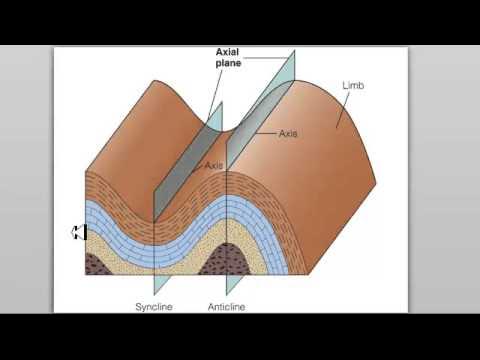
- 🔍 Deformation of the Earth's crust occurs along tectonic plate margins, leading to the formation of various geological structures like folds, faults, joints, and foliation.
- 🌐 The Earth's geosphere is divided into the core, mantle, and crust, with the crust further divided into oceanic and continental types.
- 🌊 Oceanic crust is denser than continental crust, which allows the less dense continental crust to float in high relief on the denser mantle.
- 🌏 Alfred Wegener's continental drift theory proposed that all continents were once part of a supercontinent, Pangaea, which broke apart over time.
- 🧩 Wegener provided three main pieces of evidence for his theory: geological, fossil, and climate evidence, which showed similarities across continents that are now separated.
- 🔭 The acceptance of Wegener's theory was initially limited due to a lack of explanation for the forces moving the continents.
- 🌑 The development of technology in the 1940s led to the discovery of the driving force behind continental movement: mantle convection currents.
- 🌈 Tectonic plates are made up of the lithosphere, which includes the crust and the upper mantle, and there are eight major and several minor plates identified.
- 📏 There are three types of plate boundaries: convergent (where plates meet and create trenches or mountains), divergent (where plates move apart and new crust is formed), and transform (where plates slide past each other, causing earthquakes).
- 🏞️ The Philippines lies on the boundary of the Philippine plate, making it prone to geological hazards due to the tension and energy release at plate boundaries.
Q & A
What are the two main types of geologic processes that change the Earth's appearance?
-The two main types of geologic processes that change the Earth's appearance are endogenic and exogenic processes.
What is the significance of the Earth's crust deformation?
-Deformation of the Earth's crust is significant as it produces various geologic structures such as folds, faults, joints, and foliation, which are the result of the crust being deformed along tectonic plate margins.
How does the density of oceanic and continental crust compare?
-The oceanic crust is denser compared to the continental crust.
What is the concept of continental drift, and who proposed it?
-Continental drift is the concept that all continents were once joined together in a single massive landmass, which was proposed by geophysicist Alfred Wegener.
What was the name of the supercontinent that existed according to Wegener's theory?
-According to Wegener's theory, the supercontinent that existed was named Pangaea.
What are the three main pieces of evidence that Wegener found to support his continental drift theory?
-The three main pieces of evidence that Wegener found to support his continental drift theory are geologic, fossil, and climate evidence.
How did Wegener's theory initially fare among the scientific community, and why?
-Wegener's theory initially did not gain acceptance from the scientific community because he could not explain the force that moves the continents.
What discovery in the 1940s provided a significant advancement in understanding continental movement?
-The discovery of mantle convection currents during the 1940s provided a significant advancement in understanding the movement of continents.
What are the three major types of plate boundaries?
-The three major types of plate boundaries are convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries.
What are the two types of crustal movement that can result from tectonic plate deformation?
-The two types of crustal movement that can result from tectonic plate deformation are folding and faulting.
What is the relationship between the Philippines and the Philippine Plate, and why is this significant?
-The Philippines lies on the boundaries of the Philippine Plate, which makes the country prone to geological hazards as these boundaries are areas of high tension and energy release.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)