Advanced Networking - #5 The OSI Model [EN]
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the OSI model, a foundational concept in networking, explaining how smart communication operates from bits to services. It breaks down the seven layers, from the physical layer handling transmission technologies to the application layer dealing with end-user protocols. Each layer's role in data processing, routing, and communication is discussed, with examples like Ethernet for the data link layer and TCP/UDP for transport. The video promises future exploration of protocols like ICMP, TCP, and UDP, which are vital for internet communication.
Takeaways
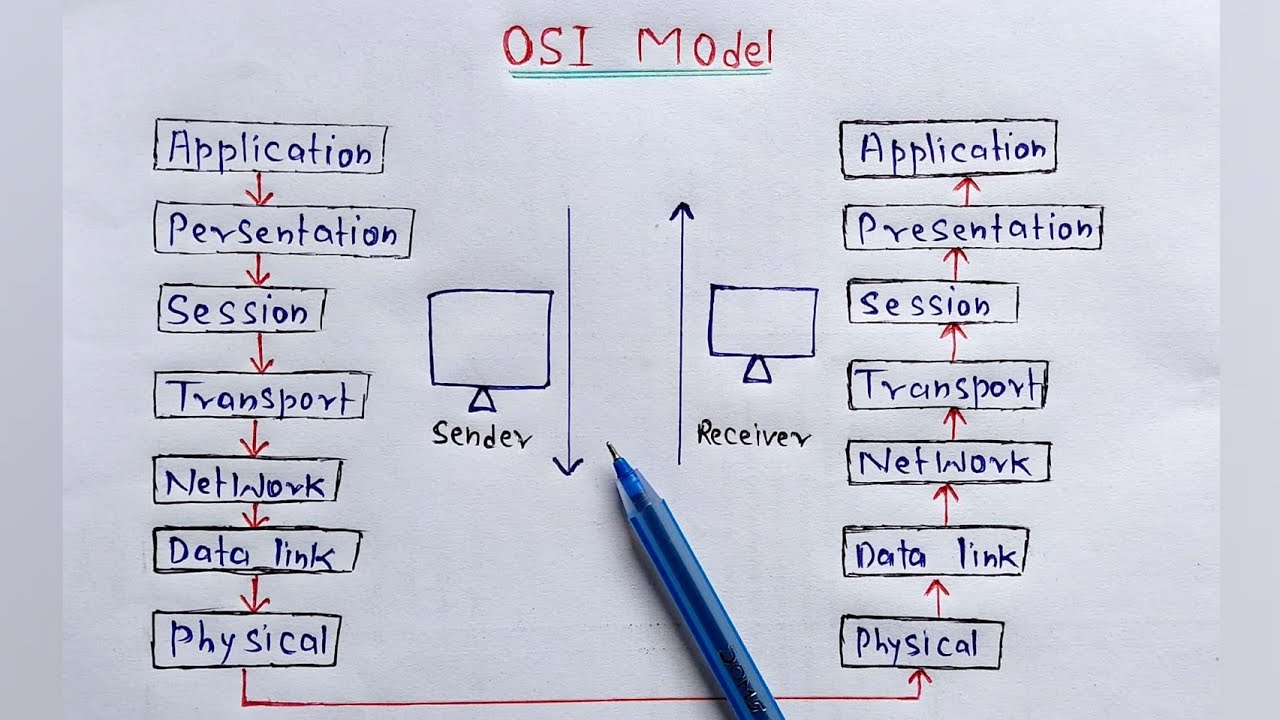
- 🌐 The OSI model, standing for Open System Interconnection, is a framework for understanding how data moves from one device to another in a network.
- 📚 The OSI model consists of seven layers, each with a specific function in the communication process, starting from the physical layer at the bottom and ending with the application layer at the top.
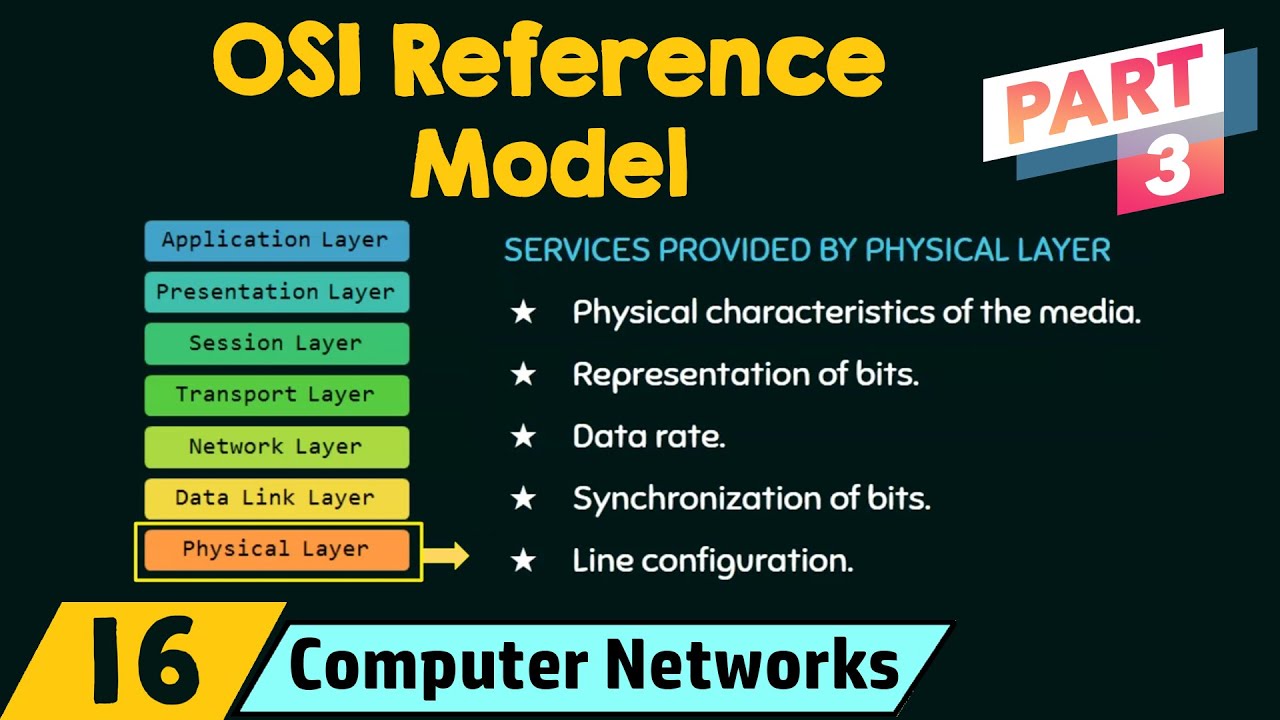
- 🔌 The physical layer (Layer 1) is responsible for the actual transmission of raw bits over a physical medium such as Ethernet cables, fiber optics, or wireless networks.
- 🔗 The data link layer (Layer 2) packages bits into frames, performs error detection, and is associated with protocols like Ethernet and PPP for point-to-point connections.
- 📦 The network layer (Layer 3) is where routing occurs, using IP addresses to direct packets through a network, with devices like routers and Layer 3 switches operating at this level.
- 🔄 The transport layer (Layer 4) manages end-to-end communication, error detection, and correction, with protocols such as TCP and UDP defining the rules for data exchange between applications.
- 🤝 The session layer (Layer 5) synchronizes data transmission between sender and receiver, ensuring that data packages arrive in the correct order and are reassembled correctly.
- 🔒 The presentation layer (Layer 6) is involved in data representation, encryption, and decryption, ensuring that data is presented to the application in a usable form.
- 🛠️ The application layer (Layer 7) is where the actual application protocols like HTTP, SSH, and email protocols operate, providing the interface for end-user applications to access network services.
- 🔍 Network devices can focus on specific layers, inspecting and modifying data as it passes through, deciding whether to redirect, process further, or drop the data based on the layer's protocols and rules.
- 🚀 The script also mentions upcoming topics like ICMP, TCP, and UDP, which are essential protocols for network communication, with ICMP used for diagnostic messaging and TCP/UDP for data transfer with different reliability and speed characteristics.
Q & A
What is the OSI model?
-The OSI model, which stands for Open System Interconnection, is a conceptual framework used to understand how data communication occurs between different devices on a network. It is structured as a stack with seven layers, each with a specific function in the communication process.
What is the purpose of the physical layer in the OSI model?
-The physical layer is the lowest layer in the OSI model and it deals with the physical means of transmitting raw bits over a physical medium such as twisted pair cables, fiber optics, or wireless networks.
What does the data link layer do in the OSI model?
-The data link layer is responsible for packaging raw bits into bytes and bytes into frames to create network packets. It also handles error detection through checksums to ensure data integrity.
How does the network layer in the OSI model contribute to routing?
-The network layer is responsible for routing packets through a network using logical addressing (IP addresses) and protocols like IPv4, IPv6, and ICMP. It determines the best path for data transmission.
What is the role of the transport layer in establishing communication?
-The transport layer establishes end-to-end communication between applications by providing services like TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol), which handle data transmission, error detection, and correction.
What is the session layer in the OSI model and why is it important?
-The session layer is responsible for synchronizing the sender and receiver in a network communication. It manages the establishment, management, and termination of sessions and ensures that data is correctly ordered and reassembled.
What is the main function of the presentation layer?
-The presentation layer is responsible for the representation of data to the application layer. It handles data encryption and decryption, as well as data encoding and decoding, to ensure that the application can understand and process the data.
What protocols are commonly used in the application layer of the OSI model?
-Common protocols used in the application layer include HTTP for web communication, SSH for secure shell access, email protocols like IMAP and POP3, and DHCP for dynamic host configuration.
What is the difference between TCP and UDP protocols?
-TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a connection-oriented protocol that provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of data. UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a connectionless protocol that is faster but does not guarantee reliability or order, making it suitable for applications where speed is more important than reliability.
What is ICMP and how is it used in networking?
-ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is used by network devices to communicate error messages and operational information. It is commonly used for diagnostic purposes, such as 'pings' to test network connectivity.
What are some examples of devices that operate at the physical layer?
-Examples of devices that operate at the physical layer include cables, hubs, repeaters, and networking bridges. These devices are responsible for the transmission of raw bits over a physical medium without any data interpretation.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
The OSI Reference Model (Part 3)

OSI Model: A Practical Perspective - Networking Fundamentals - Lesson 2a
What is OSI Model? full Explanation | Networking

Redes Locais - LAN - Aula 01 - Conceitos, Histórico e o Modelo ISO/OSI

Redes de computadores - Protocolo TCP IP - Informática para concursos - Professor Danilo Vilanova

Lec-2: Introduction to Computer Network | OSI MODEL in easiest Way in Hindi | Need of OSI model
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
