What is a Singularity? | Eternally Curious #11
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the concept of a singularity, starting with a mathematical analogy of division by zero, which is undefined in real-world mathematics. It then delves into the physics of black holes, explaining the Schwarzschild radius and the event horizon. The video clarifies that the singularity, a point of infinite density, is not the black hole itself but its core, where our known laws of physics break down. The script teases the possibility of wormholes, time travel, and other universes, while acknowledging the limits of our current understanding and inviting viewers to subscribe for more on the topic.
Takeaways
- 🧠 A singularity is a concept in mathematics and physics where an equation or situation has no solution or becomes nonsensical, often due to division by zero.
- 📚 The term 'singularity' is derived from the idea of being 'one' or 'unique', but in this context, it represents an exception to the rules of mathematics.
- 🔍 The script uses the example of a simple mathematical function where division by zero occurs, illustrating the concept of a singularity in a practical sense.
- 🌐 The Riemann sphere in the complex plane is mentioned as a construct that allows for division by zero in certain mathematical contexts, showing an alternative approach to handling singularities.
- 🌌 Einstein's field equations and the Schwarzschild solution are discussed as foundational to understanding singularities in the context of black holes.
- 🌀 The Schwarzschild radius is defined as the critical size at which an object's escape velocity equals the speed of light, leading to the formation of a black hole.
- 🌍 The Earth's Schwarzschild radius is given as an example to illustrate the scale at which a massive object would need to be compressed to form a black hole.
- 🕳 The script humorously compares the concept of a black hole to a congressional budget, highlighting the idea of something from which nothing can escape.
- 🔮 The singularity within a black hole is described as a point of infinite density where the known laws of physics break down, contrasting it with the event horizon which is the boundary of the black hole.
- 🤔 There is ongoing speculation about the nature of singularities, including possibilities like wormholes, time travel, and connections to other universes, indicating the mystery and fascination surrounding these phenomena.
- 🔬 The existence of black holes has been confirmed through experimental evidence, lending credibility to the theoretical concept of singularities, despite the lack of direct observation.
Q & A
What is a singularity?
-A singularity is an imaginary point in spacetime where all known laws of physics break down and make no sense.
How does the script describe the concept of dividing by zero?
-The script explains that dividing by zero is nonsensical in normal arithmetic, likening it to a construct that doesn't exist in the real world but is instead an idea.
Who solved Einstein's field equations for a single spherical non-rotating mass?
-Karl Schwarzschild solved Einstein's field equations for a single spherical non-rotating mass.
What is the Schwarzschild radius?
-The Schwarzschild radius is the radius of a sphere such that if all the mass of an object were compressed within that sphere, the escape velocity from the surface would equal the speed of light.
Why can't anything escape from within the Schwarzschild radius?
-Nothing can escape from within the Schwarzschild radius because the escape velocity would need to be faster than the speed of light, which is impossible as nothing can exceed the speed of light.
What analogy is used to describe the size of the Earth's Schwarzschild radius?
-The script compares compressing the Earth to a size of a penny to illustrate the tiny Schwarzschild radius of only 8mm for a massive object like Earth.
What is the event horizon in the context of a black hole?
-The event horizon is the threshold around a black hole beyond which nothing can return; it marks the boundary of the black hole.
What happens at the center of a black hole according to the script?
-At the center of a black hole, known as the singularity, all known laws of physics break down and the object's radius is theoretically zero, leading to infinite density.
Is the singularity a physical place?
-No, the singularity isn't a physical place; it's hypothetical and occupies no space with infinite density.
What kind of speculation exists about the nature of singularities?
-There is speculation that singularities could involve phenomena like wormholes, time travel, and portals to other universes, but we don't know for sure.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
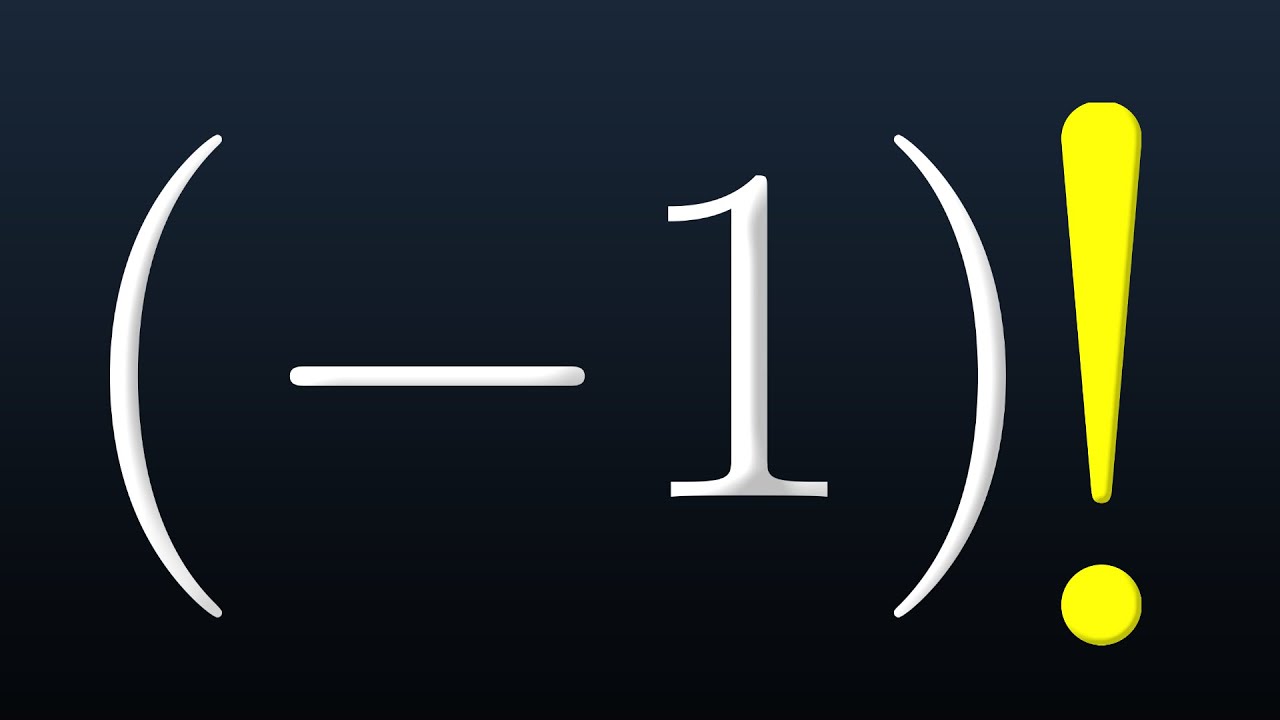
The Secret Behind -1 Factorial

Complex Numbers 01 | Introduction to Complex Numbers | Class 11 | JEE

מבוא לתורת הקבוצות - 1 - ממה מורכבת המתמטיקה?

Problems with Zero - Numberphile

2. Divisibility Theory | Division Algorithm | Number Theory | Ravina Tutorial | in Hindi
Kalkulus Part. 6 - Fungsi dan Jenisnya, Daerah asal dan Daerah Hasil
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
