The Gravity of the Situation: Crash Course Astronomy #7
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the fundamental concept of gravity, explaining its perpetual yet distance-decreasing force and its impact on our perception of physics. It discusses mass, density, and how gravity influences motion, from everyday experiences on Earth to the complexities of space orbits. The episode covers the history of gravitational understanding, from Newton and Hooke to Kepler's laws, and explores the idea of escape velocity, highlighting the continuous yet weakening nature of gravity even as objects move further away.
Takeaways
- 🌍 We live on a planet, which is an unusual condition in the vast emptiness of the universe, often referred to as 'space'.
- 🚀 Gravity is a fundamental force that acts differently on a planet compared to deep space, where it weakens rapidly with distance.
- 📚 The concept of mass is crucial to understanding gravity; it's a measure of how much 'stuff' an object contains, irrespective of its size or density.
- 🔍 Historically, gravity was a fact of life until scientists like Robert Hooke and Isaac Newton began to mathematically investigate its principles.
- 🪐 Gravity is an attractive force that pulls objects together, with the force's strength depending on the masses involved and the distance between them.
- 📉 The force of gravity weakens with the square of the distance from the object exerting the force, making it a dominant factor in celestial mechanics.
- 💫 Gravity can cause objects to accelerate, as seen when a rock falls to the ground, gaining speed as it falls due to the continuous action of gravity.
- 🛰 Orbiting is a state where objects move under the influence of gravity, with the simplest form being a straight line, as in the case of a falling rock.
- 🌌 Kepler discovered that planets orbit the Sun in ellipses, not perfect circles, which was a significant advancement in our understanding of celestial motion.
- 🚀 The escape velocity is the minimum speed needed for an object to break free from the gravitational pull of another body, varying based on mass and size.
- 👨🚀 Astronauts in space appear 'weightless' not because gravity is absent, but because they are in a state of free fall, experiencing no resistance to their motion.
- 🌌 Even light, which has no mass, is affected by gravity, bending its path as it passes massive objects, demonstrating that gravity can warp the fabric of space.
Q & A
What is the primary difference between living on a planet and being in deep space in terms of physics?
-The primary difference is gravity. On a planet, gravity pulls objects toward its center, causing them to fall back down if thrown, whereas in deep space, objects would continue moving away at a constant speed if not influenced by other forces.
Why did Robert Hooke and Isaac Newton have a feud over the concept of gravity?
-They had a feud over who first conceived the mathematical understanding of gravity. Both were investigating the concept, and the dispute was about originality and priority in the discovery.
What is mass and how is it related to an object's resistance to changes in motion?
-Mass is a measure of how much 'stuff' makes up an object. It's related to an object's resistance to changes in motion because an object with more mass is harder to move or stop than one with less mass due to its greater inertia.
How does the force of gravity from an object affect another object?
-The force of gravity between two objects depends on their masses and the distance between them. The closer the objects are, the stronger the gravitational force, and the greater their masses, the stronger the attraction.
Why does the force of gravity weaken with the square of the distance?
-The force of gravity weakens with the square of the distance due to the inverse-square law, which states that the intensity of a physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source.
What is the significance of an object accelerating when it falls towards the Earth?
-The acceleration signifies that the force of gravity is acting on the object, increasing its velocity as it falls. This acceleration is due to the continuous application of the gravitational force over time.
What is an orbit and what are the different types of orbits mentioned in the script?
-An orbit is a path followed by an object under the influence of a gravitational force. The script mentions straight lines, circles, ellipses, parabolae, and hyperbolae as different types of orbits.
How does the concept of escape velocity relate to the force of gravity?
-Escape velocity is the minimum speed needed for an object to break free from the gravitational influence of another body. It is related to the force of gravity because the object must overcome the gravitational pull to escape.
Why are astronauts on the International Space Station considered to be in a state of 'weightlessness'?
-Astronauts are in a state of 'weightlessness' because they are in free fall around the Earth. There is no surface pushing back against them, so they do not experience the sensation of weight, even though gravity is still acting on them.
How does the script explain the concept of mass affecting the motion of light?
-The script explains that even though photons, particles of light, have no mass, they can still be affected by gravity. This is because gravity can warp space, and light follows the curvature of space, changing its direction as it passes a massive object.
What is the role of Johannes Kepler in understanding orbits as described in the script?
-Johannes Kepler is credited with discovering that planets orbit the Sun in ellipses, not perfect circles as previously thought. This discovery expanded our understanding of orbits beyond just circular paths.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

FISICA! forza d’attrito, fisica attrito, attrito statico e dinamico, forza d’attrito esercizi

Hukum Gravitasi Umum Newton | Materi Fisika Kelas 10

hukum newton 1,2 dan 3

As 3 Leis de Newton EXPLICADAS
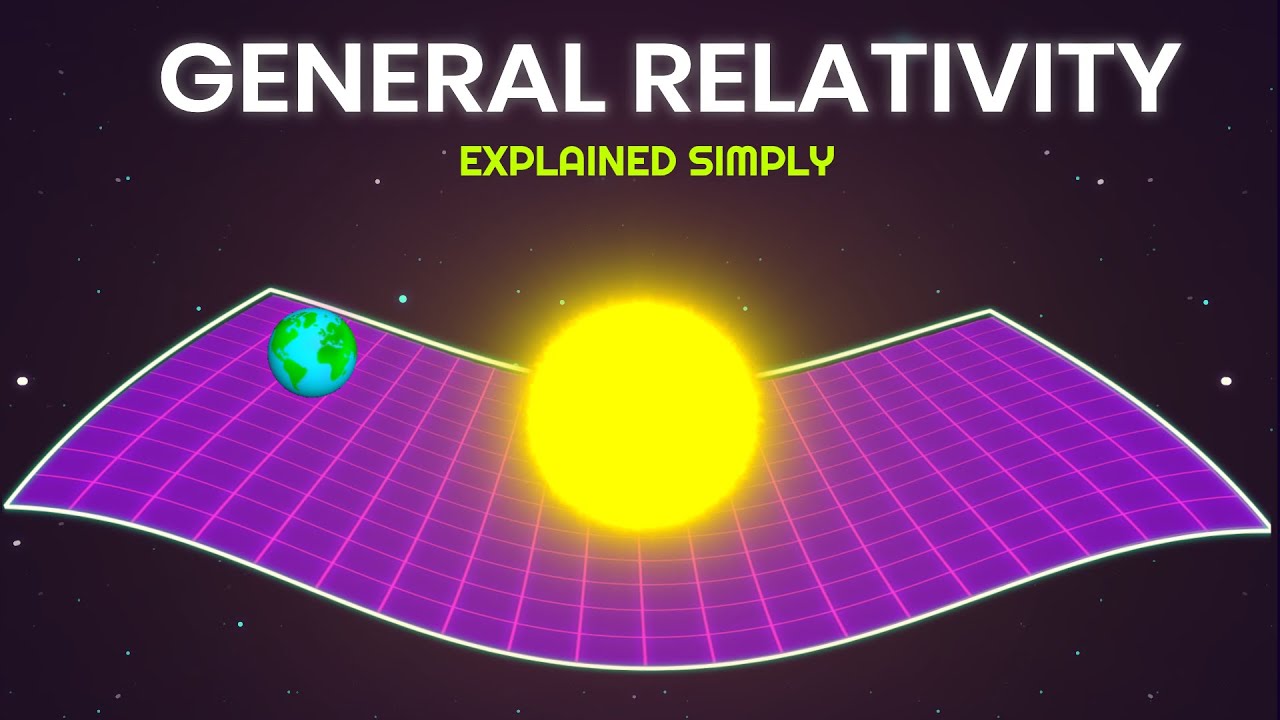
If light has no mass, why is it affected by gravity? General Relativity Theory

GRavity 1 Newton's Law of Gravity
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
