12. Biology | Cell Structure and Function | Basic Concepts of Cell Biology | MDCAT 2025
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful introduction to cell biology, focusing on cells as the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms. It explains the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, with an emphasis on the structure and functions of key organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum. The lesson also explores the concept of living organisms at the cellular level and addresses key biological processes. Interactive questions are included to engage students and help reinforce learning, making the topic both informative and engaging for viewers.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms.
- 😀 Viruses are not considered living organisms because they lack cellular structure.
- 😀 Eukaryotic cells have distinct organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes, each with specific functions.
- 😀 The structure of a typical eukaryotic cell includes the cell membrane, nucleus, and various organelles.
- 😀 Cells can be prokaryotic (without a nucleus) or eukaryotic (with a nucleus), with eukaryotic cells being more complex.
- 😀 The smallest unit of living things is the cell, but molecules like atoms, electrons, protons, and neutrons also play a role in cellular function.
- 😀 Mitochondria are the 'powerhouse' of the cell, responsible for energy production.
- 😀 Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is involved in the synthesis of proteins and lipids.
- 😀 The Golgi apparatus is responsible for packaging and distributing proteins in the cell.
- 😀 Cells are responsible for all life functions, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
Q & A
What is the fundamental unit of all living things?
-The fundamental unit of all living things is the cell. Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life.
Why are viruses not considered living organisms?
-Viruses are not considered living organisms because they do not have a cellular structure. They lack the basic components of a cell, such as a cell membrane and other essential structures.
What are the two types of molecules mentioned in the script, and how do they differ?
-The two types of molecules mentioned are micro molecules and macro molecules. Micro molecules have a smaller molecular weight, while macro molecules have a larger molecular weight.
What are some examples of micro molecules?
-Examples of micro molecules include oxygen, water, and other small molecules that play critical roles in cellular processes.
What are macro molecules, and can you provide examples?
-Macro molecules are large molecules with a high molecular weight. Examples include carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, which are essential for the structure and function of cells.
What are the basic components of a eukaryotic cell as described in the script?
-A typical eukaryotic cell includes a cell membrane and various organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum. The membrane may or may not have a covering of additional structures.
Which organelles are double-membraned in eukaryotic cells?
-In eukaryotic cells, the mitochondria and the nucleus are examples of organelles with double membranes.
What is the difference between single and double membrane-bound organelles?
-Single membrane-bound organelles are surrounded by one lipid bilayer, while double membrane-bound organelles have two lipid bilayers. For example, mitochondria have a double membrane, while lysosomes have a single membrane.
What is the importance of understanding both the structure and function of cells?
-Understanding both the structure and function of cells is essential because it provides insight into how cellular components work together to maintain life processes. This knowledge helps explain how cells contribute to the overall functioning of organisms.
Why is it important to study the organization of information in cells?
-Studying the organization of information in cells helps us understand how cells process and transmit genetic and biochemical data, which is crucial for cellular function, growth, and division.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

SEL : STRUKTUR DASAR DAN FUNGSI ORGANEL - BIOLOGI 11 SMA

Struktur dan Fungsi Sel Tumbuhan (Animasi) | Bagian-bagian sel tumbuhan

Cell Theory - Biology - MCAT, AP Biology, GSCE, DAT, NEET, ACT

Overview of Cell Structure

What Are Cells? (The Cell Theory)
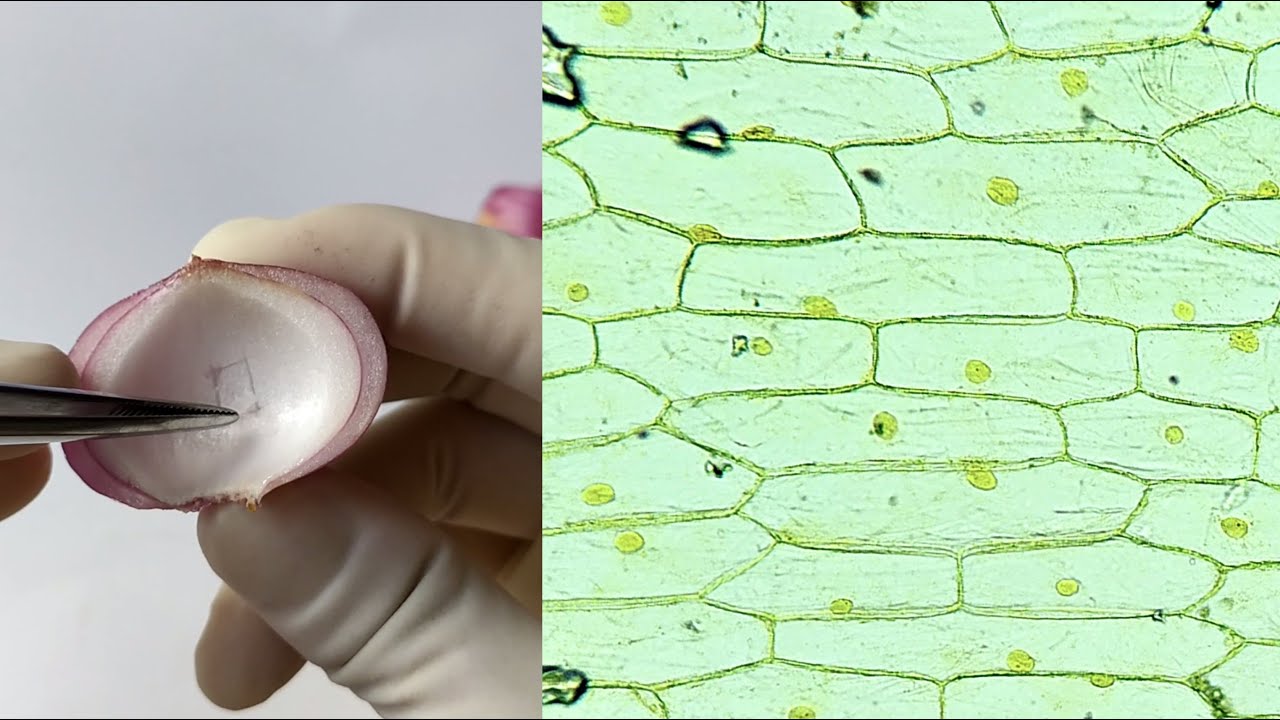
Onion Epidermal Cell Peel Slide Preparation Practical Experiment
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
