Materi SKB & UKOM NERS /sistem kardiovaskuler
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth explanation of four key cardiovascular system nursing diagnoses: decreased cardiac output, activity intolerance, ineffective peripheral perfusion, and hypervolemia. The presenter details the signs, symptoms, and key diagnostic criteria for each condition, along with example case studies to illustrate the application of these diagnoses in real-life clinical situations. Key points include recognizing the influence of activity on vital signs, identifying abnormal heart rhythms and capillary refill times, and understanding fluid imbalances. The video also emphasizes important keywords that help in identifying and addressing these diagnoses, offering valuable insights for nursing professionals preparing for SKB and Ukom exams.
Takeaways
- 😀 Decreased cardiac output occurs when the heart fails to pump enough blood to meet the body's metabolic needs, with key signs including changes in heart rhythm and contractility.
- 😀 For decreased cardiac output, ECG abnormalities and TV abnormalities that are not influenced by activity are critical indicators for diagnosis.
- 😀 Activity intolerance is characterized by insufficient energy to perform daily activities, with symptoms including fatigue and increased heart rate during activity.
- 😀 In cases of activity intolerance, key signs include abnormal vital signs during or after activity, such as increased blood pressure and heart rate.
- 😀 Ineffective peripheral perfusion refers to decreased blood circulation at the capillary level, with symptoms such as delayed capillary refill, decreased peripheral pulses, and cold extremities.
- 😀 Key signs of ineffective peripheral perfusion include capillary refill time longer than 3 seconds, peripheral pulses that are absent, and skin discoloration.
- 😀 Hypervolemia is an increase in fluid volume, with symptoms such as edema, weight gain, and increased jugular venous pressure (JVP).
- 😀 For hypervolemia, swelling (edema) and rapid weight gain are key signs, often accompanied by other symptoms like shortness of breath and peripheral edema.
- 😀 In diagnosing peripheral perfusion issues, a capillary refill time above 3 seconds and the inability to palpate peripheral pulses are key signs to look out for.
- 😀 It is important to recognize that the presence of abnormal vital signs (TV and ECG) influenced by activity helps in diagnosing activity intolerance, while those not influenced by activity suggest decreased cardiac output.
Q & A
What is the definition of 'decreased cardiac output' in nursing diagnosis?
-Decreased cardiac output refers to the inadequacy of the heart to pump blood to meet the body's metabolic needs.
What are the major signs for diagnosing decreased cardiac output?
-The major signs include changes in heart rhythm, preload, afterload, and contractility.
What are the minor signs of decreased cardiac output?
-The minor signs are changes in perilous, afterload, contractility, and behavior.
Which keywords help identify decreased cardiac output during assessments?
-The key indicators are abnormalities in the ECG and CTV, which are not affected by activity.
How do you identify activity intolerance as a nursing diagnosis?
-Activity intolerance is diagnosed when there is insufficient energy to carry out daily activities, evidenced by fatigue and changes in vital signs like increased heart rate and blood pressure during or after activity.
What major signs indicate activity intolerance?
-Major signs of activity intolerance include complaints of fatigue and an increase in heart rate above 20% of the resting condition during activity.
What is the definition of ineffective peripheral perfusion?
-Ineffective peripheral perfusion refers to decreased blood circulation at the capillary level, which can interfere with the body's metabolism.
What are the key signs for diagnosing ineffective peripheral perfusion?
-Key signs include capillary refill time above 3 seconds, peripheral pulses that cannot be felt, cold extremities, and cyanosis.
What major signs would indicate a diagnosis of hypervolemia?
-Major signs of hypervolemia include orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, peripheral edema, and weight gain in a short time.
How would you recognize hypervolemia based on a patient’s symptoms?
-Hypervolemia is suggested when a patient exhibits edema, weight gain in a short period, and changes like an increased jugular venous pressure (JVP).
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
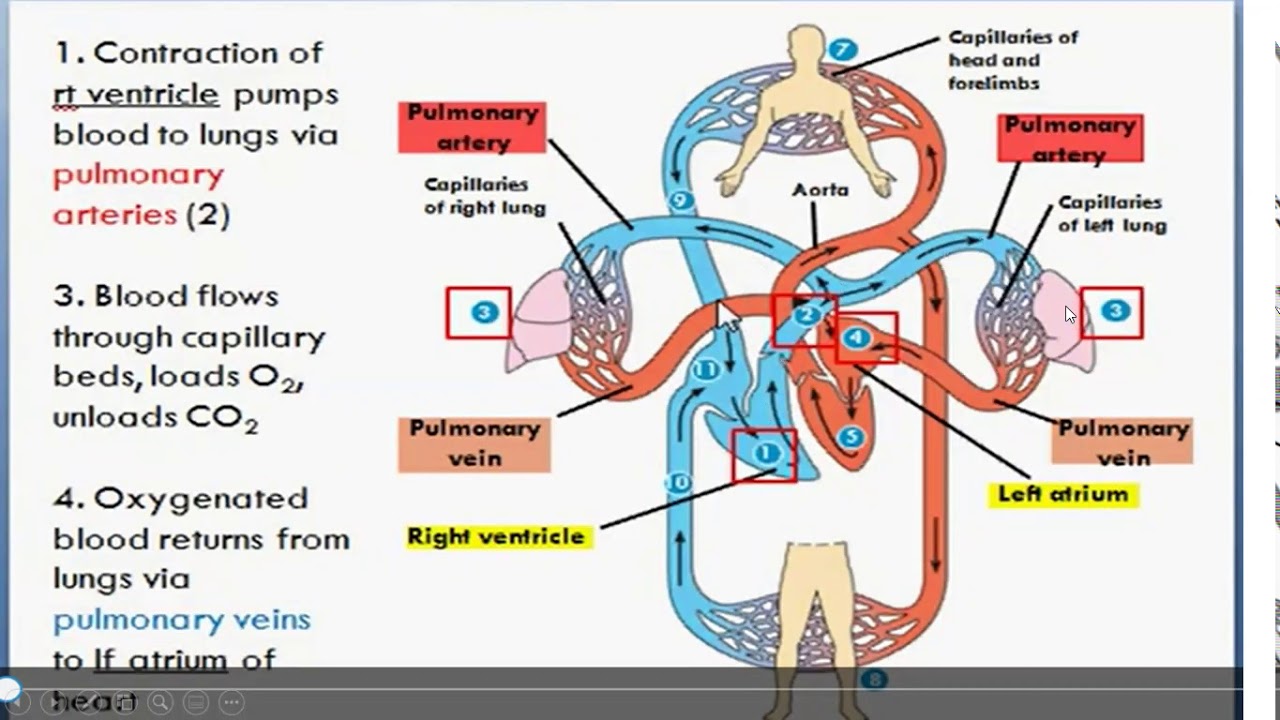
Sistem Kardiovaskuler

Respiratory and Cardiac Aging Changes: Gerontology - Fundamentals of Nursing | @LevelUpRN

✅APRENDIENDO a HACER UN PAE #5: Haciendo el PLAN DE CUIDADOS | PLACE | Enfermeria

Hypervolemia - Fluid Volume Excess (Overload) Nursing NCLEX | Water Intoxication

Henti Jantung: Konsep dan Tata Laksana (Part 1 / 3)

CICLO CARDÍACO : Coração como bomba - Fisiologia ( capítulo 9) │Guyton e Hall
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
