Genetika Mikroba
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into microbiology and genetics, focusing on microbial inheritance and the genetic mechanisms that enable microorganisms to adapt, multiply, and cause disease. It explains the differences between DNA and RNA, as well as the structure and function of genes, chromosomes, and plasmids in bacteria. The script also covers bacterial genetic transfer mechanisms such as transformation, transduction, and conjugation, along with antibiotic resistance and how microorganisms evolve resistance through mutations and genetic adaptations. Overall, it provides a comprehensive introduction to microbial genetics and its practical implications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Genetics of microorganisms involves understanding heredity, variation, and how microorganisms maintain viability, adapt, replicate, and cause diseases.
- 😀 DNA and RNA are the key components of genetic material, with DNA being double-stranded and RNA single-stranded, differing in nitrogenous bases and sugars.
- 😀 DNA contains genetic information for cellular functions, while RNA plays a crucial role in translating that information into proteins.
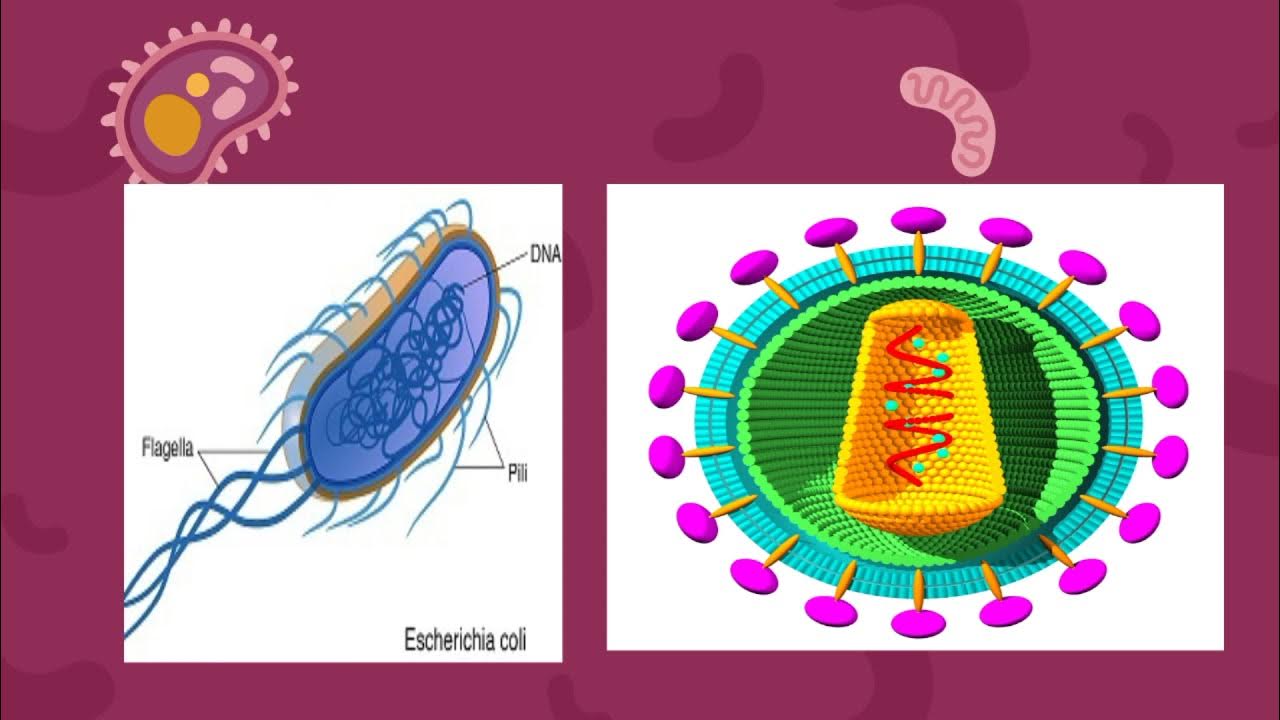
- 😀 The relationship between genes, chromosomes, and DNA is vital in understanding genetic inheritance, with DNA serving as the blueprint for gene expression.
- 😀 In prokaryotic cells like bacteria, genetic material can exist in plasmids, small DNA molecules separate from the chromosomal DNA, often involved in gene transfer.
- 😀 Plasmids can replicate independently of chromosomal DNA and carry genes that may confer advantages, like antibiotic resistance.
- 😀 Bacteria can undergo genetic transformation, transduction, and conjugation, which involve the exchange of genetic material between bacteria.
- 😀 Phenotype refers to visible traits, while genotype represents the underlying genetic makeup, both playing a role in bacterial morphology and behavior.
- 😀 Bacteria can undergo mutations that affect their ability to synthesize essential substances or their sensitivity to antibiotics, leading to changes in growth or resistance.
- 😀 Antibiotic resistance in bacteria can result from mechanisms like enzyme production that neutralize drugs, changes in cell permeability, or alterations in drug target sites.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the lecture in the transcript?
-The main focus of the lecture is on microbiology, specifically discussing the genetics of microorganisms, including topics such as DNA, RNA, heredity, and microbial resistance to antibiotics.
How is DNA different from RNA in terms of structure?
-DNA is double-stranded, while RNA is single-stranded. Additionally, DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, whereas RNA contains ribose. The nitrogenous bases in DNA include adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, while in RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil.
What is the relationship between genes, chromosomes, and DNA?
-Genes are sequences of DNA that provide the instructions for producing specific proteins. DNA is organized into chromosomes within the cell's nucleus. The chromosome contains multiple genes, which are responsible for determining hereditary traits.
What is the process of DNA replication?
-DNA replication is the process by which DNA is copied before cell division. The DNA double helix is unwound, and each strand serves as a template for the formation of a new complementary strand, resulting in two identical DNA molecules.
What are plasmids and what role do they play in bacteria?
-Plasmids are small, circular DNA molecules found in bacteria. They are extrachromosomal and can replicate independently of chromosomal DNA. Plasmids often carry genes that provide advantages to bacteria, such as antibiotic resistance.
How do bacteria evolve to become resistant to antibiotics?
-Bacteria can evolve antibiotic resistance through several mechanisms, including mutations in their genetic material, acquisition of resistance genes via plasmids, and alteration of their cell membrane or ribosomes, making them less susceptible to the drugs.
What is the role of transcription in gene expression?
-Transcription is the process in which a segment of DNA is copied into RNA. This RNA then serves as a template for protein synthesis. Transcription is the first step in gene expression and leads to the creation of messenger RNA (mRNA).
What are the five main types of phenotypic changes in bacteria due to mutations?
-The five main types of phenotypic changes due to mutations in bacteria are: (1) loss or gain of the ability to produce certain products, (2) changes in the ability to metabolize nutrients, (3) antibiotic resistance, (4) changes in sensitivity to environmental factors, and (5) changes in cell surface components.
What is transformation in bacterial genetics?
-Transformation is the process by which bacteria take up free DNA from their environment and integrate it into their genome. This can lead to genetic changes, such as the acquisition of antibiotic resistance or new metabolic abilities.
What are the different mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in microorganisms?
-There are several mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in microorganisms, including the production of enzymes that degrade antibiotics, changes in cell permeability that prevent antibiotics from entering, mutations in drug targets, and the ability to pump out antibiotics using efflux pumps.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)