Deformasi Batuan 1
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the concept of rock deformation, a process where external forces cause changes in the shape or structure of rocks. It explains the types of stress—uniform and differential—leading to deformation, such as stretching, compression, or shearing. Different deformation behaviors, including brittle and ductile, are explored, highlighting how temperature, pressure, and composition influence the outcomes. The video also covers methods to measure deformation, such as strike and dip measurements, and explains geological structures like folds and faults that result from these stresses. The importance of these processes in understanding geological formations is emphasized throughout.
Takeaways
- 😀 Deformation is the process that changes the shape or geometry of rocks due to external forces acting on them.
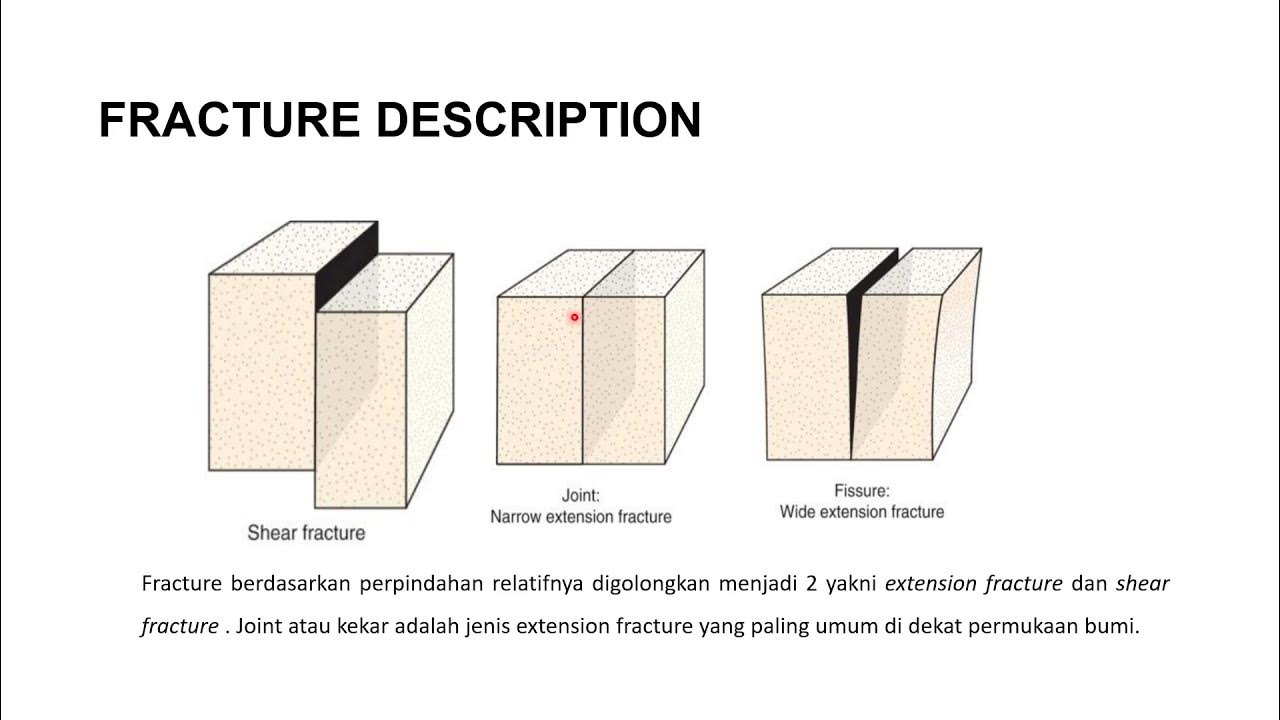
- 😀 Deformation can result in geological structures such as folds, faults, and fractures in rocks.
- 😀 Stress is the force acting on rocks that leads to deformation and can cause changes in volume or size.
- 😀 There are two types of stress: uniform stress (equal in all directions) and differential stress (uneven in different directions).
- 😀 Stress causes deformation, and the magnitude of deformation depends on the amount of stress applied to the material.
- 😀 There are three types of stress: tensional stress (pulling apart), compressional stress (pushing together), and shear stress (sliding past).
- 😀 Different types of stress cause different types of deformation such as stretching, folding, or slipping.
- 😀 Deformation can be elastic (temporary) or permanent, depending on whether the stress exceeds the elastic limit of the rock.
- 😀 Rocks can either be brittle (fracture easily) or ductile (bend without breaking), which is influenced by temperature, pressure, and the rock's composition.
- 😀 Temperature, pressure, deformation speed, and rock composition significantly affect whether a material undergoes brittle or ductile deformation.
- 😀 Rocks subjected to low pressure and temperature tend to fracture, whereas rocks at greater depths with high pressure and temperature tend to bend without breaking.
Q & A
What is deformation in geology?
-Deformation in geology refers to the process that causes a change in the shape or geometry of rocks due to external forces. This can result in features like folding, faulting, or fracturing of rocks.
What are the main types of stress that cause deformation in rocks?
-The main types of stress that cause deformation are uniform stress (which acts equally from all directions) and differential stress (where stress is not uniform and varies in direction).
How does compressional stress affect rocks?
-Compressional stress causes rocks to be pushed together, resulting in shortening, thickening, and potentially leading to folding or faulting.
What is the difference between brittle deformation and ductile deformation?
-Brittle deformation occurs when rocks fracture or break under stress without significant bending, typically at low temperatures or pressures. Ductile deformation, on the other hand, occurs when rocks bend or stretch without breaking, generally at high temperatures or pressures.
What are the factors that influence whether a rock undergoes brittle or ductile deformation?
-The key factors include temperature (higher temperatures promote ductile deformation), pressure (higher pressure can lead to ductile deformation), the speed of deformation (faster deformation tends to cause brittle behavior), and the composition of the rock (minerals like feldspar are more brittle, while minerals like mica are more ductile).
What is the relationship between stress and strain in rock deformation?
-Stress refers to the force applied to a rock, while strain is the resulting deformation. As stress increases, strain also increases, leading to more significant deformations like folding, faulting, or fracturing.
How do temperature and pressure affect rock deformation at different depths in the Earth?
-At greater depths, temperature and pressure increase, which generally causes rocks to deform in a ductile manner, bending without breaking. Near the Earth's surface, where temperatures and pressures are lower, rocks are more likely to fracture or undergo brittle deformation.
What is the process of folding in rock deformation?
-Folding occurs when compressional stress causes rocks to bend, forming ridges and valleys, known as anticlines and synclines. This process is commonly associated with tectonic plate movements.
What is the significance of the 'elastic limit' in rock deformation?
-The elastic limit is the point at which a rock can no longer return to its original shape after stress is removed. Beyond this limit, rocks undergo permanent deformation, transitioning from elastic to ductile behavior.
How is the deformation of rocks measured in the field?
-Deformation can be measured by determining the strike and dip of rock layers, which indicate the orientation of rocks. These measurements help to understand the extent and type of deformation, such as folding or faulting.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)