Primary & Secondary Storage - GCSE Computer Science
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a detailed overview of primary and secondary storage types in computing. It explains the differences between RAM, ROM, and virtual memory, highlighting their roles in data and program storage. The video also covers secondary storage options, including optical, magnetic, and solid-state drives, and compares their characteristics such as capacity, speed, portability, durability, reliability, and cost. Viewers are encouraged to consider these factors when choosing the right storage type. The content is specifically aimed at the OCR GCSE Computer Science course, but is applicable to most exam boards.
Takeaways
- 😀 Primary storage is essential for a computer as it stores data and programs currently in use, including RAM, ROM, and virtual memory.
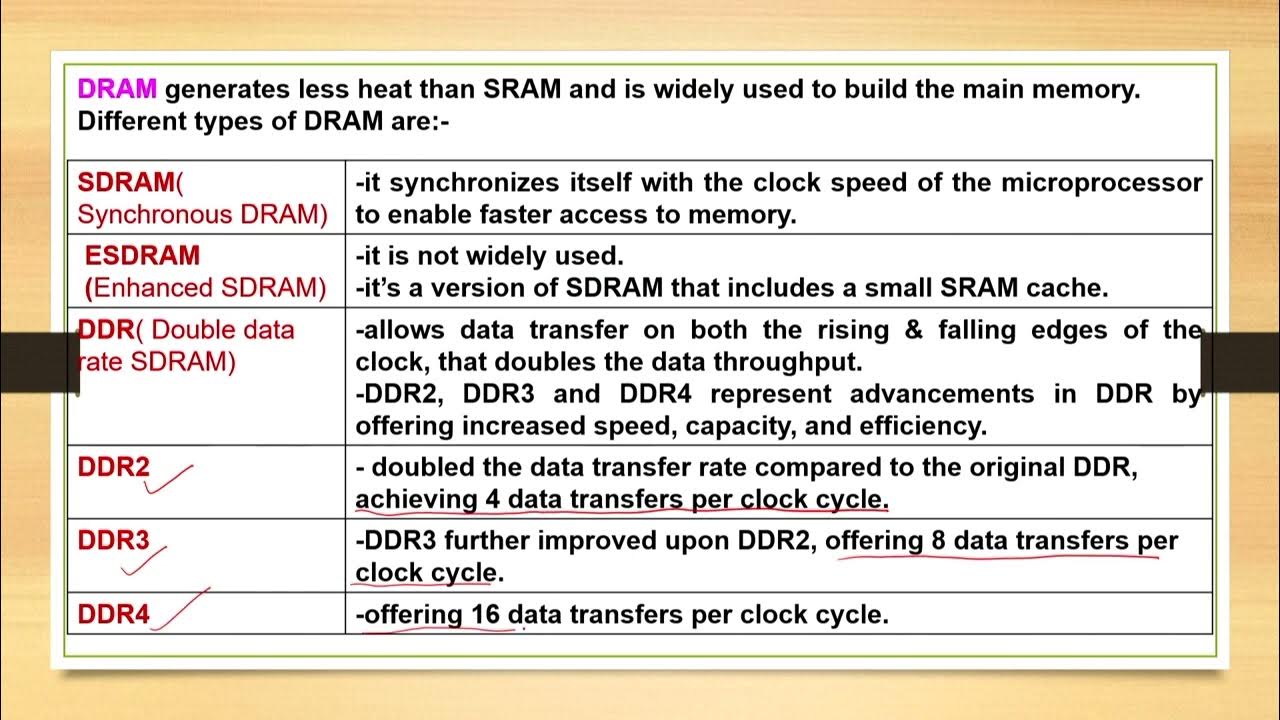
- 😀 RAM (Random Access Memory) is volatile and stores data temporarily, making it faster for running applications but losing all data when the power is off.
- 😀 ROM (Read-Only Memory) is non-volatile and retains data even when the computer is powered off, typically storing essential boot-up instructions.
- 😀 Flash memory, a type of ROM, is non-volatile and commonly used in portable devices such as SD cards and USB sticks, with limited write cycles.
- 😀 Virtual memory supplements RAM by using hard disk space as temporary storage, but it can slow down computer performance when overused.
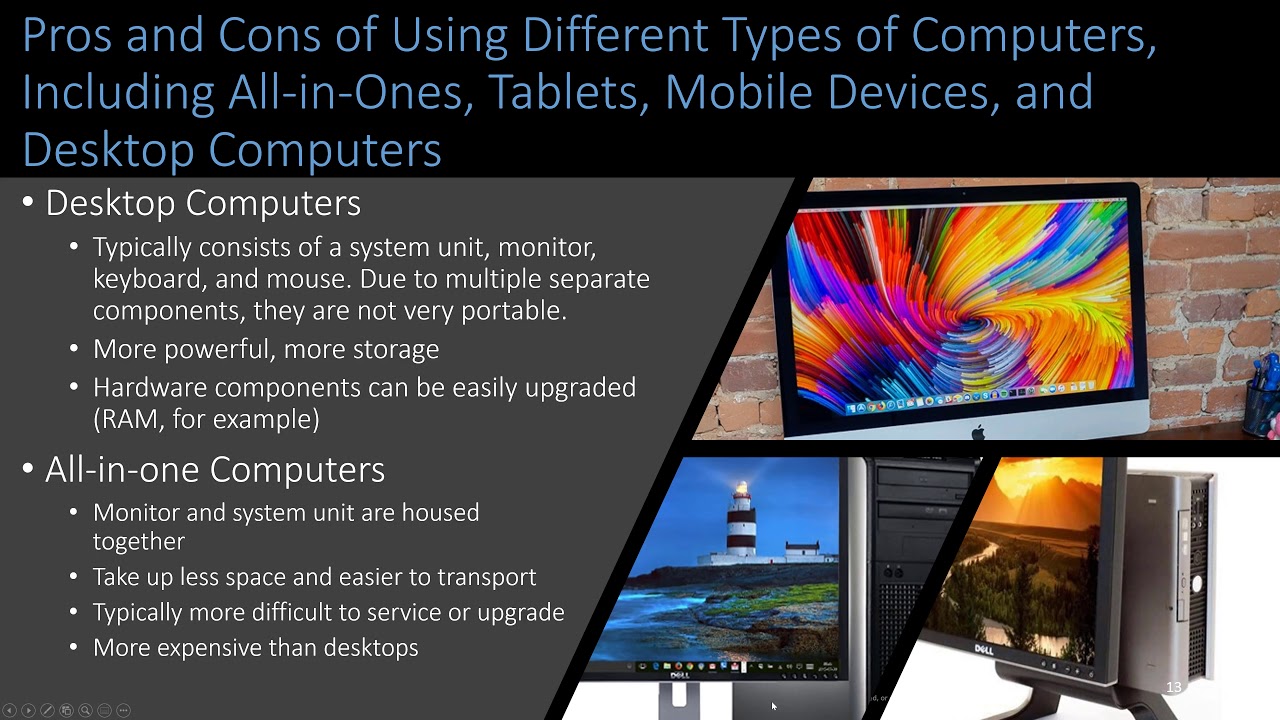
- 😀 Secondary storage provides long-term, non-volatile storage for data and programs, including optical, magnetic, and solid-state types.
- 😀 Optical storage includes CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs, which are relatively cheap but have varying capacities suited for different uses (e.g., music, movies, games).
- 😀 Magnetic storage, like HDDs (Hard Disk Drives), is slower but offers large capacity at a relatively low cost, making it ideal for mass data storage.
- 😀 Solid-state drives (SSDs) are more expensive than HDDs but offer faster read and write speeds, lower power consumption, and are more durable since they have no moving parts.
- 😀 Six factors to consider when choosing secondary storage include capacity, speed, portability, durability, reliability, and cost, which can be remembered by the phrase 'crazy spiders play dodgeball really cheerfully'.
- 😀 Understanding primary storage (RAM, ROM, virtual memory) and secondary storage (optical, magnetic, solid-state) is crucial for making informed decisions about computer systems.
Q & A
What are the three main types of primary storage?
-The three main types of primary storage are RAM (Random Access Memory), ROM (Read-Only Memory), and virtual memory.
What is the main purpose of RAM in a computer?
-RAM is used to store data, applications, and the operating system that are currently in use. It is volatile, meaning it loses its data when the power is turned off.
What is ROM and how does it differ from RAM?
-ROM stands for Read-Only Memory and is non-volatile, meaning it retains its contents even when the power is off. Unlike RAM, which is writable, ROM cannot be overwritten and is used to store essential instructions like those for booting the computer.
What is the role of virtual memory in a computer system?
-Virtual memory acts as supplemental storage on the hard disk when the computer's RAM is full. It temporarily stores data and instructions from RAM, but using virtual memory can slow down the computer's performance.
What are the three types of secondary storage mentioned?
-The three types of secondary storage are optical storage, magnetic storage, and solid-state storage.
What is optical storage and what are some examples?
-Optical storage uses light to read and write data on discs. Examples include CDs (Compact Discs), DVDs (Digital Versatile Discs), and Blu-ray discs, which vary in capacity and are used for different purposes such as storing music, movies, and games.
How does magnetic storage (HDD) work?
-Magnetic storage, such as hard disk drives (HDD), uses magnetized rigid plates that rotate and a read/write head that moves above the surface. This setup allows for large capacity storage but results in slower access speeds.
What are the advantages of solid-state drives (SSDs) compared to magnetic storage?
-SSDs have no moving parts, making them faster, more reliable, and less prone to damage from physical impacts. They also consume less power, generate less heat, and are lightweight, but they are generally more expensive than magnetic drives.
What are the six main factors to consider when choosing secondary storage?
-The six main factors are capacity, speed, portability, durability, reliability, and cost. A mnemonic to remember these is 'Crazy spiders play dodgeball really cheerfully.'
What is the significance of flash memory in the context of ROM?
-Flash memory is a type of ROM that is non-volatile and can be rewritten, which makes it ideal for use in portable devices like SD cards and USB sticks. It is a solid-state memory with a limited number of write cycles.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)