Introduction to Solubility equilibria
Summary
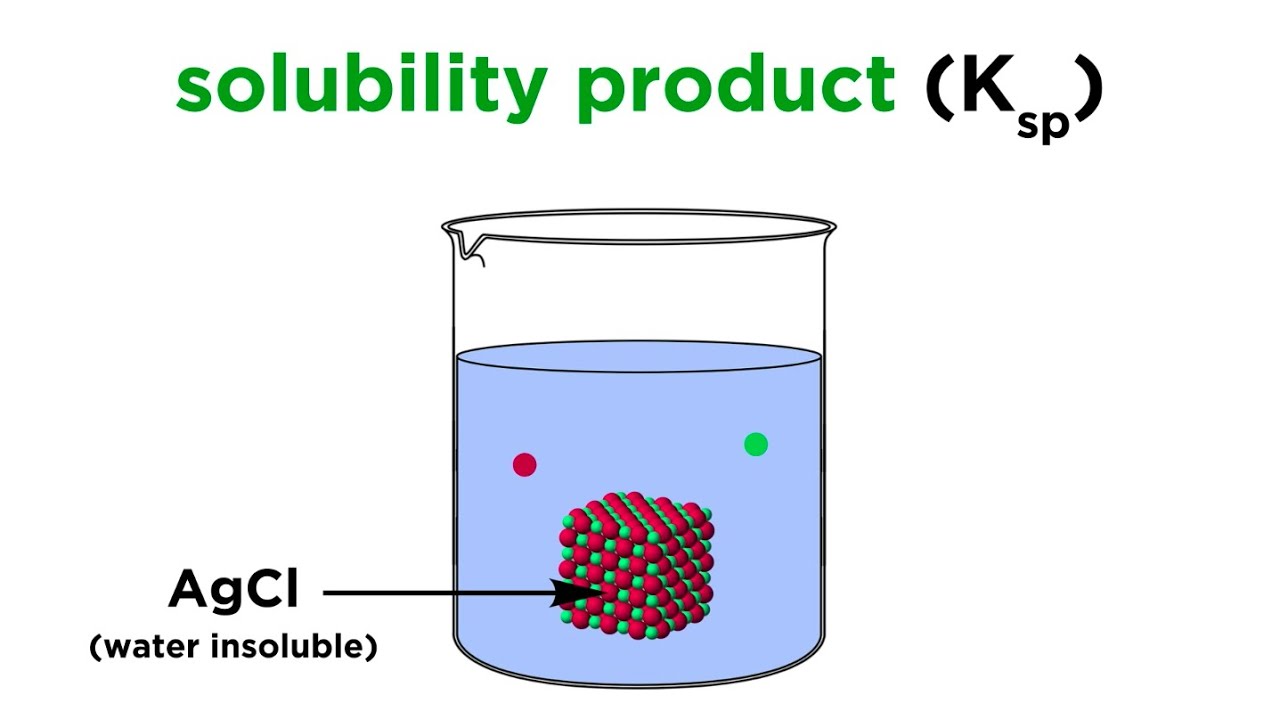
TLDRIn this video, the presenter introduces the essential concepts of solubility and solubility equilibria, emphasizing that everything dissolves to some extent, and there is no such thing as 'insoluble.' The solubility of a substance is the maximum concentration of solute that will dissolve in water at standard conditions. The solubility product (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that relates to the solubility of salts. The video explains how factors like temperature and ions can influence solubility, and stresses the importance of understanding equilibrium expressions, charges of ions, and using data tables for solubility calculations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Solubility refers to the maximum amount of a solute that can dissolve in one liter of water at standard conditions (25°C, 1 atm).
- 😀 There is no such thing as 'insoluble'; everything dissolves to some extent, and some substances are 'sparingly soluble'.
- 😀 Solubility product (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that relates to the solubility of salts in water.
- 😀 The concept of solubility is linked to equilibrium reactions between undissolved solids and dissolved ions.
- 😀 Solubility is different from solubility product (Ksp), where solubility can change with conditions, but Ksp is constant unless temperature changes.
- 😀 In solubility product (Ksp) expressions, only the concentrations of dissolved ions are considered, not the solid salt itself.
- 😀 Ksp values can be used to predict how much of a solute will dissolve under specific conditions.
- 😀 The dissolving of salts can be represented by equilibrium reactions, where the concentration of dissolved ions determines the Ksp value.
- 😀 Temperature, pH, and the presence of other ions can affect the solubility of a substance, but Ksp itself only changes with temperature.
- 😀 Understanding ion charges is crucial for writing correct Ksp expressions (e.g., group 1 elements are +1, group 2 are +2).
Q & A
What is the main focus of this video?
-The main focus of the video is to introduce the basic concepts of solubility and solubility equilibria, explaining their significance in chemistry.
What should students do with the solubility rules they have learned previously?
-Students are advised to remove the traditional solubility rules from their minds, as they are not relevant at this level of study. Instead, they will learn about solubility in terms of how much of a substance dissolves at equilibrium.
What is solubility defined as in this context?
-Solubility is defined as the maximum concentration of a solute (a solid) that will dissolve in one liter of water at standard temperature (25°C) and pressure (1 atmosphere).
What is a saturated solution?
-A saturated solution is one that contains the maximum amount of dissolved solute at a given temperature and pressure, meaning no more solute can dissolve.
What is the solubility product (Ks)?
-The solubility product (Ks) is an equilibrium constant that relates to the solubility of a salt, based on the concentrations of its dissolved ions in a saturated solution.
What is the key concept about solubility and solubility rules that is emphasized in the video?
-The key concept is that there is no such thing as 'insoluble'—everything dissolves to some extent, and salts are considered sparingly soluble if they dissolve in very small amounts.
What does the term 'sparingly soluble' mean?
-'Sparingly soluble' refers to substances that dissolve in only small amounts in water, like lead hydroxide, rather than being completely soluble or insoluble.
How does the dissolution of salts relate to equilibrium?
-The dissolution of salts is an equilibrium process between the undissolved solid and the dissolved ions. At equilibrium, a certain amount of the salt dissolves, and the concentrations of the ions are constant.
Why do we not include solids or pure liquids in the equilibrium constant expression?
-Solids and pure liquids are not included in equilibrium constant expressions because their concentrations do not change during the reaction and are therefore considered constant.
How can temperature affect solubility and the solubility product (Ks)?
-Temperature can affect the solubility of a substance, with higher temperatures generally allowing more solute to dissolve. However, the solubility product (Ks) is a constant unless the temperature changes.
What must students understand about the charges of ions in solubility equilibria?
-Students must understand the charges of basic ions, such as the +1 charge of group 1 ions and the +2 charge of group 2 ions. This knowledge helps in interpreting the formulas of salts and in writing correct equilibrium expressions.
How does the video suggest that solubility can be influenced by other factors?
-The video suggests that solubility can be influenced by factors such as temperature, the presence of other ions, and pH changes, but emphasizes that the solubility product (Ks) remains constant unless the temperature changes.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)