Cara Mudah‼️Menentukan Bilangan Kuantum (Utama, Azimut, Magnetik, Spin)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host explains how to determine quantum numbers, which describe the position of electrons in an atom. The process includes four main quantum numbers: principal (n), azimuthal (l), magnetic (m), and spin (s). The host walks through the concept of electron configuration, demonstrating how to calculate the values for each quantum number using examples like sulfur and oxygen. The video also covers the relationship between these quantum numbers and atomic orbitals, offering clear explanations and visuals. It aims to help viewers understand how quantum numbers relate to electron placement and energy levels in atoms.
Takeaways
- 😀 Quantum numbers describe the position of electrons in an atom, including four types: principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin.
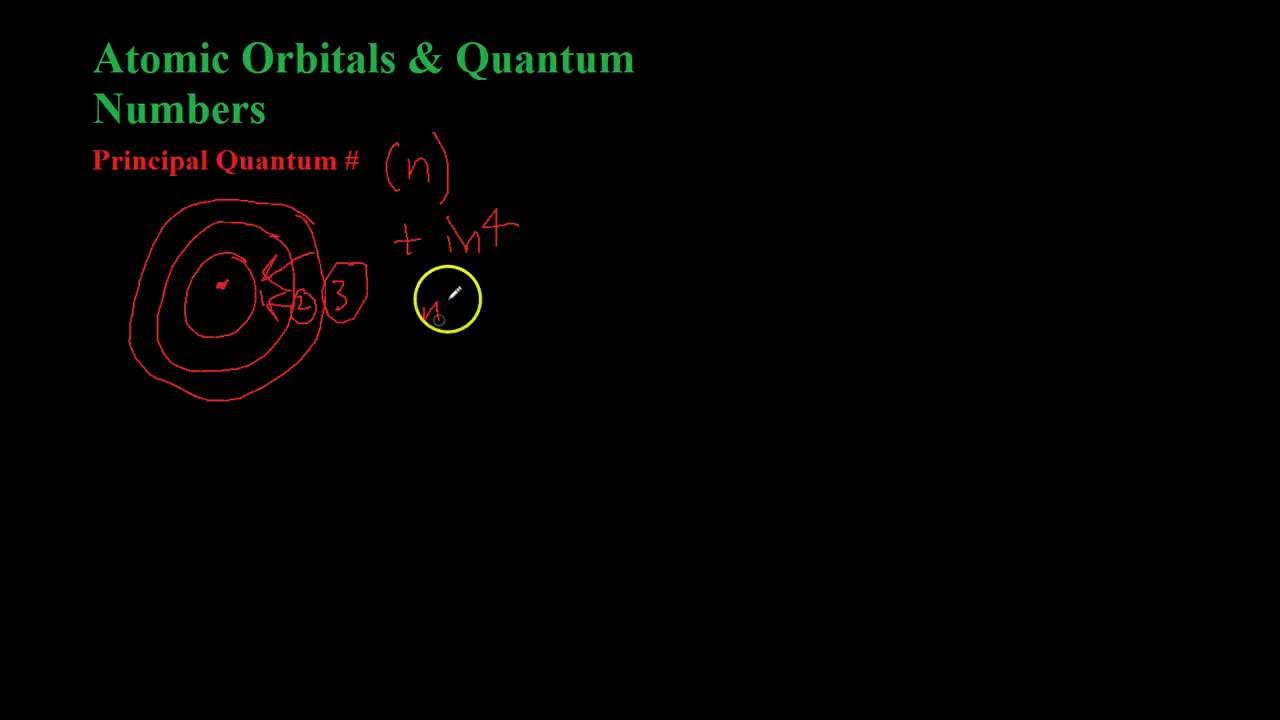
- 😀 The principal quantum number (n) indicates the electron's shell or energy level and can take values 1, 2, 3, and so on.
- 😀 The azimuthal quantum number (l) defines the sublevel or orbital type (s, p, d, f) and can take values from 0 to n-1.
- 😀 The magnetic quantum number (m) determines the orientation of the orbital in space, with values ranging from -l to +l.
- 😀 The spin quantum number (s) describes the spin of the electron, which can be +1/2 or -1/2.
- 😀 In the quantum model, electrons fill orbitals starting from the lowest energy level according to the Aufbau principle.
- 😀 For sulfur (atomic number 16), the principal quantum number (n) is 3, and the azimuthal quantum number (l) is 1, indicating it is in the p orbital.
- 😀 Oxygen (atomic number 8) has an electron configuration of 1s² 2s² 2p⁴, with the electron in the 2p orbital.
- 😀 The magnetic quantum number is represented by the orientation of the electron within the orbital, with orbital diagrams used to visualize electron positions.
- 😀 When determining quantum numbers, the spin of the last electron is shown by an upward or downward arrow in an orbital diagram.
- 😀 The video provides clear examples for sulfur and oxygen to demonstrate how quantum numbers are determined and used in atomic configurations.
Q & A
What are the four quantum numbers described in the script?
-The four quantum numbers are: the principal quantum number (n), the azimuthal quantum number (l), the magnetic quantum number (m), and the spin quantum number (s).
How is the principal quantum number (n) defined and what does it represent?
-The principal quantum number (n) defines the energy level or shell where an electron is located. Its values are positive integers (1, 2, 3, etc.), corresponding to different energy levels in an atom.
What does the azimuthal quantum number (l) represent, and how is it determined?
-The azimuthal quantum number (l) represents the sublevel or orbital shape of an electron. Its value depends on the principal quantum number (n) and ranges from 0 to (n-1). For example, if n = 2, l can be 0 or 1.
How does the magnetic quantum number (m) relate to the orbital of an electron?
-The magnetic quantum number (m) describes the orientation of an electron's orbital. The value of m ranges from -l to +l, including 0. For example, if l = 1 (p-orbital), m can be -1, 0, or +1.
What is the significance of the spin quantum number (s), and what values can it have?
-The spin quantum number (s) indicates the direction of the electron's spin. It can have two possible values: +1/2 (spin-up) or -1/2 (spin-down).
Can you explain how to determine the quantum numbers for the sulfur atom (atomic number 16)?
-For sulfur (atomic number 16), its electron configuration is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁴. The principal quantum number (n) for the last electron is 3, the azimuthal quantum number (l) is 1 (since it is in a p-orbital), the magnetic quantum number (m) is -1, and the spin quantum number (s) is -1/2 (if the electron spins downward).
What is the role of orbital diagrams in determining quantum numbers?
-Orbital diagrams visually represent how electrons are distributed in orbitals. The arrows (representing electron spins) and the placement of electrons in the diagram help determine the quantum numbers of each electron.
How is the quantum number azimuthal (l) related to the type of orbital (s, p, d, f)?
-The azimuthal quantum number (l) determines the type of orbital. For l = 0, the orbital is s; for l = 1, the orbital is p; for l = 2, the orbital is d; and for l = 3, the orbital is f.
What is the maximum number of electrons that can be in the M-shell (third energy level)?
-The M-shell can hold a maximum of 18 electrons. It consists of the s, p, and d orbitals, with the s orbital holding 2 electrons, the p orbital holding 6 electrons, and the d orbital holding 10 electrons.
In the context of the quantum numbers, what does the equation 'n - 1' help determine?
-The equation 'n - 1' is used to determine the value of the azimuthal quantum number (l) by subtracting 1 from the principal quantum number (n). For example, if n = 3, then l can be 0, 1, or 2, corresponding to s, p, or d orbitals.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)