Everything Routers do - Part 1 - Networking Fundamentals - Lesson 5
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson on networking fundamentals, we explore the essential role of routers in facilitating communication between different networks. The video covers key concepts such as IP addresses, MAC addresses, and the difference between routers and hosts. It explains the process of routing, including how routers maintain routing tables and populate them using directly connected routes, static routes, and dynamic routes. The lesson provides a clear overview of how data moves across the internet, offering crucial knowledge for anyone interested in understanding network communication.
Takeaways
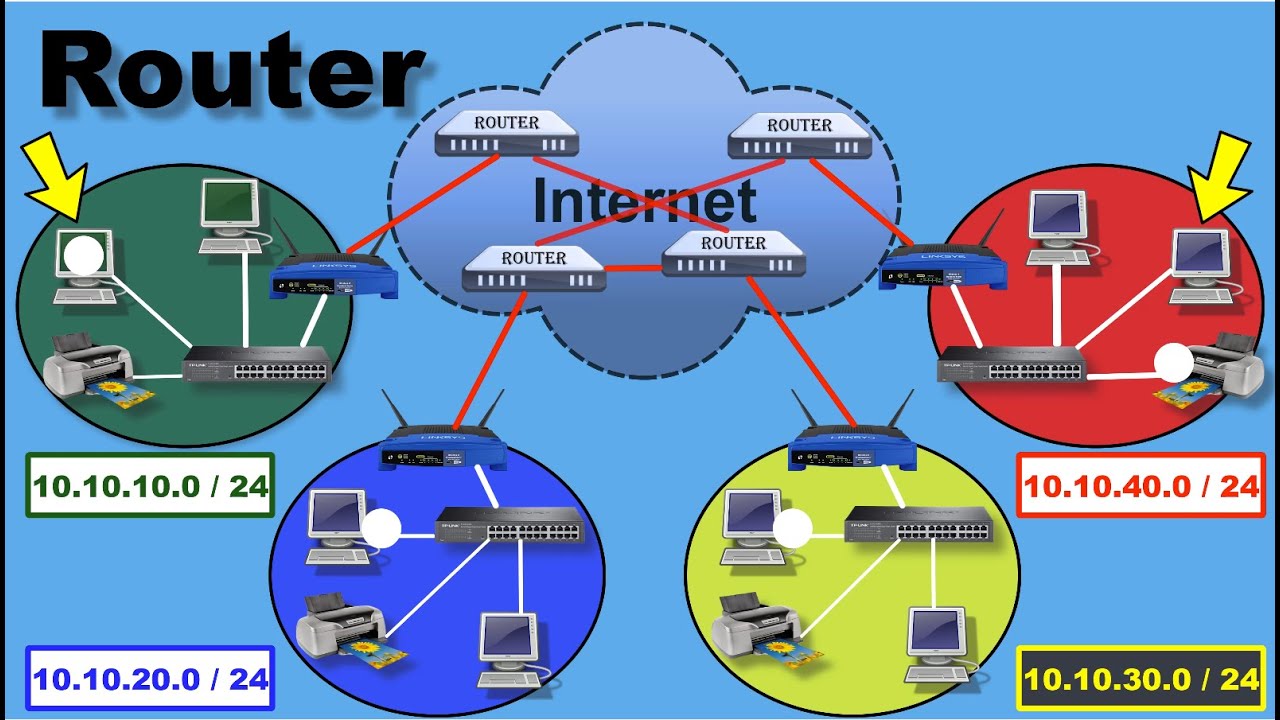
- 😀 Routers are devices that forward packets between different networks, allowing communication across the internet.
- 😀 A host is a device that does not forward packets not addressed to itself, while a router forwards packets to other networks.
- 😀 Routers, like hosts, have both an IP address and a MAC address to facilitate communication with other devices in a network.
- 😀 Routing tables in routers store information about how to reach various networks and determine where to send data packets.
- 😀 A directly connected route exists in a router's routing table for each network that the router is physically connected to.
- 😀 Static routes are manually configured by administrators, allowing routers to know how to reach specific networks.
- 😀 Dynamic routing allows routers to automatically share routing information and update their routing tables through protocols like RIP, OSPF, and BGP.
- 😀 Routing protocols help routers communicate and learn about networks they are not directly connected to, ensuring efficient packet forwarding.
- 😀 If a router does not know how to reach a destination network, it will drop the packet unless there is a static or dynamic route available.
- 😀 The main functions of routers include forwarding packets and maintaining routing tables that are populated via direct connections, static routes, and dynamic routing protocols.
- 😀 Understanding routers and routing tables is crucial for ensuring data flows smoothly between networks in a complex internet infrastructure.
Q & A
What is the main focus of this lesson?
-The main focus of this lesson is to explain how routers work and how they facilitate communication between networks.
What are the primary differences between a router and a host?
-A router forwards packets not addressed to itself, while a host simply receives packets addressed to it. Routers have an ip address and a mac address, but they perform the function of routing data between networks, unlike hosts which are end devices in a network.
What is the purpose of a routing table in a router?
-A routing table in a router is a map of networks that the router knows about. It contains routes, which are instructions on how to reach specific networks, helping the router forward packets to their correct destinations.
How are routes added to a router’s routing table?
-Routes can be added to a router's routing table in three ways: through directly connected routes, static routes, or dynamic routes. Directly connected routes are added when a router is directly connected to a network, static routes are manually configured by an administrator, and dynamic routes are learned automatically through routing protocols.
What is a directly connected route?
-A directly connected route exists for every network that a router is physically connected to. It indicates which interface the router uses to reach specific networks.
What happens when a router receives a packet with a destination it doesn't know how to reach?
-When a router receives a packet with a destination IP address it doesn't know how to reach, the router will drop the packet.
What is a static route, and how is it used in routing?
-A static route is a route manually configured by an administrator to provide the router with specific instructions on how to reach a particular network. For example, a static route can tell a router to send packets destined for a network to another router.
What is a dynamic route, and how does it differ from a static route?
-A dynamic route is automatically learned by routers through communication with each other using dynamic routing protocols. Unlike static routes, which are manually configured, dynamic routes are updated dynamically as routers exchange routing information.
What are dynamic routing protocols, and why are they important?
-Dynamic routing protocols are methods that allow routers to exchange routing information and automatically update their routing tables. These protocols help routers learn about networks they are not directly connected to and are essential for ensuring efficient and adaptable network routing.
Can a router forward a packet that is not destined for itself?
-Yes, a router can forward a packet that is not destined for itself. The router examines the destination IP address of the packet and uses its routing table to determine how to forward the packet to the appropriate destination.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Jaringan Komputer dan Internet (JKI) | Materi Informatika Fase D Kelas 8 BAB 5 | Kurikulum Merdeka

XI_Informatika_Mengenal Jaringan Komputer
How router works | what is router? full Explanation | Computer Networking

Everything Switches do - Part 1 - Networking Fundamentals - Lesson 4

Teoría Redes de Ordenadores - Bachillerato

Introduction To Networking - Different Types Of Networks | Networking Fundamentals Part 2 (revised)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
