O Sistema Excretor Humano
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the human excretory system is explained, focusing on how the body filters blood and eliminates excess or toxic substances, such as urea, salts, and carbon dioxide. The kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra work together to form and excrete urine, while sweat and respiration also play roles in eliminating waste. The video discusses the three stages of urine formation—filtration, reabsorption, and secretion—and highlights the importance of the excretory system in maintaining the body's internal balance. Viewers are encouraged to engage with the content, like, share, and subscribe for more educational videos on biology.
Takeaways
- 😀 The excretory system is responsible for filtering the blood and eliminating excess substances that can be toxic to the body.
- 😀 Excretion helps maintain homeostasis by controlling the balance of water and minerals in the body.
- 😀 Excretory products, such as ammonia, urea, and carbon dioxide, are produced during metabolic processes like cellular respiration.
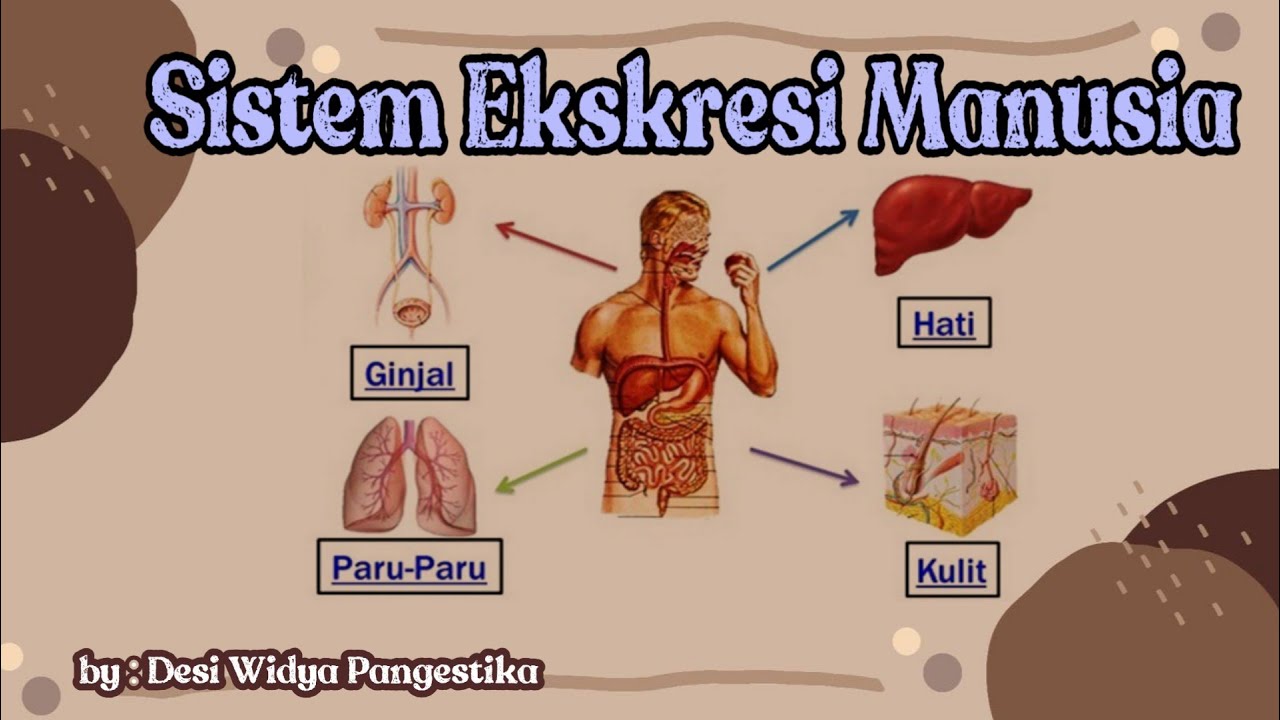
- 😀 Excreta are primarily eliminated through urine, respiration, and sweat, but feces are not considered excretory products.
- 😀 Urine is made up of 95% water, along with urea, uric acid, salts, and other substances.
- 😀 The formation of urine involves three stages: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
- 😀 The kidneys are the main organs of the excretory system, and they filter blood to produce urine.
- 😀 The kidneys contain nephrons, which are the functional units responsible for blood filtration and urine production.
- 😀 The ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder, where it is stored until it is eliminated through the urethra.
- 😀 The sweat glands help eliminate toxins from the body, including sodium chloride, urea, uric acid, and water, while also regulating body temperature.
- 😀 The respiratory system also expels excretory products, such as carbon dioxide, which is a byproduct of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the human excretory system?
-The primary function of the human excretory system is to filter the blood and eliminate excess and potentially toxic substances from the body, which are typically by-products of metabolic processes.
What is the difference between excreta and feces?
-Excreta refers to substances eliminated from the body after undergoing metabolic processes, such as through urine, sweat, and respiration. Feces, on the other hand, are not considered excreta as they do not pass through cellular metabolic processes.
Which substances are typically eliminated through the excretory system?
-Substances eliminated through the excretory system include nitrogenous compounds like ammonia, urea, uric acid, carbon dioxide, and excess salts.
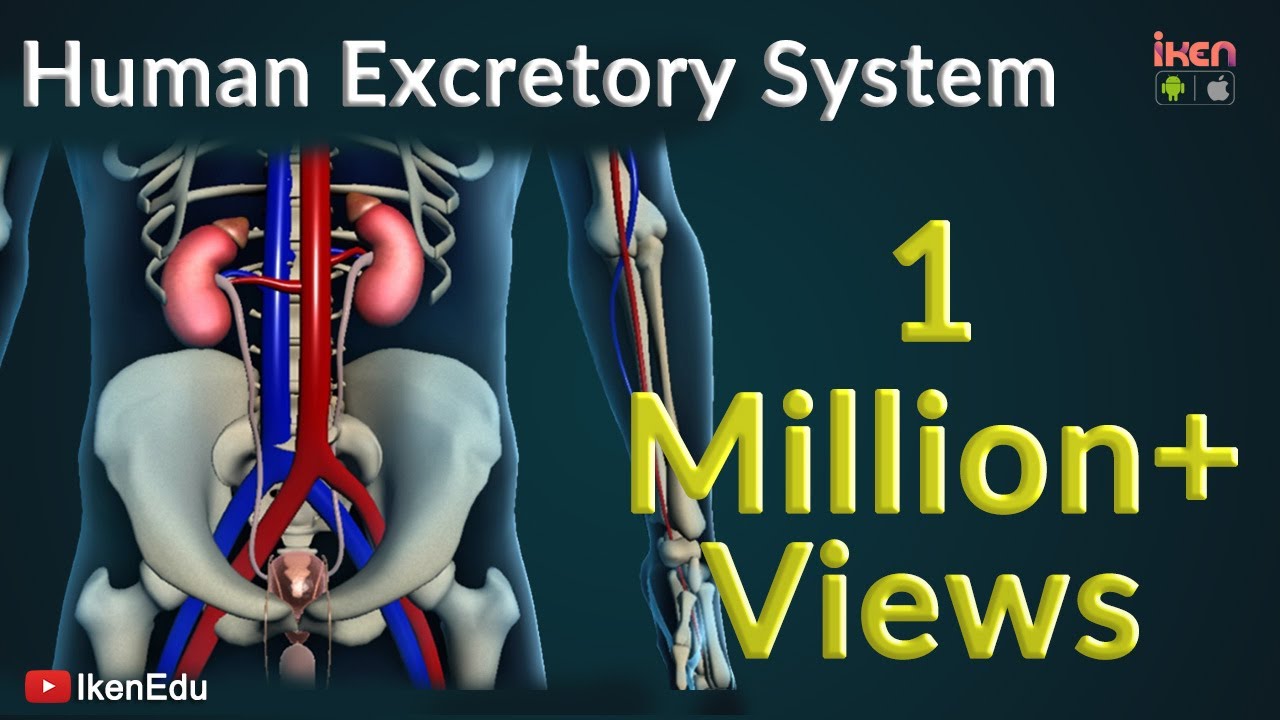
What is the main organ involved in the excretion of urine?
-The kidneys are the primary organs involved in the production and excretion of urine.
How is urine formed in the kidneys?
-Urine is formed in three stages: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Blood is filtered in the glomerulus, reabsorbing important substances like water, glucose, and salts, and secreting waste products into the urine.
What is the role of the ureters in the excretory system?
-The ureters are tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
How much urine is typically excreted by the human body each day?
-Despite filtering around 180 liters of fluid daily, only about 1 to 2 liters of urine are excreted from the body each day.
What is the function of the bladder in the excretory system?
-The bladder stores urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body through the urethra.
How does sweating contribute to excretion in the human body?
-Sweating helps regulate body temperature and also excretes substances like salt, urea, uric acid, and water, assisting in the elimination of waste.
What is the role of respiration in the excretory process?
-Respiration expels carbon dioxide, a by-product of cellular metabolism, through the lungs, contributing to the body's excretion process.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)