Sistem Saraf: Anatomi Neuron | Ilmu Biomedik Dasar | Brainy Panda
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the structure and function of the human nervous system, focusing on neurons and neuroglia. It details the anatomy of a neuron, highlighting its three main parts: the cell body, axon, and dendrites. The video further explores the role of organelles within the neuron, including the Nissl bodies responsible for protein synthesis, and explains how lipofuscin, a pigment that increases with age, marks neuron aging. The function of axons, dendrites, and myelin sheaths in transmitting electrical signals is also discussed, emphasizing how these structures support the efficient functioning of the nervous system.
Takeaways
- 😀 The human nervous system consists of two main types of cells: neurons and neuroglia.
- 😀 Neuroglia support neurons by providing nutrients, oxygen, and other necessary functions.
- 😀 Neurons transmit signals or action potentials throughout the body.
- 😀 Neurons have three main parts: the cell body, axon, and dendrites.
- 😀 The cell body (also known as the perikaryon) contains the nucleus and organelles like mitochondria, lysosomes, and Golgi bodies.
- 😀 The Nissl body, unique to neurons, helps produce proteins essential for neuron growth and regeneration.
- 😀 Lipofuscin, a pigment accumulated in older neurons, acts as a marker of neuron aging but does not harm the neuron.
- 😀 Neurons have two types of extensions: dendrites (short extensions for receiving signals) and axons (long extensions for sending signals).
- 😀 Dendrites contain receptors that receive chemical messages from other cells to initiate electrical signals.
- 😀 The axon transmits action potentials, with its end called the axon terminal, which connects to muscles, other neurons, or glands.
- 😀 Myelin sheaths, which cover axons, speed up the transmission of signals, and gaps between these sheaths are called nodes of Ranvier.
Q & A
What are the two main types of cells in the nervous system?
-The two main types of cells in the nervous system are neurons and neuroglia. Neuroglia support neurons by providing them with nutrients, oxygen, and other essential functions.
What is the primary function of neurons in the human body?
-The primary function of neurons is to transmit signals, known as action potentials, throughout the body.
What are the three main parts of a neuron?
-A neuron consists of three main parts: the cell body (soma), axon, and dendrites.
What is the role of the cell body in a neuron?
-The cell body, also known as the perikaryon, contains the nucleus and organelles such as the mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes, which are essential for the neuron’s functions and growth.
What is the function of the Nissl bodies in a neuron?
-Nissl bodies, made of rough endoplasmic reticulum, are involved in protein synthesis. These proteins help in neuron growth and repair, particularly for the regeneration of axon parts.
What is lipofuscin, and how is it related to aging neurons?
-Lipofuscin is a brownish-yellow pigment that accumulates in aging neurons as a result of lipid oxidation. It serves as a marker of cellular aging but does not harm the neuron.
What are dendrites, and how do they contribute to neuron function?
-Dendrites are short, branched extensions from the cell body that receive chemical signals from other neurons. These signals trigger ion exchanges that generate action potentials in the neuron.
What is the function of the axon in a neuron?
-The axon transmits action potentials from the cell body to the axon terminal, which then sends the signals to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
What is the role of the axon hillock and trigger zone in action potential generation?
-The axon hillock connects the cell body to the axon, and the trigger zone, located between the axon hillock and initial segment, is where the action potential is first initiated.
How does myelin contribute to the conduction of nerve impulses?
-Myelin, a fatty substance that wraps around axons, speeds up the transmission of action potentials. It forms myelin sheaths with gaps known as nodes of Ranvier, where action potentials jump, enhancing signal conduction efficiency.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Sistem Saraf (Overview) | Ilmu Biomedik Dasar | Brainy Panda
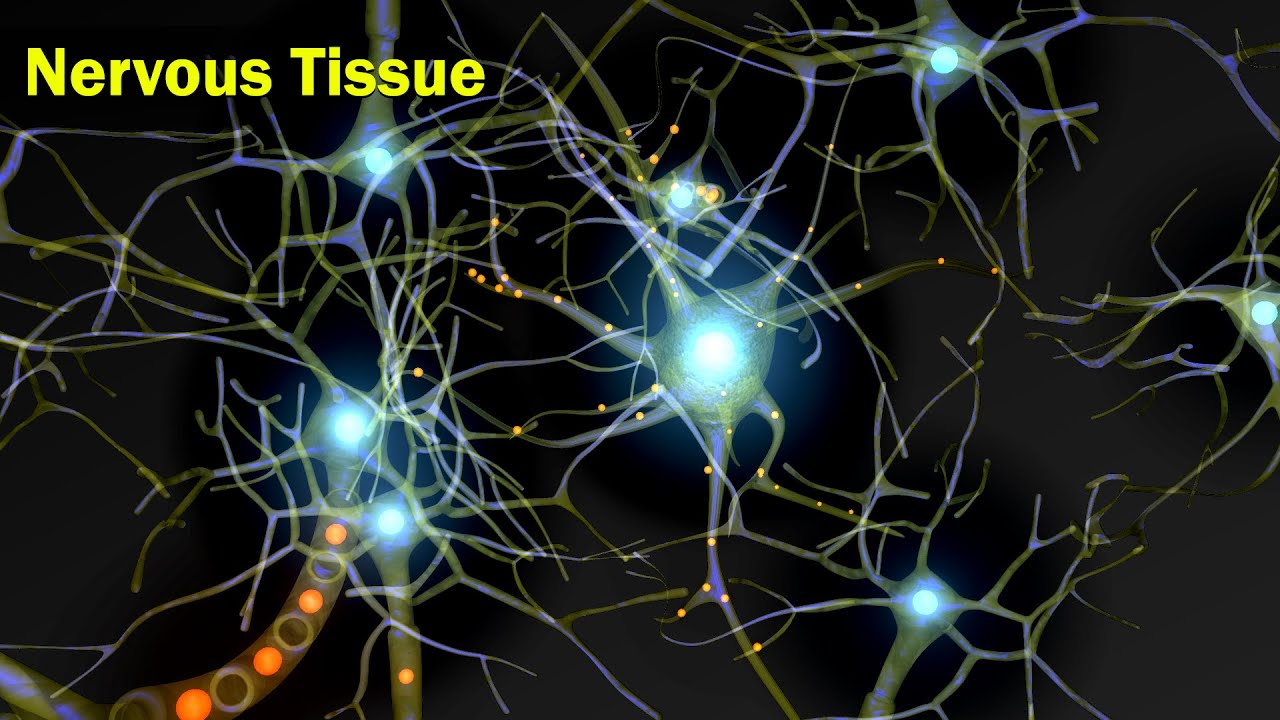
Nervous Tissue | Structural Organization in Animals | Anatomy | Inter 2nd year Class 11 Biology

BAB 2 Sistem Koordinasi Manusia || Sistem Saraf Manusia || IPA SMP/MTs Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka

Overview of the CNS (Pars, Neurons, Neuroglia, White & Grey Matter, Development) - Anatomy

Nervous System

Neurônios e Células da glia: Estruturas, funções e classificações
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
