MK Kuantitatif - Linier Programming Metode Simpleks
Summary
TLDRThe video provides a comprehensive explanation of linear programming, focusing on the Simplex method. It contrasts the graphical method, which is limited to two-variable problems, with the more versatile Simplex method that can handle problems with multiple variables. The tutorial covers how to convert a general linear program into standard form, how to create and fill a Simplex tableau, and how to perform iterations to find an optimal solution. Emphasizing the importance of interpreting coefficients and basic variables, the presenter guides viewers through the necessary steps to solve optimization problems using the Simplex method.
Takeaways
- 😀 The difference between graphical and simplex methods in linear programming: graphical methods are limited to problems with only two variables, while the simplex method can handle problems with more than two variables.
- 😀 Simplex method is used for finding optimal solutions, whether for maximization or minimization problems, even if there are multiple variables involved.
- 😀 The first step in using the simplex method is converting the problem into a standard form, ensuring all constraints are non-negative and written as equations instead of inequalities.
- 😀 Constraints in the standard form are converted by adding slack variables (for less-than constraints) or subtracting surplus variables (for greater-than constraints) to turn inequalities into equalities.
- 😀 If the objective function is a minimization problem, it needs to be converted to maximization by multiplying it by -1.
- 😀 The second step is to create a simplex table with columns for the basic variables, decision variables, and constraints, which includes all the coefficients from the constraints and the objective function.
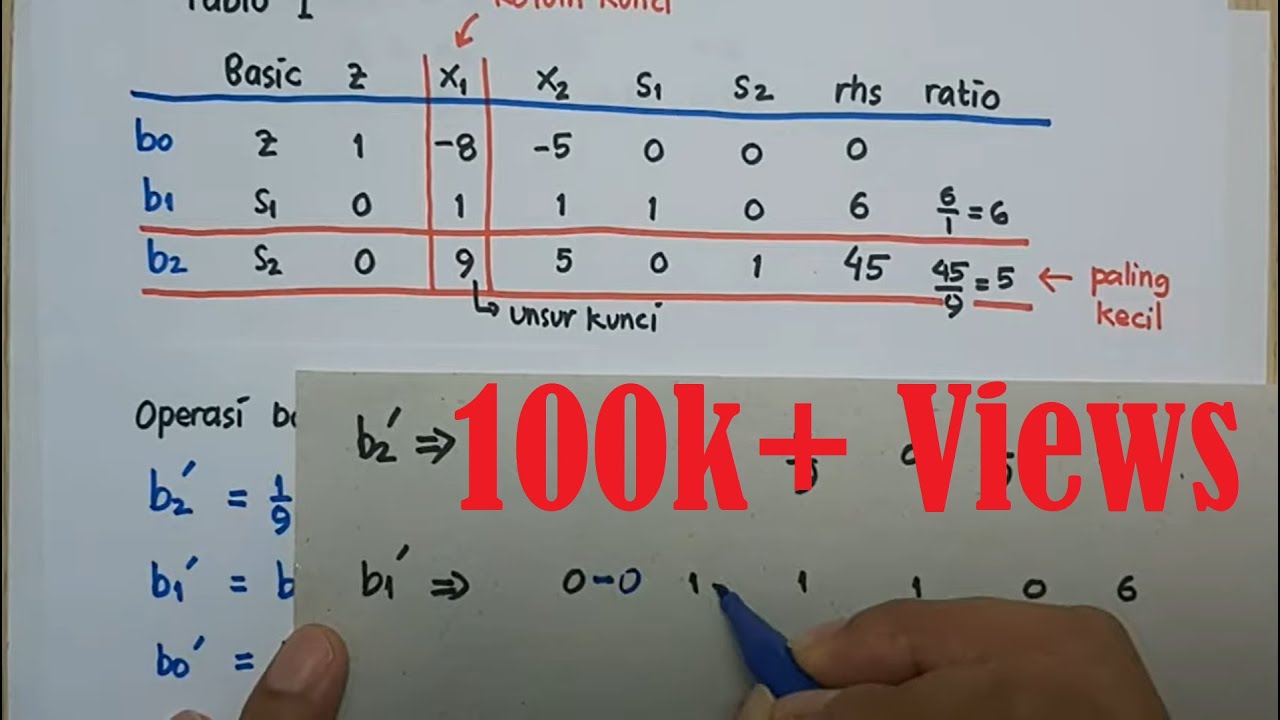
- 😀 Iteration is the third step, starting with identifying the key column (for maximization, this is the column with the highest negative coefficient in the objective function row) and then finding the key row by calculating ratios of right-hand side values to corresponding column values.
- 😀 The key value is determined by the intersection of the key column and key row, and from there, the pivoting process begins, which involves updating the table with new values.
- 😀 After pivoting, the updated simplex table is used to continue iterations until all the coefficients in the objective function row are non-negative, indicating an optimal solution.
- 😀 If the table still contains negative coefficients after the first iteration, further iterations are necessary to reach the optimal solution, which might require additional steps like adjusting the basis variables.
Q & A
What is the main focus of this script?
-The script primarily explains the Simplex method in Linear Programming, focusing on how to convert general forms into standard forms, construct a Simplex table, and perform iterations to find an optimal solution.
Why is the graphical method limited to problems with two variables?
-The graphical method is limited to problems with two variables because it relies on a Cartesian diagram with only two axes: horizontal and vertical. This method becomes impractical for problems with more than two variables.
What does the Simplex method help solve?
-The Simplex method helps find optimal solutions for optimization problems, whether it's for maximization or minimization, particularly when the problem has two or more variables.
What is the first step in applying the Simplex method?
-The first step is to convert the general form of the linear programming problem into the standard form. This includes ensuring all constraints have non-negative right-hand sides and converting inequalities into equalities by adding slack or surplus variables.
How do you handle negative right-hand sides in constraints?
-If the right-hand side of a constraint is negative, you multiply the entire inequality by -1 to ensure that the right-hand side becomes non-negative.
What is the purpose of slack and surplus variables?
-Slack variables are added to inequalities where the constraint is 'less than or equal to' to convert it into an equality. Surplus variables are subtracted from inequalities where the constraint is 'greater than or equal to'. These adjustments are essential for converting the problem into a form suitable for the Simplex method.
What do you do when the objective function is a minimization problem?
-When the objective function is a minimization problem, you multiply the entire objective function by -1 to convert it into a maximization problem. This ensures the Simplex method can be applied.
What is the second step in the Simplex method after transforming the problem into standard form?
-The second step is to create the Simplex table. This table includes variables such as decision variables and slack/surplus variables and organizes them in a matrix to perform iterations.
How do you determine the pivot column in the Simplex table?
-The pivot column is determined by identifying the most negative coefficient in the objective function row when seeking a maximum. For a minimization problem, you would select the most positive coefficient.
What does the pivot row represent in the Simplex method?
-The pivot row is determined by dividing the right-hand side values of the constraints by the corresponding pivot column values. The smallest non-negative ratio identifies the pivot row, which shows the next variable that will enter the basis.
What does it mean for the Simplex method to have reached an optimal solution?
-The Simplex method reaches an optimal solution when there are no more negative coefficients in the objective function row for maximization (or no positive coefficients for minimization). This indicates that the current solution is the best possible solution under the given constraints.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Metode linear programing | Metode Simplex | Matematika Bisnis | OR 2022

Riset Operasi #4 - Linear Programming dengan Metode Simpleks | Tutor Manajemen by Gusstiawan Raimanu

The Art of Linear Programming

ART TEACHES MATHEMATICS IN THE MODERN WORLD-LESSON 1: INTRO TO LINEAR PROGRAMMING

Analisis Sensitivitas : Penambahan Kendala Baru | Kelompok 10 Teknik Riset Operasi
Metode Simpleks (Contoh soal untuk kasus maksimisasi)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
