Membran Sel - Materi Kuliah Biologi Sel
Summary
TLDRThis educational video discusses the structure and function of the cell membrane, focusing on phospholipids. The video explains how phospholipids form a bilayer with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails, crucial for the membrane's role in separating the cell's interior from its environment. The concept of amphipathic molecules is explored, showing how this property allows for the formation of stable layers in aqueous environments. Additionally, the video delves into how membrane fluidity is affected by the type of fatty acids and the role of cholesterol in regulating fluidity, ensuring the membrane remains functional across varying temperatures.
Takeaways
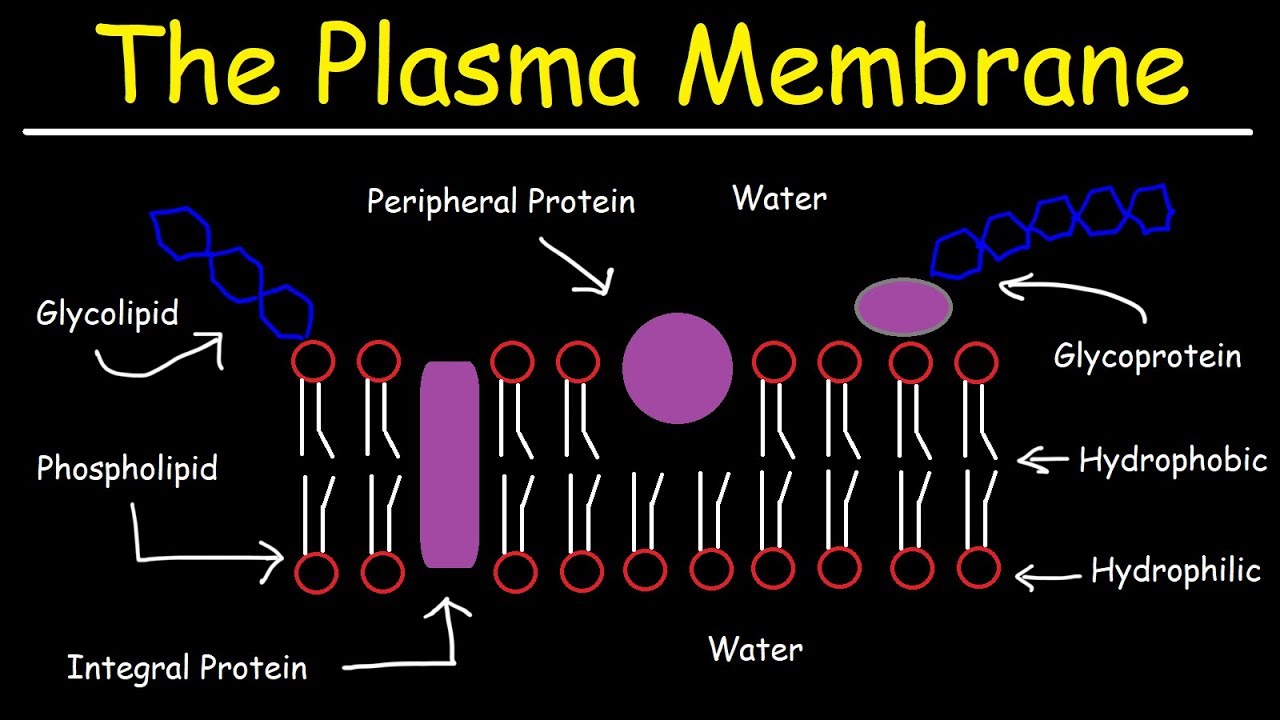
- 😀 The cell membrane is primarily composed of phospholipids, proteins, and cholesterol.
- 😀 Phospholipids have a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and a hydrophobic (water-repellent) tail, which allows them to form a bilayer structure.
- 😀 The hydrophilic head of phospholipids interacts with water, while the hydrophobic tail avoids water, creating a stable bilayer.
- 😀 Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, meaning they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts within the same molecule.
- 😀 In the presence of water, phospholipids naturally arrange into two layers to protect the hydrophobic tails from water exposure.
- 😀 Membrane proteins can be embedded within the bilayer, with hydrophilic regions exposed to the aqueous environment and hydrophobic regions interacting with lipid tails.
- 😀 Saturated fatty acids in phospholipids lead to a more rigid and less fluid membrane, while unsaturated fatty acids cause more fluidity due to their bent structure.
- 😀 Cholesterol stabilizes membrane fluidity by limiting the movement of phospholipids at high temperatures and preventing rigidity at low temperatures.
- 😀 At high temperatures, cholesterol reduces the movement of phospholipids to prevent the membrane from becoming too fluid.
- 😀 At low temperatures, cholesterol prevents the membrane from freezing by maintaining some fluidity, allowing the phospholipids to move more freely.
Q & A
What is the main component of the cell membrane?
-The main component of the cell membrane is phospholipids. These molecules consist of a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails, which help to form the membrane structure.
What is the structural difference between a phospholipid and a triglyceride?
-A phospholipid is structurally similar to a triglyceride, but one of the fatty acid chains is replaced by a phosphate group and a choline molecule. This gives the phospholipid both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
Why are the fatty acid tails of phospholipids hydrophobic?
-The fatty acid tails of phospholipids are hydrophobic because they consist of long chains of carbon and hydrogen (CH), which are nonpolar and do not interact well with water.
What makes the head of a phospholipid hydrophilic?
-The head of a phospholipid is hydrophilic because it contains polar or negatively charged groups, such as phosphate (P) and choline (N), which attract water molecules.
What is the difference between a lipid bilayer and a micelle?
-A lipid bilayer forms when phospholipids arrange themselves in two layers with hydrophobic tails facing inward and hydrophilic heads facing outward. In contrast, a micelle forms when the phospholipids have a conical shape, with the hydrophobic tails clustered in the center, away from water, and the hydrophilic heads facing outward.
Why is the lipid bilayer structure important for cell membranes?
-The lipid bilayer structure is crucial because it forms a stable barrier between the interior of the cell and its external environment, preventing the diffusion of hydrophilic substances while allowing lipid-soluble molecules to pass through.
How do gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide pass through the cell membrane?
-Oxygen and carbon dioxide can diffuse directly through the lipid bilayer because they are nonpolar and lipid-soluble, which allows them to bypass the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids.
What role do proteins play in the cell membrane?
-Proteins in the cell membrane can either be embedded within the bilayer or attached to its surface. These proteins have regions that interact with both the hydrophobic interior and the hydrophilic exterior, facilitating various functions such as transport, signaling, and structural support.
How do the saturation levels of fatty acids affect membrane fluidity?
-Saturated fatty acids, which have no double bonds, allow the phospholipids to pack tightly together, reducing membrane fluidity. Unsaturated fatty acids, with one or more double bonds, cause the phospholipids to bend, preventing tight packing and increasing fluidity.
What role does cholesterol play in maintaining the fluidity of the membrane?
-Cholesterol helps stabilize the membrane by preventing excessive fluidity at high temperatures and reducing the likelihood of the membrane becoming too rigid at low temperatures. It achieves this by inserting itself between the phospholipids, limiting their movement.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)