Apparato cardiocircolatorio 01: Cuore - Configurazione esterna
Summary
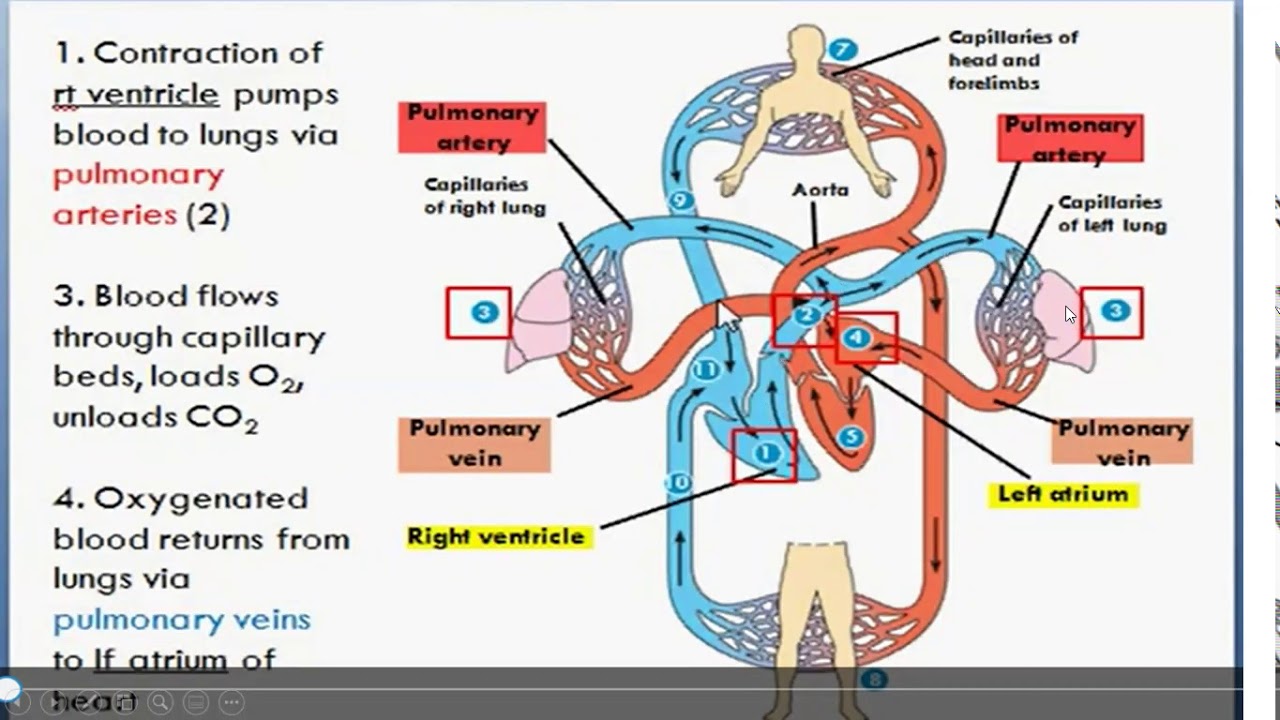
TLDRThis video script offers an in-depth exploration of the anatomy of the cardiovascular system, focusing on the heart's external structure. It covers the heart's conical shape, its location in the mediastinum, and the various surfaces and margins such as the anterior, posterior, and inferior faces. The script describes key features like the atrioventricular sulcus, interventricular grooves, and the coronary sulcus. It also highlights the important vessels surrounding the heart, including the pulmonary trunk and aorta, and their connection to the atria. The video uses detailed anatomical descriptions to engage viewers in understanding the heart's structure and function.
Takeaways
- 😀 The heart has a conical shape with a base at the top and an apex at the bottom.
- 😀 It is located within the mediastinum, the connective space between the lungs, along with other vital organs like large blood vessels, the esophagus, and the trachea.
- 😀 The heart is surrounded by a fibrous cavity called the pericardium, which will be explored later in the lesson.
- 😀 The heart's external surface can be divided into an anterior-superior face (sternal and costal region) and a posterior-inferior face (diaphragmatic region).
- 😀 The right margin is acute, while the left margin is obtuse, with the left side being more curved.
- 😀 The heart has a base primarily covered by large vascular structures, and its apex is located at the fifth intercostal space near the midclavicular line.
- 😀 Major external grooves include the atrioventricular groove (dividing the atrial and ventricular parts), the interventricular grooves (anterior and posterior), and the coronary groove.
- 😀 The coronary groove accommodates the major coronary arteries and is located between the atria and ventricles.
- 😀 The atrial part of the heart is characterized by the large vessels entering and exiting, such as the pulmonary trunk and the aorta, as well as the auricles of both atria.
- 😀 The heart’s ventricular face shows the conical emergence of both ventricles, with fewer visible structures on the posterior side, apart from the longitudinal grooves.
Q & A
What is the shape of the heart described in the transcript?
-The heart is described as having the shape of a truncated cone, with a base at the top and an apex at the bottom and laterally.
Where is the heart located within the body?
-The heart is located within the mediastinum, the connective space between the two lungs, alongside other organs like large blood vessels, the esophagus, trachea, and major bronchi.
What is the pericardium, and what is its role?
-The pericardium is a fibrous cavity that surrounds the heart, providing protection and reducing friction during the heart's beating. It will be analyzed in more detail later.
How is the surface of the heart divided?
-The heart's surface is divided into an anterior-superior face (also called the costal face), and a posterior-inferior face (also called the diaphragmatic face).
What are the two margins of the heart mentioned?
-The two margins are the acute margin (right margin) and the obtuse margin (left margin). The obtuse margin is more rounded compared to the acute margin.
Where is the apex of the heart located?
-The apex of the heart corresponds to the left ventricle and is located at the level of the fifth intercostal space along the midclavicular line.
What are the major grooves (sulci) observed on the heart's surface?
-The major grooves are the atrioventricular sulcus, interventricular sulcus (anterior and posterior), and the coronary sulcus. These grooves help distinguish different sections of the heart.
What is the atrioventricular sulcus, and what does it indicate?
-The atrioventricular sulcus is a groove that separates the atrial and ventricular portions of the heart. It is most visible on the posterior part of the heart and less so on the anterior part due to the overlap of large blood vessels.
What are the key vessels connected to the heart, and how are they positioned?
-The main vessels connected to the heart are the pulmonary trunk, the aorta, and the vena cava. The pulmonary trunk emerges from the right ventricle, while the aorta originates from the left ventricle, and the vena cava connects to the right atrium.
Where is the base of the heart located, and what does it consist of?
-The base of the heart corresponds to the area where large blood vessels enter and exit the heart, and it is located near the thoracic vertebrae, from the fifth to the eighth vertebrae.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)