BAB 6: PEWARISAN SIFAT DAN BIOTEKNOLOGI | Part 1: Pewarisan Sifat | IPA Kls 9 SMP Kurikulum Merdeka
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Miss Maya explains the principles of genetic inheritance, focusing on chromosomes, DNA, and genes. Through Mendel's classic experiments on pea plants, viewers learn about dominant and recessive genes, as well as how traits are inherited. The video introduces monohybrid and dihybrid crosses, showcasing how genetic traits are passed on across generations. With a clear breakdown of genetic terminology and Mendel’s laws, this video provides a solid foundation for understanding genetics. Stay tuned for the next video on biotechnology, and don’t forget to like, comment, and subscribe for more educational content.
Takeaways
- 😀 Genetic inheritance is the transmission of traits from parents to offspring through chromosomes, DNA, and genes.
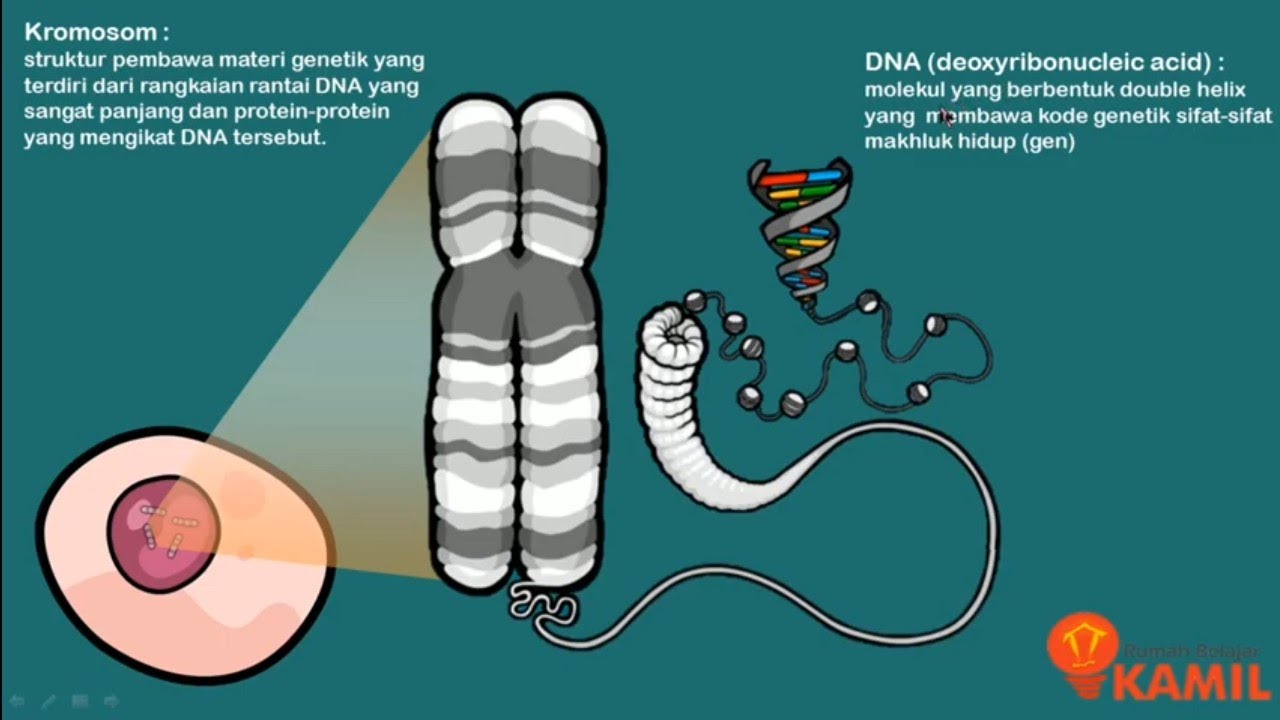
- 😀 Chromosomes are structures made up of DNA and proteins, containing genetic information, and humans have 46 chromosomes in most cells.
- 😀 DNA, organized in a double-helix structure, carries genetic codes that are vital for inheritance.
- 😀 Genes are segments of DNA that determine specific traits, and different versions of genes are called alleles (dominant or recessive).
- 😀 Dominant genes are written with capital letters (e.g., M for sweet), and recessive genes are written with lowercase letters (e.g., m for sour).
- 😀 A genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual, while a phenotype is the observable trait resulting from the genotype.
- 😀 Mendel’s experiments with pea plants revealed how traits are inherited and formed the foundation of modern genetics.
- 😀 Mendel’s First Law (Law of Segregation) states that allele pairs separate independently during gamete formation.
- 😀 A monohybrid cross involves one trait difference and shows a predictable 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits in offspring.
- 😀 A dihybrid cross involves two traits and demonstrates Mendel's Second Law (Law of Independent Assortment), with a 9:3:3:1 ratio in offspring.
- 😀 Understanding genetic inheritance helps explain why siblings can share some physical traits but also differ in others, even when having the same parents.
Q & A
What are the key components of genetic material in humans?
-The key components of genetic material in humans are chromosomes, DNA, and genes. Chromosomes are made of DNA and proteins, DNA contains genetic instructions, and genes are segments of DNA that encode for proteins determining traits.
How are traits passed from parents to offspring?
-Traits are passed from parents to offspring through genetic material, which is carried by chromosomes. These chromosomes contain DNA, and specific genes on the DNA determine inherited traits.
What is the role of DNA in genetic inheritance?
-DNA carries genetic instructions that determine the inherited traits of an organism. The sequence of DNA encodes genes, which are then expressed to produce proteins responsible for these traits.
What are the two main stages of protein synthesis?
-The two main stages of protein synthesis are transcription, where the DNA is copied into mRNA in the nucleus, and translation, where the mRNA is used by ribosomes to synthesize proteins.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
-Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, including the specific alleles it possesses, while phenotype is the observable physical expression of those genetic traits, such as flower color or plant height.
How does Mendel's Law of Segregation apply to inheritance?
-Mendel's Law of Segregation states that alleles for a trait separate randomly during the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells), meaning each parent passes only one allele for each trait to their offspring.
What is a monohybrid cross?
-A monohybrid cross is a genetic cross that involves the inheritance of a single trait. It typically shows how dominant and recessive alleles for one characteristic are inherited in offspring.
What is a dihybrid cross?
-A dihybrid cross is a genetic cross that involves the inheritance of two traits simultaneously. It demonstrates how alleles for two different traits assort independently during gamete formation, as explained by Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment.
How did Mendel's experiments with pea plants contribute to genetics?
-Mendel's experiments with pea plants led to the development of the basic laws of inheritance. By studying traits like flower color and plant height, he established the principles of dominance, segregation, and independent assortment.
What is the ratio of phenotypes observed in the F2 generation of a monohybrid cross?
-In a monohybrid cross, the F2 generation typically shows a 3:1 ratio of the dominant to the recessive phenotype, meaning 75% of the offspring will express the dominant trait and 25% will express the recessive trait.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

BAB 6 PEWARISAN SIFAT DAN BIOTEKNOLOGI Part 1 (IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka)

MATERI GENETIKA: BIOLOGI KELAS 12 SMA

Kamu unik, dan genmu adalah buktinya! Simak video ini....bagaimana DNA membentuk dirimu🧍🏻👋🏻
IPA Kelas 9 : Pewarisan Sifat I (Materi Genetik : Kromosom, DNA dan RNA)

Genetic Recombination and Gene Mapping
Bab 3 Pewarisan Sifat #1 (Materi Genetik) | IPA SMP Kelas 9 | K13
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
