The Nucleus - Structure and Function Cell physiology Animation
Summary
TLDRThe nucleus is a key cellular structure containing chromosomes made of DNA, which is wrapped around proteins called histones to form nucleosomes. This chromatin can be either transcriptionally inactive (heterochromatin) or active (euchromatin). The nucleus also contains a nucleolus, rich in RNA, and is surrounded by a membrane that is permeable to small molecules, but includes nuclear pore complexes for regulated import and export. Key functions of the nucleus include messenger RNA synthesis and regulation of cell division.
Takeaways
- 😀 The nucleus is the major part of the cell, housing chromosomes made of DNA.
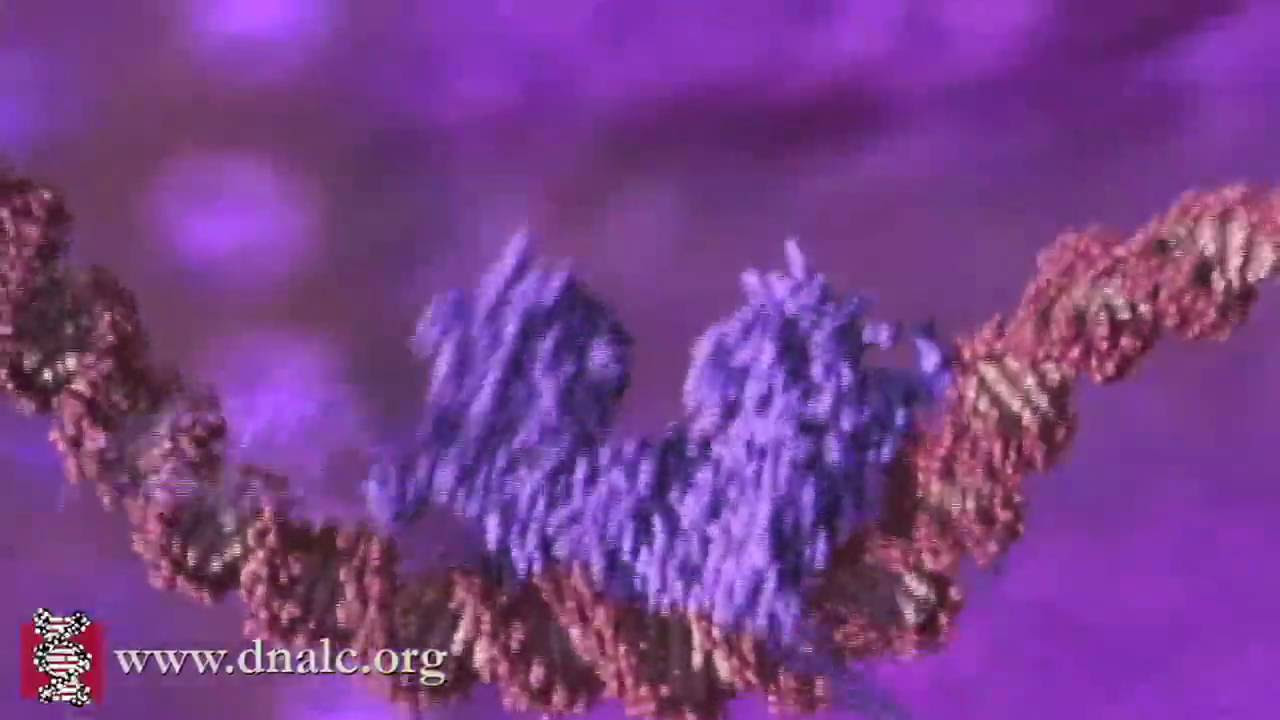
- 😀 DNA, which is nearly 2 meters long, is wrapped around proteins called histones.
- 😀 A nucleosome is the basic unit of chromatin, consisting of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer.
- 😀 A histone octamer is made up of two copies of each of four histone proteins: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4.
- 😀 Chromatin can be transcriptionally inactive (heterochromatin) or active (euchromatin).
- 😀 Each cell nucleus contains approximately 25 million nucleosomes.
- 😀 The nucleus houses a nucleolus, which is rich in RNA and involved in various cellular processes.
- 😀 The nuclear membrane is permeable to small molecules but regulated by nuclear pore complexes.
- 😀 Nuclear pore complexes control the import and export of materials into and out of the nucleus.
- 😀 The major functions of the nucleus include messenger RNA synthesis and regulation of cell division.
Q & A
What is the major component of the nucleus?
-The major component of the nucleus is chromosomes, which are made up of giant DNA molecules.
What is DNA wrapped around in the nucleus?
-DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones to form nucleosomes.
What is a nucleosome?
-A nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin, consisting of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer.
What proteins make up the histone octamer?
-The histone octamer is composed of two copies each of the histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4.
What is the difference between euchromatin and heterochromatin?
-Euchromatin is transcriptionally active chromatin, while heterochromatin is transcriptionally inactive.
How many nucleosomes are typically found in a single nucleus?
-There are approximately 25 million nucleosomes in each nucleus.
What is the nucleolus, and what does it contain?
-The nucleolus is located within the nucleus and contains a patchwork of granules rich in RNA.
What is the role of nuclear pore complexes?
-Nuclear pore complexes control the transport of molecules, allowing small molecules to pass while regulating larger molecules such as messenger RNA.
What are the major functions of the nucleus?
-The major functions of the nucleus include messenger RNA synthesis and regulation of cell division.
Why is the membrane of the nucleus permeable only to small molecules?
-The membrane is selectively permeable to small molecules to maintain control over the movement of substances into and out of the nucleus, ensuring proper cellular function.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآن5.0 / 5 (0 votes)