Aula teórica Controle químico do biofilme dentário supragengival
Summary
TLDRThe video focuses on the importance of managing supragingival biofilm in dental care. It explains how mechanical cleaning methods, such as brushing and flossing, are the primary ways to control plaque but may not always be sufficient. The use of chemical agents, including chlorhexidine, cetylpyridinium chloride, and other compounds, is explored as a supplementary or alternative solution. The video emphasizes the balance between mechanical and chemical control, highlighting their roles, effectiveness, and potential side effects. The goal is to provide a comprehensive approach to biofilm management in oral hygiene, ensuring long-term dental health.
Takeaways
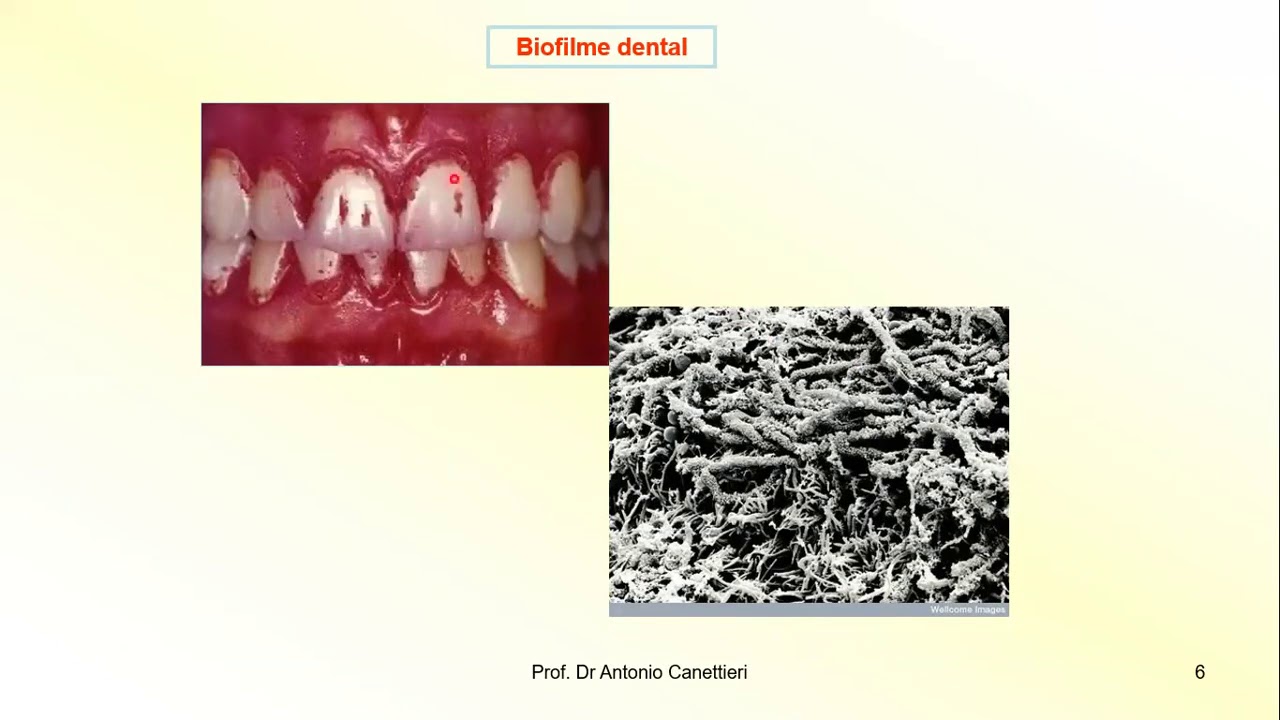
- 😀 Supragingival biofilm is the plaque that forms on the crown and exposed root surfaces of teeth, consisting of bacteria and an intermicrobial matrix.
- 😀 Mechanical control (brushing and flossing) is the primary method to manage biofilm but has limitations, especially for those who cannot perform proper cleaning.
- 😀 Chemical agents can aid in biofilm control when mechanical cleaning is insufficient or not possible.
- 😀 Chlorhexidine is considered the gold standard for chemical biofilm control due to its high substantivity and effectiveness in reducing plaque and gingivitis.
- 😀 Chlorhexidine has side effects, including tooth staining and altered taste, but remains one of the most effective agents for controlling biofilm.
- 😀 Other chemical agents, such as cetylpyridinium chloride, essential oils, and fluoride compounds, are also used, but their effectiveness varies.
- 😀 Chemical agents work by inhibiting bacterial colonization, growth, and metabolism, or by disrupting the biofilm structure.
- 😀 Substantivity is an important property for chemical agents, referring to their ability to remain in the mouth long enough to be effective.
- 😀 Chemical agents should be used as an adjunct to mechanical cleaning and not as a primary method for biofilm removal.
- 😀 Biofilm control is crucial in preventing gingivitis and other oral diseases, and proper oral hygiene practices are key to maintaining oral health.
Q & A
What is supragingival biofilm, and where does it form?
-Supragingival biofilm forms on the visible surfaces of teeth, particularly on the crown and root surfaces when exposed. It consists of microcolonies of bacteria embedded in a matrix that helps them stick to surfaces.
What is the main method for controlling supragingival biofilm?
-The primary method for controlling supragingival biofilm is mechanical removal, such as brushing, flossing, and other cleaning tools.
Why is mechanical control of biofilm not always effective?
-Mechanical control is often ineffective because many individuals lack proper technique, motivation, or consistency in maintaining oral hygiene. Additionally, some areas may be difficult to reach, resulting in plaque buildup.
When is chemical control of biofilm necessary?
-Chemical control is necessary when mechanical methods are insufficient, such as in hard-to-reach areas or after procedures like oral surgery. It can be used as a substitute or adjunct to mechanical cleaning.
What are the key properties of an effective chemical agent for biofilm control?
-Effective chemical agents should have substantivity (ability to remain in the mouth), efficacy (ability to reduce bacteria), stability, and safety for use in the oral cavity.
What is the role of chlorhexidine in controlling supragingival biofilm?
-Chlorhexidine is considered the gold standard for biofilm control, offering broad-spectrum antibacterial action and providing effectiveness for up to 12 hours. However, it can cause side effects like staining of teeth and altered taste.
How does cetylpyridinium chloride differ from chlorhexidine?
-Cetylpyridinium chloride is another antibacterial agent, but it has lower substantivity than chlorhexidine, meaning it requires more frequent application to maintain its effectiveness.
What are the benefits and limitations of metal-based chemical agents like stannous fluoride and zinc citrate?
-Metal-based agents like stannous fluoride and zinc citrate help reduce plaque and gingival inflammation. However, they may cause side effects like altered taste or dry mouth.
What are phenolic compounds, and how do they impact biofilm control?
-Phenolic compounds, such as triclosan, are effective against bacterial biofilms and can reduce plaque and inflammation. However, there is a risk of bacterial resistance if overused.
What is the role of natural products like propolis in biofilm control?
-Natural products like propolis show moderate antimicrobial and anticariogenic effects. However, their efficacy can vary depending on their source, making them less predictable than synthetic agents.
What is the primary challenge of using chemical agents for biofilm control?
-The primary challenge is balancing their effectiveness with potential side effects. For example, some chemical agents may cause staining, taste disturbances, or dry mouth, which could lead to patient non-compliance.
Why is it important for dental professionals to be knowledgeable about chemical agents for biofilm control?
-It is crucial for dental professionals to be well-informed about chemical agents to effectively prescribe and monitor their use, ensuring patients achieve optimal oral health while minimizing side effects.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)