Introduction to Genetics - DNA, RNA, Genes, Nucleosides, Nucleotides, Transcription, Translation
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Medicosis Perfect Status introduces the basics of genetics, explaining how DNA forms the foundation of life. It covers the structure and function of DNA, the role of genes and alleles in inheritance, and the difference between genotype (genetic makeup) and phenotype (observable traits). Key concepts like **penetrance** (the likelihood that a gene will manifest) and **expressivity** (the range of expression in individuals) are discussed. The video also explores blood type genetics, demonstrating co-dominance and recessive traits, and how multiple alleles contribute to the diversity of genetic traits in humans.
Takeaways
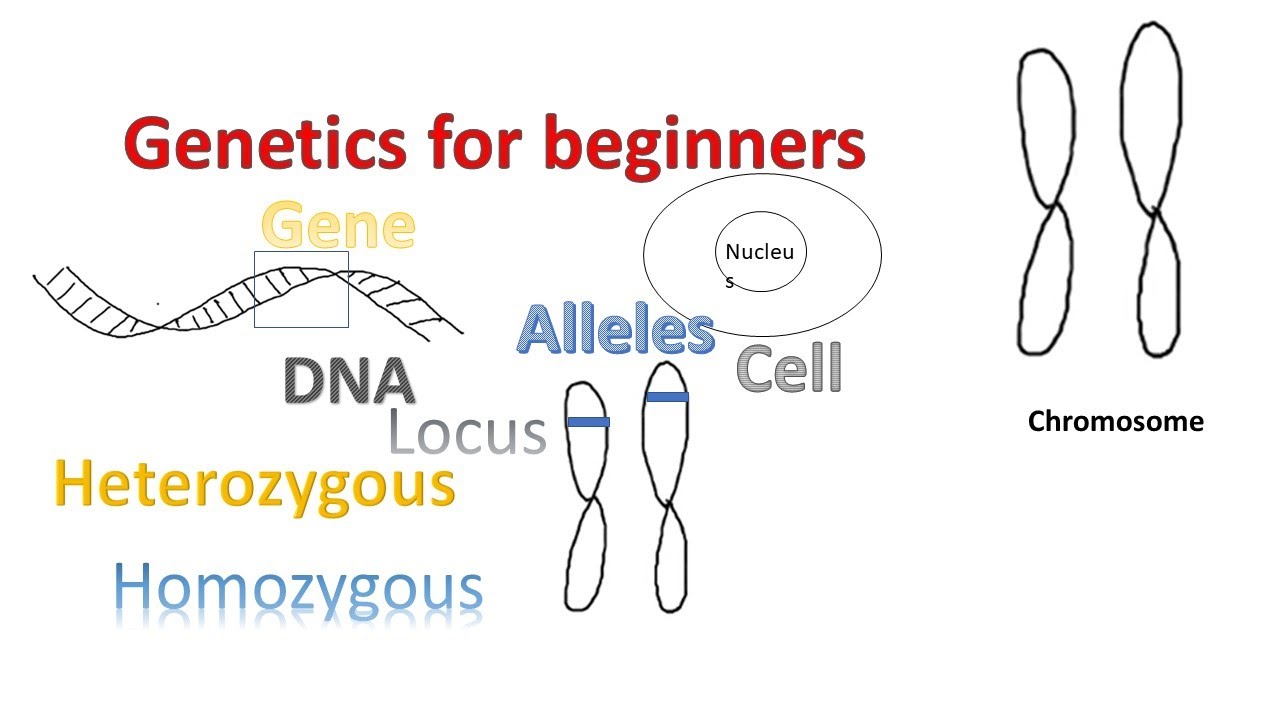
- 😀 Your body is made of systems, each system consisting of organs, tissues, cells, and a nucleus, where DNA is stored in chromosomes.
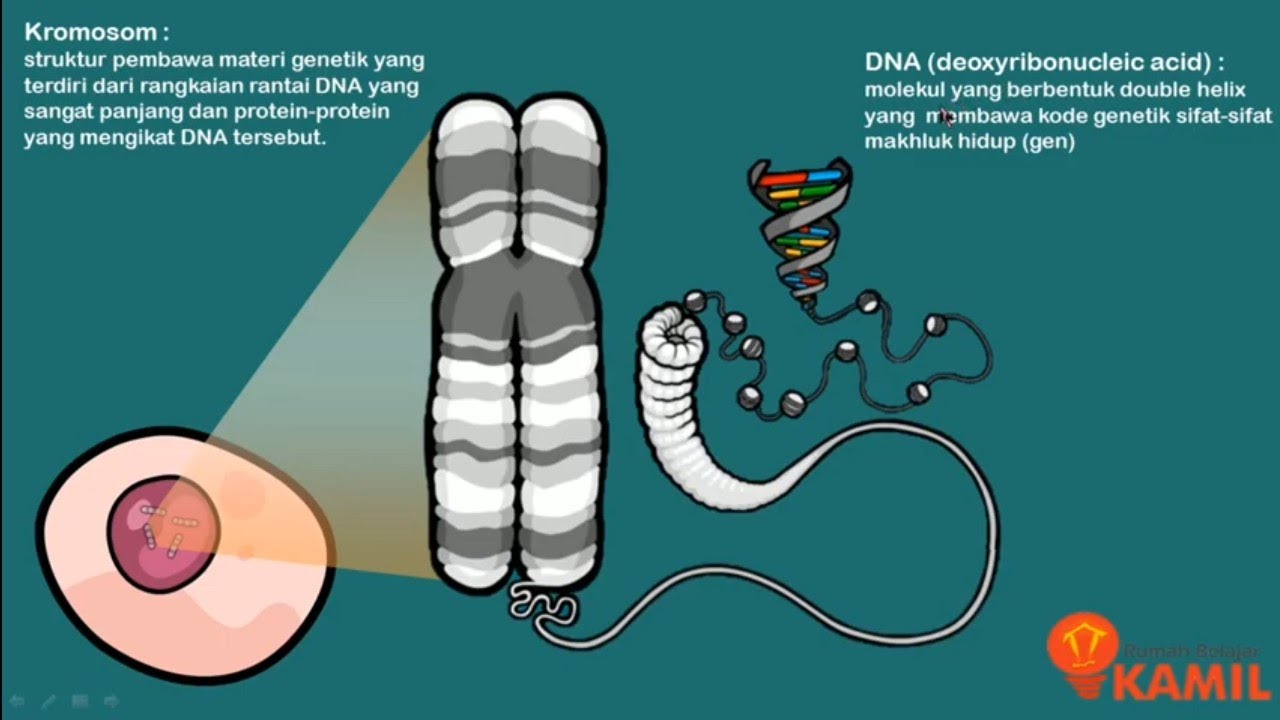
- 😀 DNA, the genetic material inside the nucleus, is composed of a sugar backbone, phosphate, and nitrogenous bases, encoding proteins such as enzymes.
- 😀 DNA is packaged into 46 chromosomes in somatic cells, and each chromosome consists of two chromatids.
- 😀 The process of DNA replication creates an identical copy of DNA, while transcription converts DNA to RNA, and translation converts RNA into proteins.
- 😀 A gene is a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein, and each gene has two forms (alleles)—one from each parent.
- 😀 Dominant alleles (like Big T) overpower recessive alleles (like small t), determining traits like height in this example.
- 😀 Homozygous individuals have two identical alleles (e.g., Big T Big T), while heterozygous individuals have two different alleles (e.g., Big T small t).
- 😀 Penetrance refers to the percentage of individuals who express a particular phenotype, while expressivity refers to the variation in the expression of a phenotype among individuals with the same genotype.
- 😀 The ABO blood group system is determined by three alleles (IA, IB, and IO), where A and B are dominant over O, and A and B are co-dominant with each other.
- 😀 Your genotype (genetic makeup) may not always match your phenotype (observable characteristics), as seen with blood type inheritance in the ABO system.
- 😀 There are six possible blood types based on combinations of IA, IB, and IO alleles, and O is recessive, meaning it only shows when both alleles are O.
Q & A
What is the basic building unit of living organisms?
-The basic building unit of living organisms is the cell. Cells combine to form tissues, organs, and systems that perform various body functions.
What role does the nucleus play in the cell?
-The nucleus is the brain of the cell because it contains the DNA, which carries the genetic instructions for the cell's functions.
What is DNA made of?
-DNA is made up of three components: a sugar backbone (deoxyribose), phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases.
What is the function of DNA in the body?
-DNA encodes the information required to produce proteins, including enzymes that perform a wide variety of essential biological functions.
How is DNA organized within the cell?
-DNA is organized into 46 chromosomes, which are located inside the nucleus. Each chromosome consists of two chromatids, and these chromatids contain many genes.
What is the difference between dominant and recessive alleles?
-Dominant alleles, represented by uppercase letters (e.g., T), mask the effect of recessive alleles, represented by lowercase letters (e.g., t). For example, the allele for tall height (T) is dominant over the allele for short height (t).
What does 'penetrance' mean in genetics?
-Penetrance refers to the proportion of individuals with a particular genotype who actually express the associated phenotype. For example, if 50% of people with a certain allele show the corresponding trait, the penetrance is 50%.
What is the meaning of 'expressivity' in genetics?
-Expressivity refers to the extent to which a gene's effect is expressed in an individual. It can vary, with some individuals showing mild symptoms and others showing severe symptoms, even with the same genotype.
What are the three alleles involved in blood type inheritance?
-The three alleles involved in blood type inheritance are IA, IB, and IO. IA and IB are dominant over IO, and they exhibit co-dominance with each other.
What is the relationship between genotype and phenotype in blood type inheritance?
-The genotype determines the genetic makeup of an individual (e.g., IAIA, IBI, etc.), while the phenotype is the observable trait, such as blood type A, B, AB, or O. The blood type is determined by the alleles inherited from both parents.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

LESSON ON CHROMOSOMES, DNA AND GENES | IN FILIPINO
Genetics for beginners | Genes Alleles Loci on Chromosomes |

Me Salva! GEN02 - Genética - Replicação do DNA - Parte 1

UNSUR-UNSUR DALAM SENI RUPA

DNA, Chromosomes, Genes, and Traits: An Intro to Heredity
IPA Kelas 9 : Pewarisan Sifat I (Materi Genetik : Kromosom, DNA dan RNA)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
