Mole Concept | Grade 9 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 2 Module 6
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the mole concept in chemistry, a method for counting atoms, molecules, and ions. It introduces Avogadro's number (6.02 × 10^23) as a fundamental constant for measuring particles in a mole. The video covers how to calculate moles, molecules, and ions through several sample problems, highlighting the relationship between moles, atomic mass, and molecular mass. Additionally, it explains the concept of molar mass, which is the mass of one mole of a substance. The video concludes with a preview of the next lesson on percentage composition in compounds.
Takeaways
- 😀 The mole concept is a way to count atoms, molecules, or ions in chemistry, similar to how we use terms like a dozen or ream for specific quantities.
- 😀 One mole is defined as the number of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) in exactly 12 grams of carbon-12, which equals 6.02 × 10^23 particles (Avogadro's number).
- 😀 The mole concept helps scientists handle large numbers of particles that are difficult to count individually due to their tiny size.
- 😀 The number of moles in a sample can be calculated using the formula: n = N / Nₐ, where n is the number of moles, N is the total number of particles, and Nₐ is Avogadro's constant.
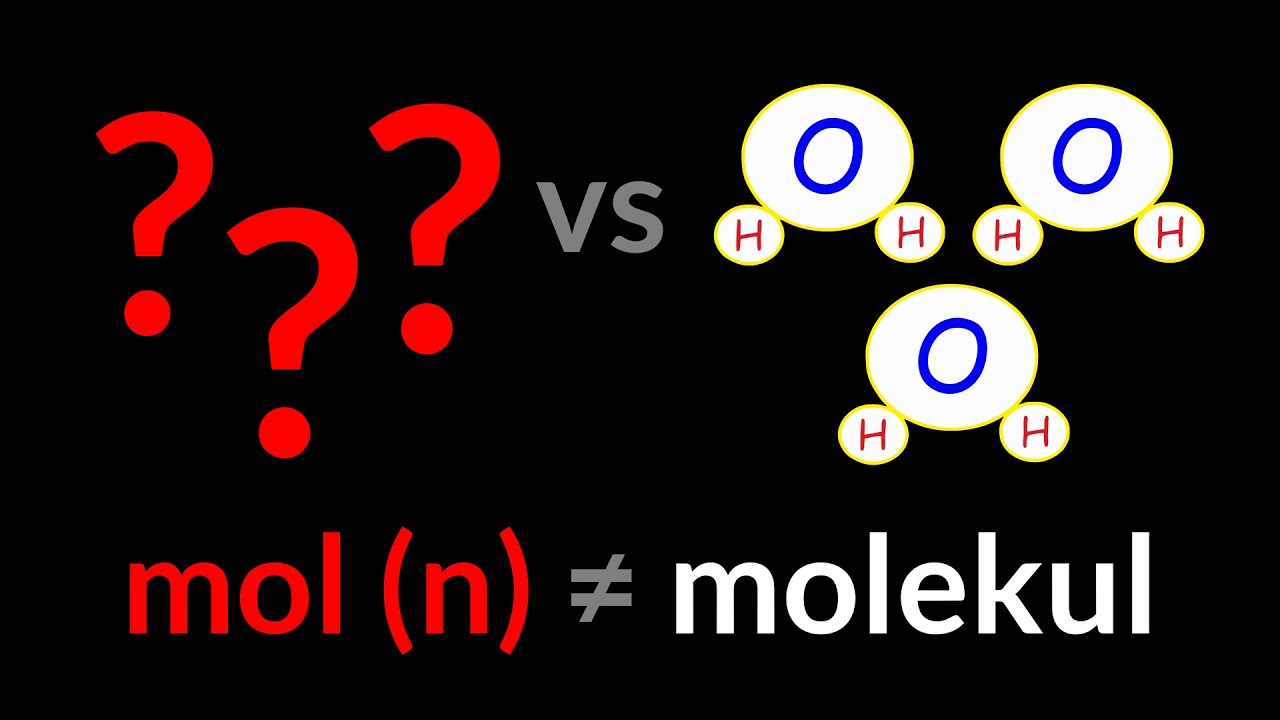
- 😀 The number of moles of a molecule does not always match the number of moles of its constituent atoms; for example, one mole of water contains two moles of hydrogen and one mole of oxygen.
- 😀 In sample problems, to convert from moles to molecules, you multiply by Avogadro's number (6.02 × 10^23 molecules per mole).
- 😀 To convert from atoms to moles, you divide by Avogadro's number (6.02 × 10^23 atoms per mole).
- 😀 The mole-to-ion conversion requires knowing how many ions are present per formula unit, like in aluminum fluoride, where one formula unit contains three fluoride ions.
- 😀 Atomic mass is the mass of one atom of an element, expressed in atomic mass units, and is used to calculate molecular mass.
- 😀 The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of the substance, typically expressed in grams per mole, and can be calculated by summing the atomic masses of the constituent elements.
Q & A
What is the mole concept and why is it used in chemistry?
-The mole concept is a way to count particles (atoms, molecules, ions) at the atomic and molecular level. It is used in chemistry because atoms and molecules are extremely small and hard to count individually, so the mole provides a convenient way to express amounts of substance in terms of a large, defined number of entities (6.02 x 10^23, known as Avogadro's number).
What is Avogadro's number and how is it used?
-Avogadro's number, 6.02 x 10^23, is the number of particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) in one mole of a substance. It is used to convert between the number of moles of a substance and the number of particles it contains.
How is one mole of a substance related to its atomic or molecular mass?
-One mole of a substance contains Avogadro's number of particles. The mass of one mole of a substance, known as the molar mass, is numerically equal to the atomic or molecular mass of the substance in grams. For example, one mole of water (H2O) has a molar mass of 18.0154 grams.
What is the difference between atomic mass and molecular mass?
-Atomic mass is the mass of a single atom of an element, measured in atomic mass units (AMU). Molecular mass, on the other hand, is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule. For example, the molecular mass of water (H2O) is calculated by adding the atomic masses of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
How do you calculate the number of molecules in a given number of moles?
-To calculate the number of molecules in a given number of moles, multiply the number of moles by Avogadro's number. For example, 4 moles of sodium chloride (NaCl) contain 4 x 6.02 x 10^23 molecules of NaCl, which equals 2.41 x 10^24 molecules.
How do you convert from atoms to moles?
-To convert from atoms to moles, divide the number of atoms by Avogadro's number. For example, 3.01 x 10^22 atoms of magnesium can be converted to moles by dividing by 6.02 x 10^23 atoms per mole, giving 0.05 moles of magnesium.
What is the relationship between moles and formula units in a compound?
-One mole of any substance contains Avogadro's number of formula units. For ionic compounds, a formula unit represents the simplest ratio of ions that make up the compound. For example, 1 mole of aluminum fluoride (AlF3) contains 6.02 x 10^23 formula units of AlF3, which contains three fluoride ions per formula unit.
What is the concept of molar mass?
-Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. It is often expressed in grams per mole (g/mol) and can be calculated by adding up the atomic masses of all the elements in the substance. For example, the molar mass of sodium chloride (NaCl) is 58.44 g/mol.
How do you calculate the number of fluoride ions in a given number of moles of aluminum fluoride?
-To calculate the number of fluoride ions in a given number of moles of aluminum fluoride, first convert moles of AlF3 to formula units using Avogadro's number, then multiply by the number of fluoride ions per formula unit. For example, 1.46 moles of AlF3 contain 2.64 x 10^24 fluoride ions.
What is the formula for calculating the number of moles of a substance?
-The number of moles of a substance can be calculated using the formula: n = N / N_a, where 'n' is the number of moles, 'N' is the total number of particles in the sample, and 'N_a' is Avogadro's number (6.02 x 10^23).
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)